AQA - Cell Biology(Cell)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/49
Last updated 3:40 AM on 11/30/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
50 Terms
1
New cards
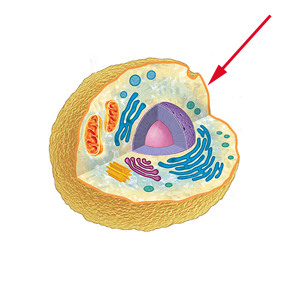
Cell membrane
Surrounds the __**cell and controls the passage**__ of substances into and out of the cell.
2
New cards
Cell wall
Found outside the cell membrane in plant and bacterial cells, provides support for the cell.
3
New cards
Chloroplast
Found in plant cells. Contain chlorophyll that absorbs light for photosynthesis.

4
New cards
Cytoplasm
Where most of the chemical reactions take place in a cell.
5
New cards
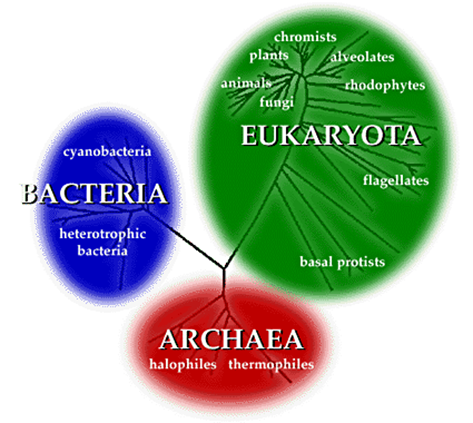
Domain
Name given to the groups suggested by Woese. There are three domains: Archae, Bacteria and Eukaryota.
6
New cards
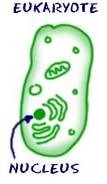
Eukaryote
Type of cell that contains a nucleus
7
New cards
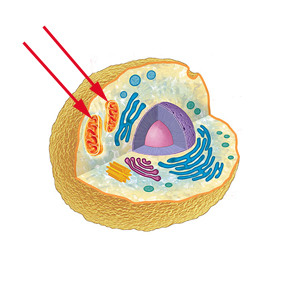
Mitochondria
Where aerobic respiration takes place.
8
New cards
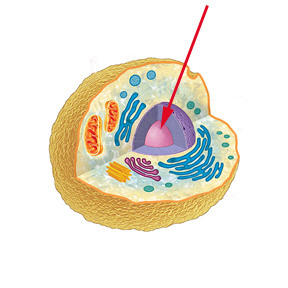
Nucleus
Contains DNA and controls cell activities.
9
New cards
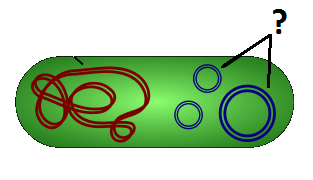
Plasmid
Small rings of DNA found in bacterial cells.
10
New cards
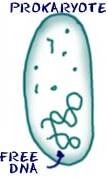
Prokaryote
Cells without a nucleus.
11
New cards
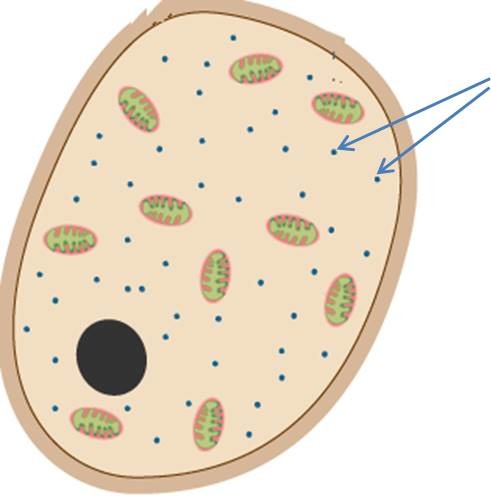
Ribosomes
Where protein synthesis occurs.
12
New cards
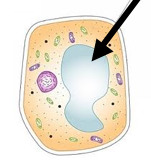
Vacuole
Found in plant cells. Contain a fluid called cell sap.
13
New cards
Cell
The basic unit of living things.
14
New cards
Differentiation
When cells become specialised to do a particular job.
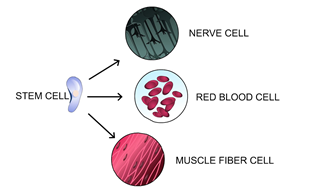
15
New cards
a
A group of tissues working together to perform a specific function.
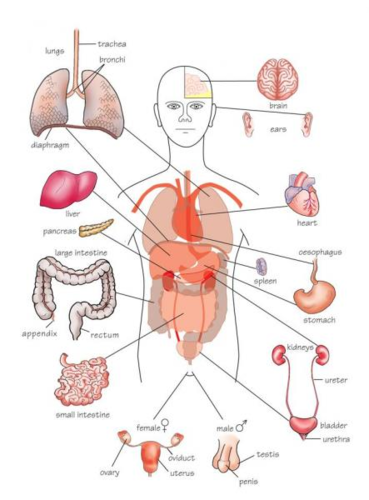
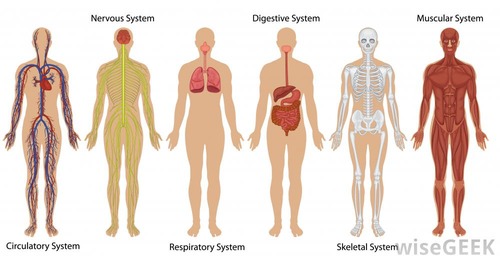
16
New cards
Organ system
Groups of organs that work together e.g. digestive system.
17
New cards
__***Specialised***__
Cells that have a particular job/function.
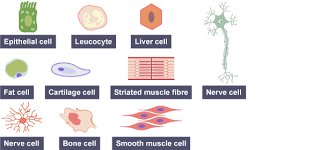
18
New cards
]]Tissue]]
A group of cells with a similar structure and function.
19
New cards
Translocation
The movement of sugars in plants.
20
New cards
%%Transpiration%%
The movement of water through the plant and leaves.
21
New cards
Epidermis (plant)
A single layer of cells that forms the outer layer.
22
New cards
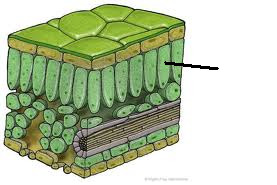
Palisade
Tissue found in the upper layer of the leaf, packed with chloroplasts for photosynthesis.
23
New cards
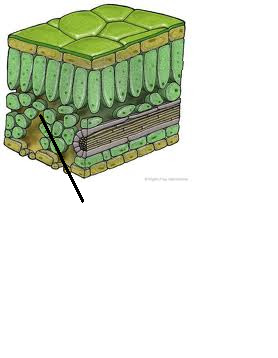
~~Spongy mesophyll~~
Tissue found in the lower layer of the leaf, with spaces between the cells to allow gases to diffuse.
24
New cards
Xylem
Water travels through xylem tissue from the roots to the leaves.
25
New cards
Phloem
Sugars are transported through the phloem cells.
26
New cards
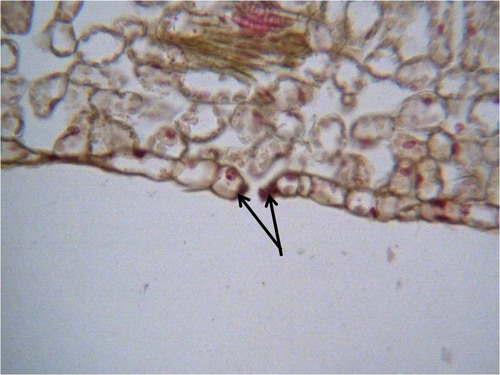
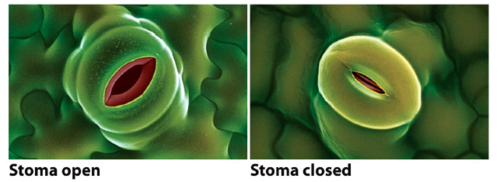
Guard cells
Cells which surround the stomata and control its opening and closing.
27
New cards
Stomata
Tiny pores in the epidermis of the leaf.
28
New cards
Electron microscope
A microscope that uses electron beams in place of light to give a higher magnification.
29
New cards
Light microscope
An instrument that uses visible light and lenses to magnify a specimen.

30
New cards
Magnification
How many times larger something appears.

31
New cards
Micrograph
Another word for a microscope image.
32
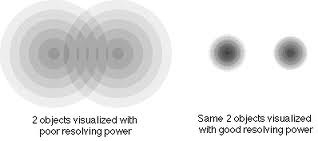
New cards
Resolving power
The ability to distinguish between two points.
33
New cards
Magnification of image
Magnification = size of image/size of real object
34
New cards
Total magnification
Magnification = magnification of eyepiece x magnification of objective lens

35
New cards
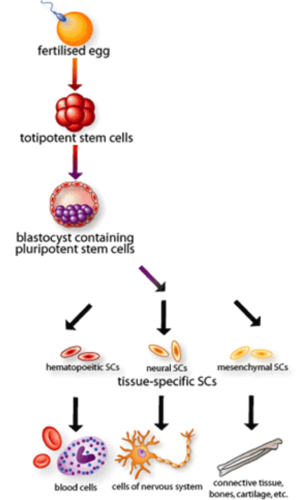
Adult stem cell
Stem cells found in some adult tissues. They are partly specialised and can become a range of different type of cell, but not all.
36
New cards
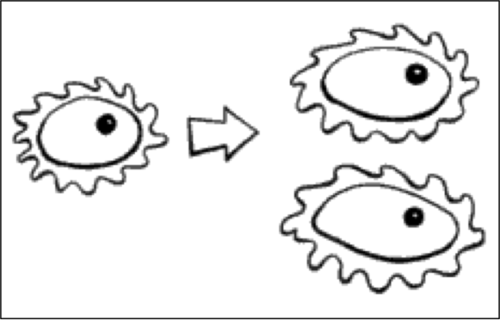
Asexual reproduction
Reproduction involving only one parent, producing genetically identical offspring.
37
New cards
Benign
Type of tumour that is slow growing, not cancerous and usually easy to remove.
38
New cards
Cancer
A condition resulting from changes in cells that leads to their uncontrolled growth, division and spread.
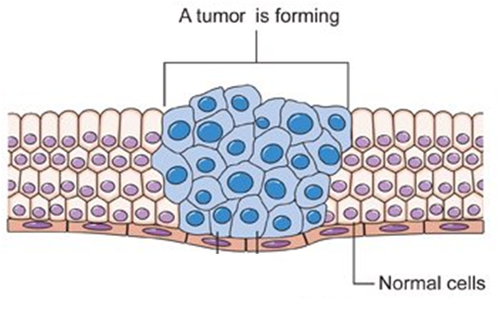
39
New cards
Carcinogen
Chemicals and other agents that cause cancer.

40
New cards
Chromosome
Long strands of DNA found in cells. Human body cells have 46 chromosomes.
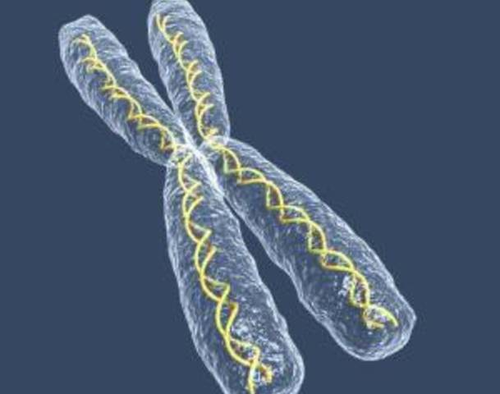
41
New cards
Daughter cell
The cells that are produced in cell division.
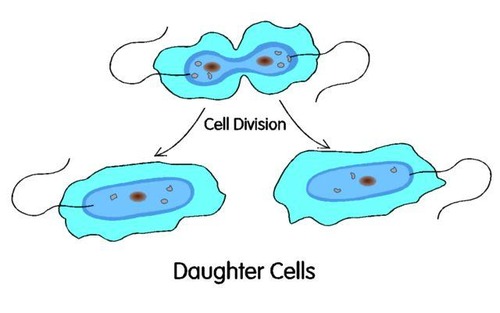
42
New cards
Embryonic stem cell
Stem cells found in early embryos. They are unspecialised and can become any type of cell in the body.
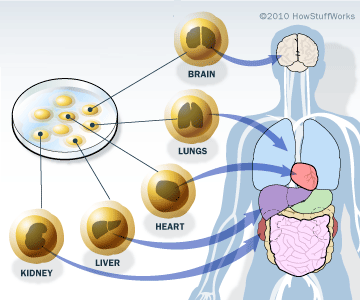
43
New cards
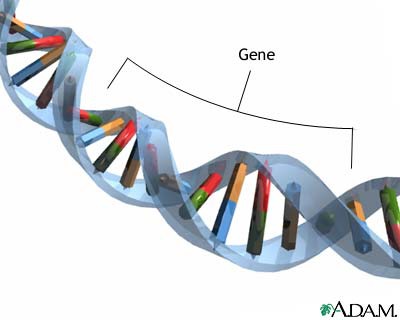
Gene
A short section of DNA that contains the instructions for making a protein.
44
New cards
Malignant
Type of tumour that grows quickly and can spread through other tissues. These tumours can lead to the formation of secondary tumours elsewhere.
45
New cards
Meristem
Region of plant tissue in which stem cells are produced and so where much of the plant growth occurs.
46
New cards
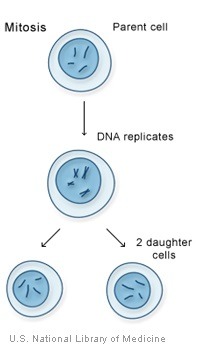
Mitosis
Type of cell division that produces two new (identical) cells.
47
New cards
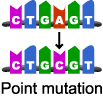
Mutation
A change in the DNA of a cell.
48
New cards
Therapeutic cloning
Producing stem cells with the same genes as the patient.
49
New cards
Tumour
Name given to the growths produced from extra cells.
50
New cards
Zygote
Another term for a fertilised egg cell.