EOPA Study Guide
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/125
Last updated 1:31 PM on 5/3/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
126 Terms
1
New cards
When breeding animals, sometimes AI is used. What does AI stand for, and how does it differ from natural service?
Artificial insemination, there is no male and female contact, sperm is taken from the male and introduced to the female artificially.
2
New cards
What does DNA stand for? What does RNA stand for? What is the difference between these two?
Deoxyribonucleic Acid: Contains genetic information. Ribonucleic Acid: carries the genetic information.
3
New cards
What is the difference between mitosis and meiosis? Which of these produces sex cells that are important in animal reproduction?
Mitosis: Where single cells divide into 2 identical daughter cells. Meiosis: Single cells divide into 4 cells containing half of their original genetic information. (sex cell)
4
New cards
What is estrus in animals? What are the signs of estrus in a cow? In a pig?
Cows: Mount each other, rest their chin on other cows, swelling of the vulva. Pigs: Lock their legs (standing to be mounted) swelling of the vulva.
5
New cards
Explain what embryo transfer is and how it is used in the animal industry.
Artificial method of breeding, embryos and removed from one with good quality characteristics desired by the animal producer of the scientist female and put into another.
6
New cards
Sometimes estrus synchronization is used to control the estrus cycle of a group of females. Why would this be beneficial to a farmer?
To know when all of them got pregnant and when they will have their babies, also helps with organization.
7
New cards
**Are livestock animals given feed supplements? Give some examples.**
Mineral block (to lick, ex. Salt). Protein supplements.
8
New cards
In genetics, some traits are dominant and some are recessive. What does each of these terms mean?
Dominant traits will cover up the recessive traits, there must be more than one recessive trait for it to show.
9
New cards
What is one example of a feedstuff that could be fed to pigs in order to provide them with energy?
One example of a feedstuff that could be fed to pigs in order to provide them with energy is Corn, concentrate.
10
New cards
When an animal is sick, or when it is being vaccinated to prevent sickness =, may need a shot. These shots can be given SubQ, IV or IM. What do each of these things mean?
\- SubQ: under the fatty tissue
\- IV: into a vein
\- IM: into a muscle
\- IV: into a vein
\- IM: into a muscle
11
New cards
What is the difference between a ruminant and a non- ruminant? Give an example of each.
\- Ruminant: has 4 stomach compartments (rumen, the reticulm, the omasum and the abomasum) (ex. Cows)
\- Non- ruminant has 1 stomach compartment (ex. Chickens)
\- Non- ruminant has 1 stomach compartment (ex. Chickens)
12
New cards
In animal feed, what is the difference between roughage/forage and concentrate? Which can be stored in a pasture/barn
\- Roughage/forage. stored in pasture/barn, it is anything that is not a seed (ex. Grass)
\- Concentrate stored in silos or grain bins, it is the seed that come from the roughage/forage (ex. Corn)
\- Concentrate stored in silos or grain bins, it is the seed that come from the roughage/forage (ex. Corn)
13
New cards
Common animal feedstuffs are pasture, grain, silage, haylage and hay. Define each of these and explain how they are produced.
Pasture: edible parts of plants, other than gran
14
New cards
Draw the digestive system of a horse and label the parts
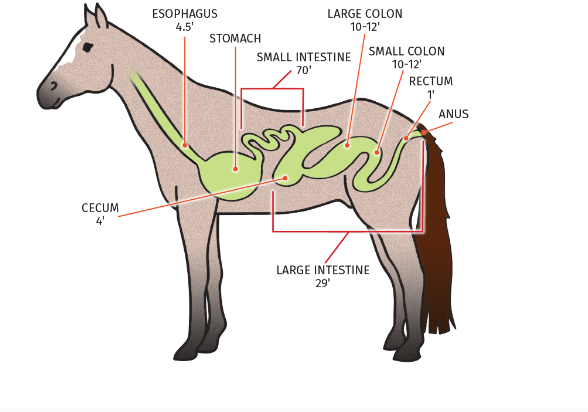
15
New cards
List the parts and functions of the male reproductive system
Penis, Scrotum, Testes, Episdidymis, Vas Deferens, Prostate, and Seminal Vesicles
16
New cards
List the parts and functions of the female reproductive system.
Ovaries, Fallopian Tubes, Uterus, Cervix, and Vagina
17
New cards
The trachea and esophagus are right beside each other in animals. What system of the body is each a part of? What does this have to do with “bloat” in cattle?
\-Trachea: Respiratory
\-Esophagus: Digestive system
\-- Because of the bloat, pressure is put on the trachea and can suffocate the cow.
\-Esophagus: Digestive system
\-- Because of the bloat, pressure is put on the trachea and can suffocate the cow.
18
New cards
What is hardware disease in cattle, what causes it and how is it treated?
A blockage caused by ingesting metal, can be treated by placing a metal, can be treated by placing a magnet into their stomach, if that doesn't work then the metal must be surgically removed
19
New cards
**When breeding animals, sometimes AI is used. What does AI stand for, and how does it differ from natural service?**
Artificial insemination, there is no male and female contact, sperm is taken from the male and introduced to the female artificially.
20
New cards
In genetics, some traits are dominant and some are recessive. What does each of these terms mean?
Dominant traits will cover up the recessive traits, there must be more than one recessive trait for it to show.
21
New cards
What does DNA stand for? What does RNA stand for? What is the difference between these two?
Deoxyribonucleic Acid: Contains genetic information. Ribonucleic Acid: carries the genetic information.
22
New cards
What is estrus in animals? What are the signs of estrus in a cow? In a pig?
Cows: Mount each other, rest their chin on other cows, swelling of the vulva. Pigs: Lock their legs (standing to be mounted) swelling of the vulva.
23
New cards
Explain what embryo transfer is and how it is used in the animal industry.
Artificial method of breeding, embryos and removed from one with good quality characteristics desired by the animal producer of the scientist female and put into another.
24
New cards
Sometimes estrus synchronization is used to control the estrus cycle of a group of females. Why would this be beneficial to a farmer?
To know when all of them got pregnant and when they will have their babies, also helps with organization.
25
New cards
Are livestock animals given feed supplements? Give some examples.
Mineral block (to lick, ex. Salt). Protein supplements.
26
New cards
Explain and give the chemical formula for photosynthesis.
Photosynthesis is The process plants use to convert light energy to chemical energy and store it in the form of sugar.
6CO2+6H2O → C6H12O6+6O2
6CO2+6H2O → C6H12O6+6O2
27
New cards
Explain and give the chemical formula for cellular respiration.
Cellular Respiration is the breaking down of glucose molecules in all living organisms to release energy.
C6H12O6 + 6O2 → 6CO2 + 6H2O
C6H12O6 + 6O2 → 6CO2 + 6H2O
28
New cards
Define transpiration and explain why it’s important in plants.
Transpiration is the loss of water through a leaf’s surface.
29
New cards
**Plants are either monocots or dicots. Describe the characteristics of each.**
Monocot is a plant that has one seed leaf when it first emerges. Also referred to as a *monocotyledon*. Dicot is a plant that has two seed leaves when it firsts emerges. Also referred to as a *dicotyledon*.
30
New cards
What are the different parts of a stem?
Nodes, Internodes, Terminal or apical bud, Lateral or axillary bud, and Petiole.
31
New cards
Define scarification and explain why this is important for germination.
To scarify a seed means to break down the seed’s outer protective coating in order to expedite the germination process.
32
New cards
Describe how a fruit is formed, starting with a flower. Include pollination and fertilization.
Fruits are the mature and ripped ovaries of flowers. The first step in fruit growth is fertilization of the carpel. Then, a fruiit arises from a series of transformation that occur during the development of the fertilized carpel, resulting in the ovary of the flower maturing and ripening. Throughout this process, the cells in the carpel of the flower change so that the the structural layers become the fruit.
33
New cards
In plant science, what are the three primary macronutrients and the three secondary macronutrients? What is each used for within the plant?
The three primary macrountrients are Carbohydrates, Fat, and Protein. The three secondary macrountrients are Calcium, Magnesium, and Sulfur. The Primary Macronutrients are used for energy metabolism and protein synthesis." (agqlabs.us.com) Secondary Macrountrients are used for "stabilizing the cell wall and favoring cell wall formation.
34
New cards
Explain pollination, cross-pollination, and self-pollination in plants.
Pollination is the act of transferring pollen grains from the male anther of a flower to the female stigma. Cross-pollination is the process of applying pollen from one flower to the pistils to another flower. Self-pollination is if pollen is transferred to it from any flower of the same plant.
35
New cards
Explain pollination, cross-pollination, and self-pollination in plants.
Pollination is the process of fertilization in which *pollen* is transferred from the *anther* in a flower’s *stamen* to the style of a flower’s *pistil*. A fertilization process that occurs when pollen from the male portions of the flower is transferred to the female portions of the flower. Cross-pollination is the process of applying pollen from one flower to the pistils to another flower. Self-pollination is if pollen is transferred to it from any flower of the same plant
36
New cards
What are the conditions that arerequired for seed germination?
Water, Oxygen, and Proper Temperature.
37
New cards
Cuttings, grafting and layering are all examples of what type of plant propagation?
**Asexual Propagation**
38
New cards
List 5 and what they do.
Auxins - promotes cell growth and differentiation, especially on the tips of plants. Cytokinin - promotes cell division and lateral growth in plants. Gibberellins - helps in breaking dormancy in seeds and buds. Abscisic acid - promotes dormancy in seeds and buds. Ethylene - promotes fruit ripening.
39
New cards
Why is record keeping important within any business or SAE?
You need good records to prepare an accurate financial statement
40
New cards
What type of file is best to use when you need a database of records?
Spreadsheet, Word Document, Slide Show or Presentation. Spreadsheet
41
New cards
What is the difference between a fixed expense and a variable expense? Give examples of each
Fixed expenses generally cost the same amount each month (such as rent, mortgage payments, or car payments), while variable expenses change from month to month (dining out, medical expenses, groceries, or anything you buy from a store)
42
New cards
When running a business what is the difference between accounts payable and accounts receivable?
Account payable charges that are typically due in full when received, and have a short time frame for payment, while Account receivable refer to the money a comapany's customers owe for goods or services they have received but not yet paid for.
43
New cards
How do you calculate the amount of interest that you have to pay when you take out a loan?
There are different methods for calculating interest, depending on what that interest rate is and how often it is applied to the loan.
44
New cards
What is a tax bracket and how does it affect the amount of money that you have to pay in taxes?
Tax bracket is a range of incomes taxed at a given rate. Tax brackets show you the tax rate you will pay on each portion of your taxable income.
45
New cards
In order to secure a loan you may need collateral. Define Collateral.
Collateral is the property does not need to be property could be any item of value if you default on the loan you will forfeit the item used to secure the loan.
46
New cards
When meat has been in the freezer too long, what is the term for what happens to the meat?
Freezer burn
47
New cards
What are the signs of meat spoilage that you can look for when cooking?
Smell, Texture and Color.
48
New cards
Define ossification
Ossification is process of bone formation (when harvesting an animal the less catilage they have the older they are.)
49
New cards
**What is the difference between intramuscular fat (marbling) and intermuscular fat? Which of these increases the quality grade of meat?**
Intramuscular: inside the muscle (increases the quality) Intermucular: around the muscle.
50
New cards
What is the difference between quality grade and yield grade in meat science?
Quality grade: amount intramuscular fat. Yield grade: How much meat is on their body.
51
New cards
Which of the particles is the largest? Which is the smallest?
Sand is the largest. Clay is the smallest.
52
New cards
Define parent material.
Parent material is the material (bedrock, sediment, or organic material) that is weathered to form soil. This is the material that the subsoil and topsoil are made from
53
New cards
What is an agricultural commodity? List several examples.
Agricultural Commodities are crops and livestock that are raised and harvested to provide food and sometimes fuel. Some example is wheat, cotton, and flaxt.
54
New cards
In agribusiness, what is the difference between purchasing something and leasing it?
“Leasing gives farmers the opportunity to obtain critical equipment without the large initial investment.” (southernagcredit.com) “When farmers purchase equipment outright, it allows them to own and completely customize their equipment to fit the need of their form.” (southernagcredit.com)
55
New cards
When crops are grown, are they mostly sold directly to the consumer from the farm, or is there a middle-man involved in marketing the commodity crops to the consumer?
They are mostly sold directly to the consumer from the farm. No sold through a middle man or a store
56
New cards
There are four types of pest control: Cultural, Mechanical, Chemical, and Biological. Give a description or example of each type of pest control.
Cultural controls are practices that reduce pest establishment, reproduction, dispersal, and survival. Mechanical control is control pest with physical methods or mechanical devices. Chemical control is the use of pesticides. Biological control is the deliberate use of natural enemies - predators, parasites, pathogens, and competitors to suppress and maintain populations of a target pest species.
57
New cards
Research and define the following crops: Wheat, Barley, Timothy, Alfalfa. What type of implement is used to harvest each of these crops?
\
Wheat is a cereal crop grown for food. Barley is a tough cereal, grown in a number of environments where other grains can’t grow. Timothy crop is a cool season perennial grass with rapid growth. Alfalfa crop is a perennial, cloverlike, leguminous plant of the pea family. The most common type of harvesting implements are small sickle, big sickle, darat, gandasa and small axe etc.
Wheat is a cereal crop grown for food. Barley is a tough cereal, grown in a number of environments where other grains can’t grow. Timothy crop is a cool season perennial grass with rapid growth. Alfalfa crop is a perennial, cloverlike, leguminous plant of the pea family. The most common type of harvesting implements are small sickle, big sickle, darat, gandasa and small axe etc.
58
New cards
What is a legume and how does it help with other crops?
Legume is a plant that has a symbiotic relationship with bacteria (rhizobia) housed in nodules on its roots, allowing it to take nitrogen from the soil and convert/uptake it as a protein source. The rhizobia convert atmospheric nitrogen into nitrogen that can be used by other plants.
59
New cards
**Define “No-Till” gardening, and explain how it works.**
"No-Till" gardening is a method of planting where the farmer does not plow or disk the soil, but the plants a new crop in the remnants of the previous year's crop.
60
New cards
**SAE’s are either categorized as Entrepreneurship, Placement, Exploratory, or Research. Define each of these and give an example of a project that would fall under each category.**
Entrepreneurship SAE is A Supervised Agricultural Experience in which students own and operate an agricultural business. (raising and selling animals or crops, building and selling agricultural equipment, and buying and reselling feed.) Placement SAE is A Supervised Agricultural Experience that requires the student to work for someone else in an agriculture related job. The work may or may not be paid. (working on a farm or a ranch, in a farm supply store or a food testing laboratory or in an agriculturally related non-profit organization.) Exploratory SAE is A Supervised Agricultural Experience designed to increase student agricultural career awareness through exploration activities. Exploration activities may include observing, interviewing, or assisting an individual in an agriculture related profession, participating in a field day or event, or giving a classroom demonstration. Research SAE is A Supervised Agricultural Experience designed for students to use the scientific method to analyze a research question or test a hypothesis. Research SAEs may be experimental projects (comparing plant growth using different growing methods), as well as non-experimental ones (developing a marketing plan or ad campaign for an agriculture commodity). (raising and selling animals or crops, building and selling agricultural equipment, and buying and reselling feed, seed or fertilizer,)
61
New cards
Ag Education includes three parts: Classroom instruction, SAE, and FFA

62
New cards
Soil is made up of air, water, minerals, and organic matter. The air and water keep the roots healthy and they provide water to the plant. The organic matter breaks down to provide nutrients to the growing plant. The minerals are just broken up pieces of rock that give the roots a place to live and grow. These minerals are different sizes and called Sand, Silt, and Clay. Draw a picture of the different sizes of these particles.
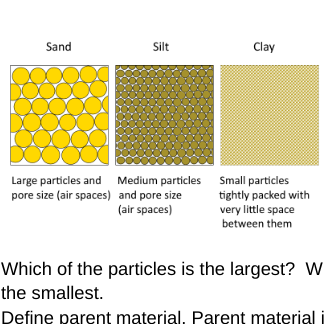
63
New cards
What term describes the castrated animals listed below
Cattle - Steer
Pigs (Hogs) - Barrow
Sheep - Wether
Goats - Wether
Pigs (Hogs) - Barrow
Sheep - Wether
Goats - Wether
64
New cards
What is the term for a mature female of the following
Hog - Sow
Cattle - Cow
Sheep - Ewe
Goats - Doe
Cattle - Cow
Sheep - Ewe
Goats - Doe
65
New cards
What is the proper term for a young female of the following
Horse - Fillies
Cow - Heifer
Sheep - Ewe Lamb
Cow - Heifer
Sheep - Ewe Lamb
66
New cards
What is the proper name for a mature male poultry of the following
\
Turkey - Gobblers
Chickens - Rooster
Turkey - Gobblers
Chickens - Rooster
67
New cards
What is the production of one or more exact genetic copies of an animal
Cloning
68
New cards
Where are the pin bones on a cow
Just below the Tail Layer
69
New cards
What is a mature female chicken kept for egg production?
Layer
70
New cards
How is the height of a horse measured?
Hands (Measured of 4”)
71
New cards
What is the proper term for a mature male of the following animals
Horse - Stallion
Cattle - Bull
Sheep - Ram
Goat - Buck
Cattle - Bull
Sheep - Ram
Goat - Buck
72
New cards
In the Dairy industry, what does the acronym BST stand for
Bovine Somatotropin
73
New cards
What is the proper term for a young male animal of the following spp?
Horse - Colt
Cattle - Bull-Calf
Hog - Boor
Sheep - Ram/Lamb
Cattle - Bull-Calf
Hog - Boor
Sheep - Ram/Lamb
74
New cards
What is an injection administered under the skin?
**Subcutaneous (SQ or Sub-Q) injection**
75
New cards
Where is the comb found on a chicken?
The comb sits on top of the hen''s head.
76
New cards
Which of the following horse headgear would utilize a bit
D-Ring Snaffle
77
New cards
What is the most common breed of chicken that is used for egg production?
White Leghorns
78
New cards
What term describes the process of giving birth in the following animals
Pigs - Farrowing
Cattle - Calving
Sheep - Lambing
Horses - Foaling
Cattle - Calving
Sheep - Lambing
Horses - Foaling
79
New cards
Homozygous
The genes an organism has from both parents are the same for a specific trait.
80
New cards
Heterozygous
The genes an organism has from the parents are different for a specific trait.
81
New cards
Phenotype
The outward expression of the genes an organism has for a specific trait.
82
New cards
Codominance
Situation in which some traits show as a mixture when the *genotype* is *heterozygous*. May be referred to as *incomplete dominance*, depending on the nature of the specific combination.
83
New cards
Dominance
the relationship between two versions of a gene
84
New cards
Recessive
a trait that is expressed only when genotype is homozygous
85
New cards
Female Plant
Pistil (Stigma, Style, Superior ovary, Ovules)
86
New cards
Male Plants
Stamen (Anther, Filament)
87
New cards
Pollination
The process of fertilization in which *pollen* is transferred from the *anther* in a flower’s *stamen* to the style of a flower’s *pistil*. A fertilization process that occurs when pollen from the male portions of the flower is transferred to the female portions of the flower.
88
New cards
A _________ **path is a plan or map showing steps** and activities to complete to develop and exhibit leadership skills.
leadership
89
New cards
A document that states the mission of the business, examines its current condition, sets goals, and outlines strategies for achieving the goals is known as a(an) _________ business plan.
strategic
90
New cards
\
When water encounters conditions where air is unsaturated, evaporation occurs and water is lost from the plant in a process called ____________________.
When water encounters conditions where air is unsaturated, evaporation occurs and water is lost from the plant in a process called ____________________.
evapotranspiration
91
New cards
Plants with alternative photosynthetic mechanisms are called C4 plants or crassulacean acid ___________ plants.
Metabolism
92
New cards
To make ATP, a glucose molecule is split into two molecules of a compound called pyruvate through a step called __________
Glycolysis
93
New cards
The mass of a given volume of dry soil that takes into consideration the solid and pore spaces of soil is the bulk _______
Density
94
New cards
The soil found naturally in a landscape without significant amendment is known as ______ soil.
Garden
95
New cards
The study of soils in their natural environment and soil conservation is called ________.
Pedology\`
96
New cards
The fertile, upper outermost layer of soils is called the topsoil, surface horizons, or ______ horizon
Subsoil
97
New cards
Salt mines that extract crude or relatively pure salts are a source of the macronutrient _________
Potassium
98
New cards
What are the levels of participation in FFA structure?
Local, State, and National
99
New cards
Explain “home project“ from the early 1900s.
Most indoor farms grow plants in a water-based nutrient solution - a technique known as hydroponics.
100
New cards
What are the duties of an agricultural business manger?
A farm business manager/accountant is responsible for the administration of management accounts, organizational budgeting and the administration of accounting processes.