Bio Unit 1
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/28
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
1
New cards
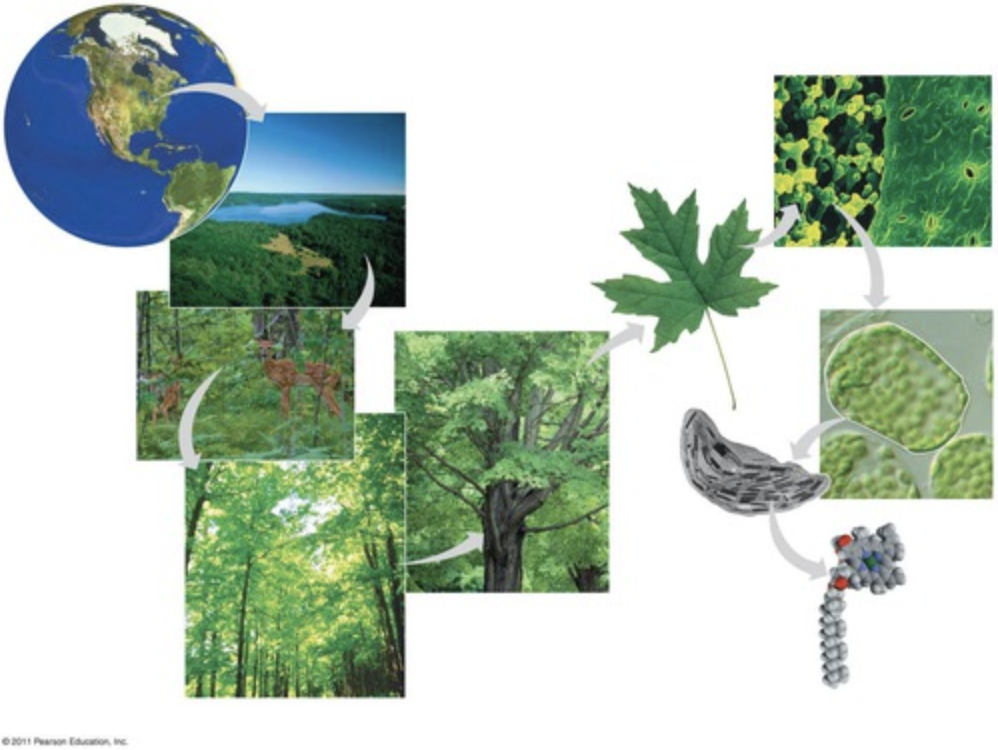
==**biology**==
the scientific study of ==***living things***==

2
New cards
%%science%%
observation, identification, experimentation, investigation and theoretical explanation of %%natural phenomina%%

3
New cards
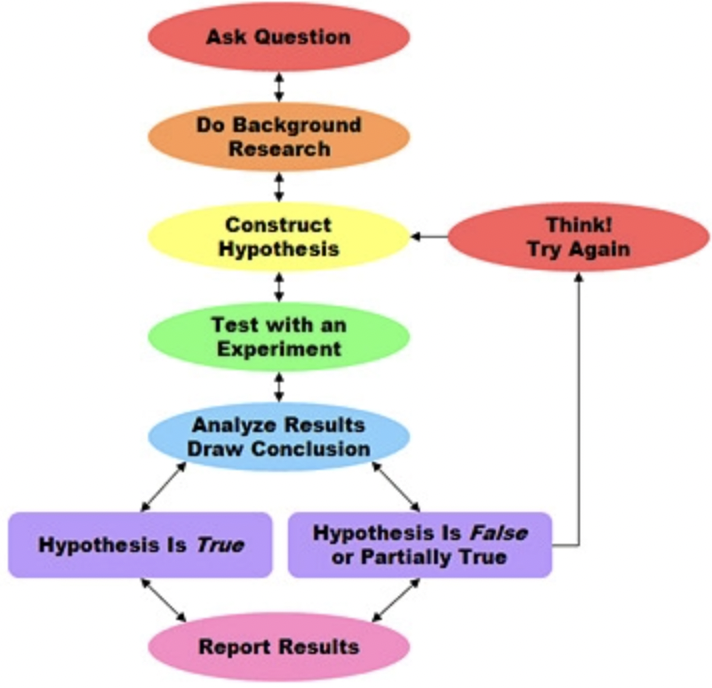
%%scientific **method**%%
the scientific method is a body of %%techniques%% for *investigating phenomena*, acquiring *new knowledge*, or correcting and integrating *previous knowledge*.
4
New cards
%%hypothesis%%
the *assumption* about what will happen during an experiment or observation based on %%reason and experience.%%

5
New cards
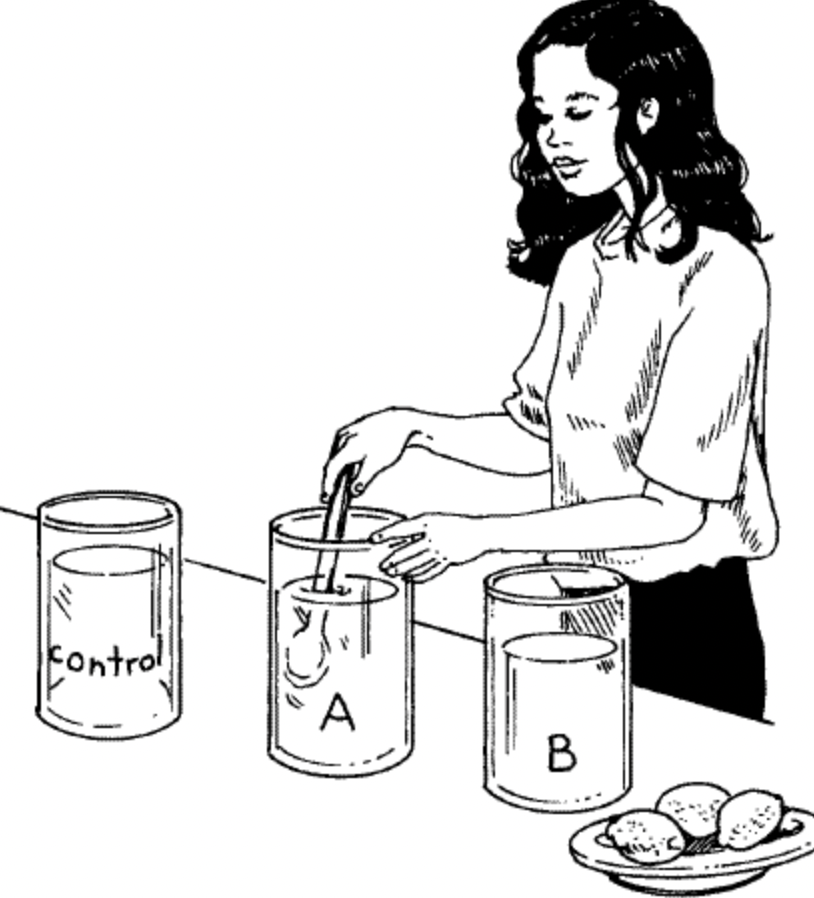
%%experiment%%
set of *organized steps* followed under controlled conditions to test a %%theory or hypothesis.%%
6
New cards
%%dependent variable%%
the variable that *depends* on the %%other variables%% - data - what is measured.
7
New cards
%%independent variable%%
__in an experiment, the factor that the scientists deliberately manipulates.__
8
New cards
%%control group%%
in an experiment, it is the group that has __no changes__ to it - the natural expected conditions.
9
New cards
qualitative data
data that represents qualities or characteristics that can be expressed by a number. categories (example smooth, rough)
10
New cards
quantitative data
data that represents a quantity; numeric data. numbers
11
New cards
%%inference%%
making an explanation for an observation
12
New cards
%%observation%%
what you see.
13
New cards
%%homeostasis%%
a state of balance reached through reactions within a cell or organism. (Greek = stays the same)
14
New cards
metabolism
The chemical processes we need for life (the total of all chemical reactions within an organism).
15
New cards
organism
any living thing that takes in food, grows, and reproduces.
16
New cards
Characteristics of Life
1\. cells & organization, 2. use of energy & metabolism, 3. responds to the environment, 4. regulations & homeostasis, 5. Growth & development, 6. reproduction, 7. evolution
17
New cards
organ
a group of different tissues that work together to perform a specific function.
18
New cards
organelle
a differentiated structure within a cell that performs a specific function. example: chloroplast, mitochondria.
19
New cards
tissue
a group of cells that are similar in structure and that work together to perform a certain function.
20
New cards
Levels of Organization
atom-molecules-macromolecules-cells-tissues-organs-organ systems-organisms-populations-communities-ecosystems-biosphere.
21
New cards
abiotic
relating to non biological factors.
22
New cards
biome
a large area dominated by characteristic plants and animals. example: rain forest, tundra
23
New cards
biotic
relating to factors that are associated with or result from the activity of living organisms
24
New cards
community
all of the populations that live and interact with each other in a particular area.
25
New cards
ecosystem
a community or group of organism living and interacting with each other and their environment.
26
New cards
population
all of the members of one species that live in a common area and whose population dynamics are different from those of other populations.
27
New cards
adenosine triphosphate
ATP: the molecule that delivers usable chemical energy for almost all processes and reactions that a cell must undergo to survive. Energy comes from backing the bonds in the phosphate tails.
28
New cards
cellular respiration
the process of breaking down glucose for the production of ATP in the presence of oxygen.
29
New cards
photosynthesis
the process by which plants and certain other organism use the energy of sunlight to convert carbon dioxide and water into sugar and oxygen.