Biology, Biology (copy) (copy)
1/400
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
401 Terms
Body Systems
Sets of organs in our bodies that do the work to keep us healthy and alive.
Atom
Tiniest part of all living and non-living things.
cells
Small part of all living things.
Molecules
Many cells working together.
Organs
Made of thousands of cells, connected by several body systems to do work to keep our bodies healthy & alive.
Kingdoms
Classifications of Living things.
Mammals
Living things with vertebra, hair or fur, gives birth to babies, feed the babies milk form their bodies & warm blooded.
Birds
May or may not fly, with vertebra, lay eggs, have feathers

Reptiles
Land & water animals, no vertebra, most lay eggs some have babies, smooth or rough scaly skin, no legs or arms.

Amphibians
Mostly water animals but can live on land, smooth or rough scaly skin, lay eggs & may have lungs.
Mollusks
Slimy animals, no skin or vertebra & no shells.

Arthropods
Hard body sections & no vertebra.

Worms
No vertebra, ears or eyes live underground & slimy.

Jellies
Have long electric tentacles, soft bodies & no vertebra.

Crustaceans
Shells soft bodies, no vertebra &Hard shells.

Fish
Gills & fins, cold blooded.

Insects
2 - 6 Legs, no vertebra, lay eggs, many eyes.

Archnids
8 Legs, no vertebra, may have wings, lay eggs.

Marsupials
Mammals but with baby pouch on outside of bodies.

Plants

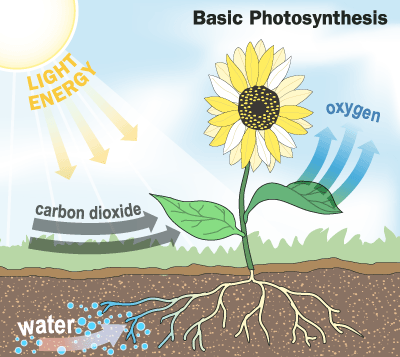
photosynthesis
Conversion of light energy from the sun into chemical energy. products of photosynthesis are glucose and oxygen
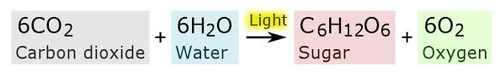
photosynthesis equation(very important)
6CO2 + 6H2O --> light energy --> C6H12O6 + 6O2
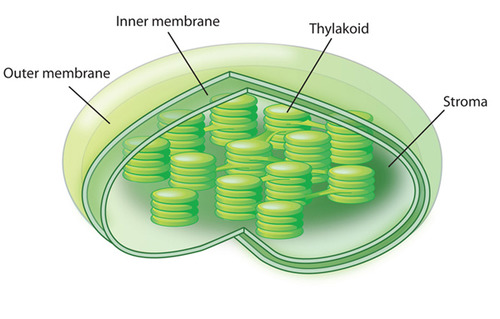
chloroplasts
A structure in the cells of plants and some other organisms that captures energy from sunlight and uses it to produce food. main function of chloroplasts is to produce food (glucose) Chloroplasts contain the pigment, chlorophyll. Chlorophyll absorbs most of the colors in the color spectrum, and reflects only green and yellow wavelengths of light. This is why we see leaves as green or yellow - because these colors are reflected into our eyes.
glucose
another name for sugar C6H12O6 three things used for making glucose are sunlight water and carbon dioxide used for energy and growth
sunlight
main source of energy
cellular respiration
C6H1206->CO2 + H20+ ENERGY (released) goal is to create ATP occurs in all living things
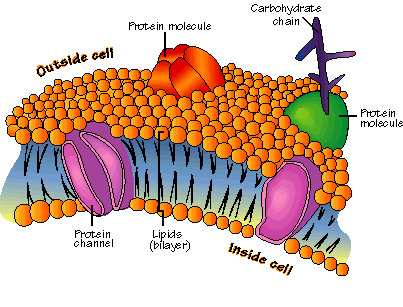
cell
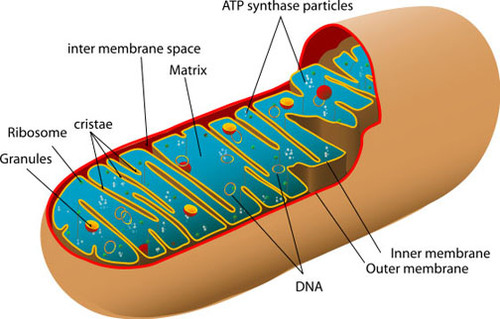
mitochondria
An organelle found in large numbers in most cells, in which the biochemical processes of respiration and energy production occur.
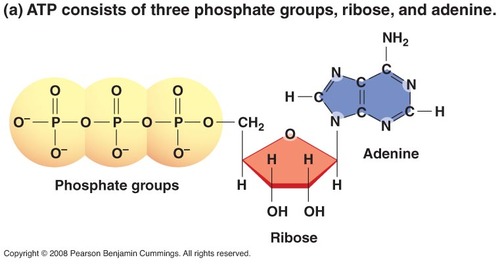
ATP
(adenosine triphosphate) main energy source that cells use for most of their work the energy is stored in ATP until it is released by the reactions remove a phosphate from ATP a simple way of remembering it is just that it's just energy
Metabolism
The sum total of all processes in an organism which convert energy and matter from outside sources and use that energy and matter to sustain the organism's life functions.
Anabolism
The sum total of all processes in an organism which use energy and simple chemical building blocks to produce large chemicals and structures necessary for life.
Catabolism
The sum total of all processes in an organism which break down chemicals to produce energy and simple chemical building blocks.
Photosynthesis
The process by which green plants and some other organisms use the energy of sunlight and simple chemicals to produce their own food.
Herbivores
Organisms that eat only plants.
Carnivores
Organisms that eat only organisms other than plants.
Omnivores
Organisms that eat both plants and other organisms.
Producers
Organisms that produce their own food.
Consumers
Organisms that eat living producers and/or other consumers for food.
Decomposers
Organisms that break down the dead remains of other organisms.
Autotrophs
Organisms that are able to make their own food.
Heterotrophs
Organisms that depend on other organisms for their food.
Receptors
Special structures that allow living organisms to sense the conditions of their internal or external environment.
Asexual reproduction
Reproduction accomplished by a single organism.
Sexual reproduction
Reproduction that requires two organisms
Inheritance
The process by which physical and biological characteristics are transmitted from the parent (or parents) to the offspring.
Mutation
An abrupt and marked change in the DNA of an organism compared to that of its parents
Hypothesis
An educated guess that attempts to explain an observation or answer a question.
Theory
A hypothesis that has been tested with a significant amount of data.
Scientific law
A theory that has been tested by and is consistent with generations of data.
Microorganisms
Living creatures that are too small to see with the naked eye.
Abiogenesis
The idea that long ago, very simple life forms spontaneously appeared through chemical reactions.
Prokaryotic cell
A cell that has no distinct, membrane-bounded organelles.
Eukaryotic cell
A cell with distinct, membrane-bounded organelles.
Species
A unit of one or more populations of individuals that can reproduce under normal conditions, produce fertile offspring, and are reproductively isolated from other such units.
Taxonomy
The science of classifying organisms.
Binomial nomenclature
Naming an organism with its genus and species name.
Pathogen
An organism that causes disease.
Saprophyte
An organism that feeds of dead matter.
Parasite
An organism that feeds on a living host.
Aerobic organism
An organism that requires oxygen.
Anaerobic organism
An organism that does not require oxygen.
Steady state
A state in which members of a population die as quickly as new members are born.
Exponential growth
Population growth that is unhindered because of the abundance of resources for an ever-increasing population.
Logistic growth
Population growth that is controlled by limited resources.
Conjugation
A temporary union of two organisms for the purpose of DNA transfer.
Plasmid
A small, circular section of extra DNA that confers one or more traits to a bacterium and can be reproduced separately from the main bacterial genetic code.
Transformation
The transfer of a DNA segment from a nonfunctional donor cell to that of a functional recipient cell.
Transduction
The process in which infection by a virus results in DNA being transferred from one bacterium to another.
Endospore
The DNA and other essential parts of a bacterium coated with several hard layers.
Strains
Organisms from the same species that have markedly different traits.
Pseudopod
A temporary, foot-like extension of a cell, used for locomotion or engulfing food.
Nucleus
The region of a eukaryotic cell that contains the cell's main DNA.
Vacuole
A membrane-bounded "sac" within a cell.
Ectoplasm
The thin, watery cytoplasm near the plasma membrane of some cells.
Endoplasm
The dense cytoplasm found in the interior of many cells.
Flagellate
A protozoan that propels itself with a flagellum.
Pellicle
A firm, flexible coating outside the plasma membrane.
Chloroplast
An organelle containing chlorophyll for photosynthesis.
Chlorophyll
A pigment necessary for photosynthesis.
Eyespot
A light-sensitive region in certain protozoa
Symbiosis
A close relationship between two or more species where at least one benefits.
Mutualism
A relationship between two or more organisms of different species where all benefit from the association.
Commonesalism
A relationship between two organisms of different species where one benefits and the other is neither harmed nor benefited.
Parasitism
A relationship between two organisms of different species where one benefits and the other is harmed.
Cilia
Hairlike projections that extend from the plasma membrane and are used for locomotion.
Spore
A reproductive cell with a hard, protective coating.
Plankton
Tiny organisms that float in the water.
Zooplankton
Tiny floating organisms that are either small animals or protozoa.
Phytoplankton
Tiny floating photosynthetic organisms, primarily algae.
Thallus
The body of a plant-like organism that is not divided into leaves, roots, or stems.
Cellulose
A substance (made of sugars) that is common in the cell walls of many organisms.
Holdfast
A special structure used by an organism to anchor itself.
Sessile colony
A colony that uses holdfasts to anchor itself to an object.
Extracellular digestion
Digestion that takes place outside of the cell.
Mycelium
The part of the fungus responsible for extracellular digestion and absorption of the digested food.
Hypha
A filament of fungal cells.
Rhizoid hypha
A hypha that is imbedded in the material on which the fungus grows.
Aerial hypha
A hypha that is not imbedded in the material upon which the fungus grows.
Sporophore
Specialized aerial hypha that produces spores.
Stolon
An aerial hypha that asexually reproduces to make more filaments.