title from merging (copy)
1/103
Earn XP
Description and Tags
this set is created by mergin two sets
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
104 Terms
Vitamin A
Deficiencies Rare due to inadequate intake, fat malabsorption dry/inflamed eyes (xerophthalmia), night blindness (nyctalopia), family conjunctiva (bitot spots) Dry, scaly skin (xerosis cutis) or hair Inc susceptibility to infection (immunosuppression)
Vitamin A
Treats: Skin disorders, severe acne (isotretinoin) Promyelocytic leukemia (all-trans retinoic acid) Prevent and treat age related macular degeneration (carotenoids) Measles (when deficient)
Vitamin A
Toxicities: Inc intracranial pressure, dizziness, nausea, headaches, blurred vision Skin irritation, dry skin, alopecia Fetal deformations (cardiac, cleft palate) w/ isotretinoin Excessive beta carotene - carotenodermia (orange skin)
Vitamin A
Foods: leafy green veggies, liver, fish oil, milk, eggs, colored fruits and veggies (beta carotene in orange,red), fortified foods like grains
Vitamin A
Retinal Retinol Retinoic acid Carotenoids = (beta-carotene)
Vitamin A
Antioxidant Helps vision (absorbs light in retinal receptors) Immune function (antioxidant) Cellular growth, dif, communication (esp epithelial cells)
Vitamin E
Tocopherol Alpha-tocopherol Tocotrienol
Vitamin E
Foods: wheat germ, nuts, seeds, vegetable/plant oils, smaller amounts in fruits and vegetables, fortified foods
Vitamin E
Antioxidant (helps prevent and treat age related macular degeneration), anti-inflammatory, immune enhancement, inhibits platelet aggregation (stops clots)
Vitamin E
Deficiencies Bc of fat malabsorption (low birthweight premies) Hemolytic anemia, acanthocytosis (misshapen RBC), muscle weakness, skeletal myopathy, ataxia, dec proprioception, vibration sensation Neuropathy, retinopathy Impaired immune response
Vitamin E
Toxicities Enterocolitis in infants Risk of bleeding/enhanced anticoagulation with warfarin
Vitamin K Phylloquinone = K1 Menaquinone = K2
Phytomenadione Phytonadione Phylloquinone Menaquinone
Vitamin K
Food: 1 - green leafy vegetables (some vegetable/plant oils), 2 - animal products and fermented foods (soybeans); made by gut bacteria
Vitamin K
coagulant - matures clotting factors, matures prothrombin Bone metabolism - osteocalcin needs vitamin ...
Vitamin K
Low availability of vit __ in breast milk so given to newborns Now should consume consistent amount of vitamin __ when on warfarin (before used to say no vit __)
Vitamin K
Deficiencies Bc of fat malabsorption, prolonged antibiotic use (blocks vitamin K metabolism because digested in gut) In newborns - hemorrhagic disease (unable to synthesize in gut, doesn't cross placenta, low in breast milk) Causes: bleeding/hemorrhage, easy bruising, increased PT/INR (nosebleeds, bleeding gums, blood in urine and stool, black stools, heavy menstrual bleeding) Can contribute to osteoporosis or osteopenia
Vitamin K
Toxicities NONE - but menadione (synthetic ___ precursor) can be toxic to infants
Vitamin D
Calciferol (D1) Ergocalciferol (D2) Cholecalciferol (D3) Calcitriol (active form)
Vitamin D
Foods: fatty fish and fish oil (little n milk, cheese, and eggs), mushrooms (and fungi), fortified milk, dairy, cereal, orange juice, formula Also sunlight
Vitamin D
Bone health- inc absorption of Ca+ and P+, inc bone remineralization at low levels and resorption at high levels Cell growth and differentiation, immune, anti-inflammatory Endocrine and cardiovascular functions
Vitamin D
Treats: low bone density (osteopenia, osteoporosis), supplement in breast milk
Vitamin D
Deficiencies: when deficient associated with diseases and conditions but supplements don't help Due to malabsorption, less sun exposure, liver or kidney disease that alters metabolism, darker skin color Rickets in children (bowlegs, craniotables - softening of bones in skull) Osteomalacia (soft/weak) and osteoporosis in adults Associated w/ hypocalcemia (tetany/spasms/numb/seizure) Inc prevalence of chronic disease
Vitamin D
Toxicities: Hypercalcemia, hypercalciuria - bone less, kidney stones, vascular and tissue calcification and heart arrhythmias Anorexia, weight loss, polyuria, stupor
Vitamin C
Foods: fruit, vegetables (broccoli, peppers, cauliflower, cabbage), fortified foods
Vitamin C
Reducing agent, antioxidant (protects from free radical damage) Helps in regeneration of antioxidants (like vit E) Inc bioavailability and absorption of Fe (reduces to Fe2+) Enzyme cofactor - synthesis of collagen (hydroxylation of proline and lysine), carnitine, catecholamines (converts dopamine to norepinephrine) ???may prevent cancer, CVD, enhance immunity and healing
Vitamin C
Deficiencies: Weakened blood vessels and connective tissue bc lack of collagen and iron def anemia Swollen gums, subcutaneous bleeding of gums, weakened immunity, poor wound healing, anemia = fatigue, easy bruising and petechiae (bleeding under skin), joint pain, edema, hair and tooth loss (corkscrew hair)
Vitamin C
Toxicities Excessive supplements Diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, GI discomfort, fatigue Kidney stones (oxalate) Inc iron absorption/ worsen hemochromatosis
Vitamin B1
thiamine
Vitamin B1
Foods: animal product (liver/organs, poultry, fish, eggs, milk and dairy), legumes, nuts, seeds, fortified grains, breads, cereals
Vitamin B1
ATP energy production: Branched-chain ketoacid dehydrogenase Alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase (TCA) Pyruvate dehydrogenase (glycolysis to TCA) Transketolase (synthesis of ribose units for DNA and RNA in PPP) Nerve function - thiamine triphosphate
Vitamin B1
treat deficiencies and can improve ejection fraction in those with heart failure
Vitamin B1
Deficiencies - alcoholism, malnutrition, GI disorders Dry Beirberi - neuro Peripheral neuropathy, muscle wasting, leg cramps Wet Beriberi - cardio Heart failure, cardiomyopathy, edema Wernicke encephalopathy - acute/life threatening/reversible Confusion, ophthalmoplegia, nystagmus, ataxia, neuropathy Korsakoff syndrome -alcoholism amnesia/false memories, personality changes, psychosis Wernicke-Korsakoff: alcoholism, HIV-related)
Vitamin B2
Foods: animal product (liver/organs, poultry, fish, eggs, milk and dairy), legumes, vegetables, fortified grains, breads, cereals
Vitamin B2
riboflavin
Vitamin B2
ATP energy production - component of FAD and FMN in Krebs Cycle
Vitamin B2
Req for synthesis of vitamin A, folate, niacin, B6, K Req for neurotransmitter metabolism (dopa, NE) Helps maintain normal levels of homocysteine
Vitamin B2
recommended for migraine prevention (bc plays a role in mitochondrial function)
Vitamin B2
Deficiencies (rare in isolation) - alcoholism, malnutrition, GI disorders, thyroid disorders Oral: mouth and lip sores (cheilosis- fissures at corners), inflammation of mouth (stomatitis), and tongue (glossitis-magenta bright red) Skin lesions, alopecia, itchy eyes, corneal vascularization
Vitamin B2
NO toxicities (can cause bright yellow urine)
Vitamin B3
Niacin Nicotinic acid Nicotinamide
Vitamin B3
Foods: animal product (liver/organs, poultry, fish, eggs, milk and dairy), legumes, vegetables, fortified grains, breads, cereals
Vitamin B3
Produced from tryptophan
Vitamin B3
Involved in 200+ redox reactions ATP production (glycolysis, Krebs cycle) - component of NAD+ and NADP+ Synthesis of fatty acids, cholesterol, DNA, steroid hormones, vitamins (C,folate)
Vitamin B3
treat dyslipidemia ( anti-atherosclerotic - anti buildup of fats in arteries), Hartnup's disease (tryptophan deficiency)
Vitamin B3
Deficiencies - pellagra, (rare in isolation) - alcoholism, malnutrition, GI disorders, dialysis, HIV, because: Defective tryptophan absorption - Hartnup's disease Metabolism - carcinoid syndrome Meds interfering with tryptophan metabolism Symptoms: 3-4 Ds - dermatitis, diarrhea (vomiting and glossitis), dementia (headache, apathy, fatigue, depression), even death
Vitamin B3
Toxicities RARE - only from supplements red/flushed face,itching, nausea and vomiting, hyperglycemia, hyperuricemia (gout), liver damage (jaundice, elevated liver enzymes), dizziness, fatigue, low BP
Vitamin B5
pantothenic acid
Vitamin B5
Foods: animal product (liver/organs, beef, poultry, fish, yogurt, milk), plants - shiitake mushrooms, avocado, sunflower seeds, nuts, fortified grains, breads, cereals
Vitamin B5
Found everywhere - synthesis of CoA and succinyl CoA In Krebs cycle, metabolism of cholesterol and fats, steroid hormones, acetylcholine and ketones, and synthesis of heme
Vitamin B5
Deficiencies: rare in isolation, malnutrition Symptoms: dermatitis, alopecia, peripheral neuropathy - numbness and burning of hands and feet, nausea, vomiting, loss of appetite, anorexia, enteritis, abdominal cramping Irritability and restlessness, headache, fatigue
Vitamin B5
NO toxicities (except mega supplements can cause GI distress)
Vitamin B6
pyridoxine Active form = pyridoxal phosphate PLP
Vitamin B6
Foods: animal product (organs, meat, poultry, fish), plants/legumes (chickpeas), some fruits and vegetables, fortified grains, breads, cereals
Vitamin B6
Protein metabolism: Transamination of amino and keto acids, ALT, AST Decarboxylation reactions (-CO2) Synthesis of heme, niacin, histamine, glutathione, etc. Neurotransmitter synthesis (serotonin, EPI, NE, DOPA, GABA) Involved in homocysteine metabolism (with B12, folate) Role in immune function
Vitamin B6
Supplement to treat nausea and vomiting in pregnancy
Vitamin B6
Deficiencies - rare in isolation, malnutrition, GI prob, alcoholism, HIV, dialysis, med interactions risk factor for vascular and inflammatory diseases (Microcytic anemia, sideroblastic anemia (low Hgb, excess iron)) nausea, vomiting, inflammation of mouth and tongue (glossitis, cheilosis) convulsions, irritability, peripheral neuropathy
Vitamin B6
Toxicities - rare from food, from supplement Peripheral neuropathy, ataxia, nausea
Vitamin B7
Biotin
Vitamin B7
Foods: animal product (liver/organs, beef, pork, fish, eggs, milk and dairy), plants - sweet potato and avocado, seeds, nuts, yeast, fortified grains, breads, cereals
Vitamin B7
Cofactor for multiple carboxylase enzymes (add C) - in synthesis and oxidation of fatty acids, gluconeogenesis, catabolism of branched chain AA Pyruvate carboxylase, acetyl-CoA carboxylase
Vitamin B7
Modulation of cell signaling, regulation of gene expression, histone mod
Vitamin B7
Supplement - used to promote hair, nails skin by stimulating keratin production - but not sufficient evidence
Vitamin B7
Deficiencies: Bc malnutrition, alcoholism, parenteral nutrition w/out supplement, long term antibiotics and avidin (protein in raw egg whites) inhibit ____ absorption Symptoms: alopecia, scaly red rash around eyes, nose, mouth, genitals Brittle nails Depression, lethargy, hallucinations, numbness and tingling of extremities, seizures
Vitamin B9
folate
Vitamin B9
Foods: animal product (organs, meat, poultry, fish, eggs, dairy), legumes, vegetables (leafy green), fruits fortified grains, breads, cereals (deficiency common in those who avoid gluten)
Vitamin B9
Converted to tetrahydrofolic acid (THF) - coenzyme for 1-carbon methyl transfer Needed for DNA synthesis, cell division, heme synthesis, B-12-homocysteine conversion
Vitamin B9
Supplement: fortified to reduce neural tube defects pre and during pregnancy (otherwise low birthweight, preterm delivery, fetal growth retardation); insufficient evidence to support prevention of cancer, CVD, and cog decline
Vitamin B9
Deficiencies - malnutrition and malabsorption, HIV, alcoholism, interactions with methotrexate, phenytoin, sulfonamides
Vitamin B9
Deficiencies: high homocysteine and associated w/anemia, CVD, cog decline Macrocytic, megaloblastic anemia - fatigue, weakness, heart palpitations, shortness of breath nausea, vomiting, constipation, loss of appetite, weight loss, glossitis, cheilosis Changes in skin, hair, nails No neurological symptoms
Vitamin B9
Toxicities - excess ___ masks B12 deficiency (both manifest in megaloblastic anemia) but can't correct neuro symptoms of B12
Vitamin B12
cobalamin
Vitamin B12
Foods: ONLY animal product, fortified grains, breads, cereals, nutritional yeast, soy and rice milk
Vitamin B12
Supplement required for vegan/vegetarian
Vitamin B12
stored long-term (3-4 years)
Vitamin B12
Cofactor for methionine synthase (homocysteine -> methionine) which is a methyl donor to make proteins, lipids, hormones, DNA, RNA, hemoglobin, RBCs Role in neurological functio
Vitamin B12
Deficiencies because - alcoholism, malnutrition, GI disorders, dialysis, HIV, H. pylori, atrophic gastritis, lack of intrinsic factor imp in breaking down ____(pernicious anemia), medication interactions (metformin so when given with diabetes also give ____ supplement, PPIs)
Vitamin B12
Deficiencies: Macrocytic, megaloblastic anemia - fatigue, weakness Neurological - peripheral neuropathy (numbness, tingling), poor balance, confusion, poor memory, dementia, depression Nausea, vomiting, constipation, loss of appetite, weight loss, glossitis, cheilosis Can lead to high homocysteine and methylmalonic acid (MMA) - associated with CVD and cog decline
Fugitive Slave Act
One part of the Compromise of 1851, this law stated that escaped slaves must be returned to masters even if they were in the North, and set harsh punishments for those assisting runaway slave

Popular Sovereignty
Let the people decide by State, on whether slavery should be allowed in territories through voting.

Dred Scott
He was a slave who was taken to free territory. He sued for his freedom and the Supreme Court declared that slaves are property, not people.

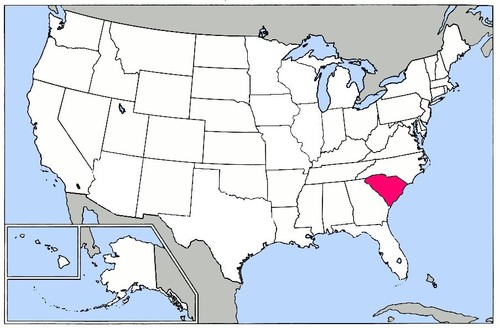
South Carolina
First state to secede/leave the Union in 1860.
Secessionists
These people believed that since the states voluntarily joined the Union, they can also choose to leave.
Abraham Lincoln
President of the U.S., 1861-1865

Cotton
number 1 Cash Crop in the South in the 1800's.

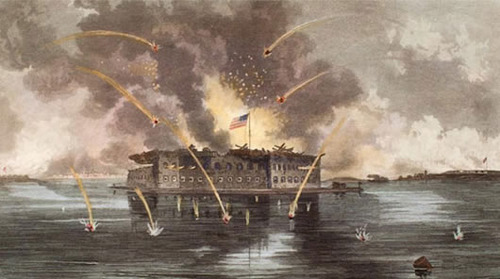
Ft. Sumter
April 12th, 1861- Confederate soldiers firing on this fort initiated the Civil War.
Give one reason why most southerners were upset about Lincoln's election in 1860.
They thought Lincoln would abolish slavery, and Lincoln did not win a single southern state in the election, the south knew they had lost the balance of power.
Compromise of 1850
Law passed that gave North and South part of what they wanted. California admitted as free state, slave trade abolished in DC, and new fugitive slave law passed; advocated by Henry Clay and Stephen A. Douglas

Underground railroad
1830, Harriet Tubman, a system that helped enslaved African Americans follow a network of escape routes out of the South to freedom in the North, went all the way to Canada

Kansas-Nebraska Act
1854 - Douglas: Created Nebraska (north) and Kansas (south) as states and gave the people in those territories the right to chose to be a free or slave state through popular sovereignty. North disliked the Act and Southerners loved it.

John Brown
Abolitionist involved in violence in Kansas. In 1859, he led a raid of a government arsenal at Harper's Ferry, Virginia, with the intention of arming slaves and starting a revolt. He became a hero of the abolitionists in the Civil War. Brown was considered a matryr by some and a madman by others.

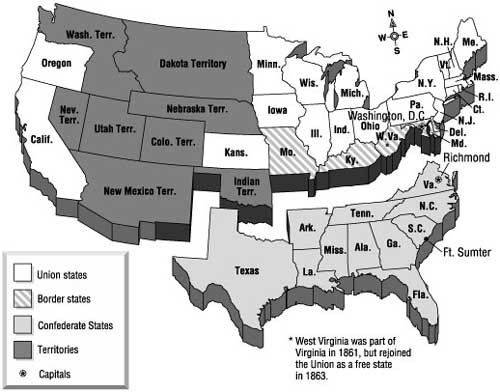
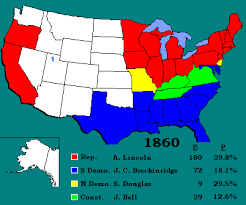
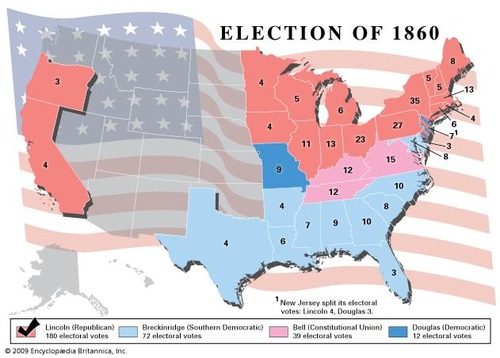
Election of 1860
Abraham Lincoln, the Republican candidate, won because the Democratic party in the South was split over slavery. As a result, the South no longer felt like it had a voice in politics and a 11 states seceded from the Union.
Harriet Beacher Stowe
The author of the book Uncle Toms Cabin that persuaded people to want to end slavery.

Stephen Douglas
The "Little Giant." He proposed the Kansas - Nebraska Act and the idea of popular sovereignty to decide the issue of slavery in the territories. He also had a series of famous debates when he defeated Abraham Lincoln for Senate in 1858 in Illinois.

sectionalism
People aligning themselves more with the region of the country they live in rather than the nation as a whole.
Martyr
A person who dies for a cause or belief.

Republican Party
Political party formed in 1854. Its main goal was to stop the spread of slave

List 3 ways the Dred Scott Decision impacted the nation:
1 - Ruled slaves were property, not people with rights. 2 - Missouri Comp. unconstitutional = slavery spreads into territories. 3 - Free African Americans lose status 4 - Abolitionist setback

"Bleeding Kansas"
(1856) a series of violent fights between pro-slavery and anti-slavery forces in Kansas who had moved to Kansas to try to influence the decision of whether or not Kansas would a slave state or a free state.
Harper's Ferry
John Brown's scheme to invade the South with armed slaves, backed by sponsoring, northern abolitionists; seized the federal arsenal; Brown and remnants were caught by Robert E. Lee and the US Marines; Brown was hanged

Lincoln-Douglas Debates
Series of 1858 Senate debates...Lincoln forced Douglas to debate issue of slavery, Douglas supported popular sovereignty. Lincoln asserted that slavery should not spread to territories, Lincoln lost to Douglas, but emerged as strong Republican candidate.
