GCSE AQA biology PAPER 1 Higher
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/292
Last updated 4:42 PM on 11/14/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
293 Terms
1
New cards
Are animal cells eukaryotic or prokaryotic?
Eukaryotic
2
New cards
Are plant cells eukaryotic or prokaryotic?
Eukaryotic
3
New cards
Are bacteria cells prokaryotic or eukaryotic?
Prokaryotic
4
New cards
are prokaryotic cells much bigger or smaller than eukaryotic?
much smaller
5
New cards
Parts of a eukaryotic cell
cell membrane, cytoplasm, nucleus
6
New cards
Parts of a prokaryotic cell
cell wall
dna loop
cell membrane
cytoplasm
plasmids
dna loop
cell membrane
cytoplasm
plasmids
7
New cards
give 5 sub cellular structures that are found in both animal and plant cells?
-nucleus
-cytoplasm
-cell membrane
-ribosomes
-mitochondria
-cytoplasm
-cell membrane
-ribosomes
-mitochondria
8
New cards
give 3 sub cellular structures that are found in plant cells but not in animal plants?
-cell wall
-chloroplasts
-permanent vacuole
-chloroplasts
-permanent vacuole
9
New cards
what the function of the nucleus ?
contains genetic material
10
New cards
Function of cell membrane
regulates what enters and leaves the cell
11
New cards
function of mitochondria
cellular respiration
12
New cards
function of chloroplast
Contains chlorophyll which absorbs light energy for photosyntheis
13
New cards
cell wall function?
provides support and protection
14
New cards
function of plasmids in bacteria cell?
contains extra genetic material that can help the bacteria cell survive
15
New cards
What are plant cell walls made of?
cellulose
16
New cards
what is a plant cells permanent vacuole filled will?
cell sap
17
New cards
give 2 differences between electron microscopes and light microscopes?
electron microscopes have a much higher magnification and a much higher resolution than light microscopes
18
New cards
what formula is used to calculate magnification of an image?
magnification = imagine size /real size
19
New cards
give a brief method for using a light microscope to look at a prepared slide
USING A LIGHT MICROSCOPE TO LOOK AT A PREPARED SLIDE
1)put the slide on the stage
2)select the lowest power lens
3)use the coarse adjustment knob to roughly focus the slide
4)use the fine adjustment(FA)knob to clearly focus the slide
5)switch to a higher power lens to increase magnification and refocus with the FA knob
1)put the slide on the stage
2)select the lowest power lens
3)use the coarse adjustment knob to roughly focus the slide
4)use the fine adjustment(FA)knob to clearly focus the slide
5)switch to a higher power lens to increase magnification and refocus with the FA knob
20
New cards
give 3 things to remember when drawing cells observed through a light microscope ?
-use a pencil
-label the main structures
-include the magnification used
-label the main structures
-include the magnification used
21
New cards
what happens when cells differentiate?
when cells differentiate they develop different sub-cellular structures that make them carry out certain functions
22
New cards
how are animal cells different to plant cells in their ability to differentiate?
most animal cells differentiate early in development and can't differentiate again
many plant cells can differentiate whenever they need to
many plant cells can differentiate whenever they need to
23
New cards
give 3 ways that a sperm cell is specialised to do its job
:to get DNA into egg cell
-tail for swimming
-lots of mitochondria to provide energy
-enzymes in head to digest egg cell membrane
-tail for swimming
-lots of mitochondria to provide energy
-enzymes in head to digest egg cell membrane
24
New cards
give 2 ways that a nerve cell is specialised to do its job
FUNCTION:carries messages around the body at high speed
-fatty sheath speeds up message transport
-long so it can carry messages over a distance
-fatty sheath speeds up message transport
-long so it can carry messages over a distance
25
New cards
how is a plant root cell specialised to do its job?
FUNCTION:helps a plant absorb water and minerals from soil.
-a long and thin extension gives a larger surface area for absorption
-a long and thin extension gives a larger surface area for absorption
26
New cards
give 2 ways that muscle cells are specialised to do their jobs?
FUNCTION:creates movement by contracting and relaxing
-long protein strands that can slide over each other ti shorten/lengthen the cell
-lots of mitochondria to generate energy
-long protein strands that can slide over each other ti shorten/lengthen the cell
-lots of mitochondria to generate energy
27
New cards
How are xylem cells specialised?
FUNCTION:Xylem cells form tubes that transport ester and minerals through the plant.
*they're dead cells with holes at either end-water and minerals can just flow right through them
*they're dead cells with holes at either end-water and minerals can just flow right through them
28
New cards
How are phloem cells specialised?
FUNCTION:transport dissolved sugars in a plant.
-few sub cellular structures so sugars flow through easily
-pores in end walls to let sugars through
-few sub cellular structures so sugars flow through easily
-pores in end walls to let sugars through
29
New cards
Where are chromosomes found?
nucleus
30
New cards
what are chromosomes made up of?
long lengths of DNA
31
New cards
how many chromosomes are there in the total human body?
there are 46 in a human body cell
32
New cards
how many pairs of chromosomes are there in the human body cell?
there are 23 pairs of chromosomes in a human body cell
33
New cards
why is the cell cycle important?
because it creates new cells which allows organisms to grow and develop
34
New cards
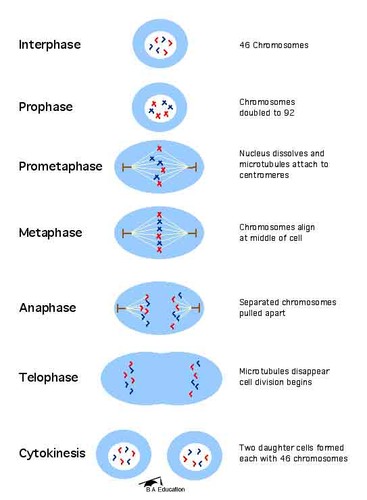
what are the three stages of the cell cycle?
1)growth
2)mitosis
3)Division
2)mitosis
3)Division
35
New cards
what happens during the growth stage of the cell cycle?
-extra sub cellular structures are made
-the DNA of each chromosome is duplicated
-the DNA of each chromosome is duplicated
36
New cards
what happens during mitosis in the cell cycle?
-chromosomes are pulled apart to opposite ends of the cell
-nucleus from around each set of chromsomes
-nucleus from around each set of chromsomes
37
New cards
what happens during division stage of the cell cycle?
-the cytoplasm and cell membrane split into two
-two cells form that are genetically identical to each other and the original cell
-two cells form that are genetically identical to each other and the original cell
38
New cards
what is a stem cell?
an undifferentiated cell that can divide to make more stem cells or differentiate into certain types of cells
39
New cards
whats the difference between stem cells from human embryos and stem cells from adults?
human embryos can differentiate into most types of cells.
stem cells from adults can only differentiate into certain cell types
stem cells from adults can only differentiate into certain cell types
40
New cards
give 2 conditions stem cells could treat
-Diabetes
-paralysis
-paralysis
41
New cards
describe how therapeutic cloning works?
TC is a treatment where an embryo is made with the same genes as a patient.
Stem cells from the embryo are used to treat the patient-the stem cells aren't rejected because they are genetically identical to the patients other cells.
Stem cells from the embryo are used to treat the patient-the stem cells aren't rejected because they are genetically identical to the patients other cells.
42
New cards
give a risk of using stem cells to treat illnesses
-stem cells can become infected with viruses
using infected stem cells to teat a patient risks transferring a viral infection to the patients
using infected stem cells to teat a patient risks transferring a viral infection to the patients
43
New cards
why do some people object to the use of stem cells from human embryos?
Human embryos are destroyed when stem cells are collected from them.
As embryos could become human beings, some people believe destroying embryos is like killing a human being.
As embryos could become human beings, some people believe destroying embryos is like killing a human being.
44
New cards
where are stem cells found in plants?
Meristems in roots and stems
45
New cards
when during a plant's life can its stem cells differentiate?
they can differentiate right throughout the plants life
46
New cards
plants can be cloned quickly and cheaply
give 2 things that are made possible by this
give 2 things that are made possible by this
-Protect rare plant species from extinction
-produce large numbers of identical crops with features like disease resistance
-produce large numbers of identical crops with features like disease resistance
47
New cards
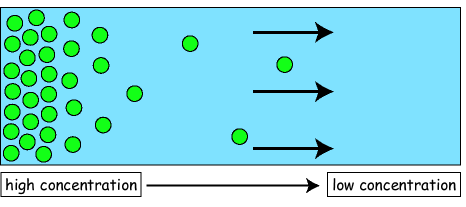
what Is diffusion?
the spreading out of particles in a solution or gas from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration
48
New cards
How is the rate of diffusion affected by temp?
the rate increases as temp increases
49
New cards
how does the rate of diffusion affect the size of the concentration gradient?
rate increases as the size of the concentration gradient increases
50
New cards
how does the surface area of the cell membrane affect rate of diffusion in and out of the cell?
rate increases as the surface area of the cell membrane increases
51
New cards
give 2 examples of substances transported by diffusion in the body
-oxygen and carbon dioxide diffuse between blood and the lungs (gas exchange)
-urea diffuses from cells into blood plasma
-urea diffuses from cells into blood plasma
52
New cards
what is osmosis?
the diffusion of water molecules from a dilute solution to a concentrated solution through a partially permeable membrane.
53
New cards
outline how the effect of different concentrations of salt solution on plant tissue can be investigated?
by comparing the change in mass of potatoes cylinders after leaving them in different concentrations of salt solutions for the same time.
(if a potato cylinder is left a salt solution with a higher concentration of water than in potatoes cells, the cylinder draws in water by osmosis and gets heavier)
(if a potato cylinder is left a salt solution with a higher concentration of water than in potatoes cells, the cylinder draws in water by osmosis and gets heavier)
54
New cards
give a brief method for investigating the effect of different concentrations of salt solutions on plant tissue
1)cut identical potatoes cylinders and record their mass
2)fill boiling tubes with a range of concentration of salt solution e.g0-1 mol/dm^3
3)put cylinder in each tube
4)after 24 hours, remove and dry the cylinders, then record their masses again.
2)fill boiling tubes with a range of concentration of salt solution e.g0-1 mol/dm^3
3)put cylinder in each tube
4)after 24 hours, remove and dry the cylinders, then record their masses again.
55
New cards
What is active transport?
the movement of substances from a more dilute solution to a more concentrated solution
56
New cards
Why does active transport require energy?
it moves substances against a concentration gradient
57
New cards
where does the energy required for active transport come from?
respiration.
58
New cards
why do plant root hair cells use active transport to absorb mineral ions from soil?
the concentration of mineral ions in soil is normally lower than the concentration of mineral ions in plant root hair cells.
this means that ions can't just diffuse in-so plant root hair cells use active transport to absorb mineral ions from soil
this means that ions can't just diffuse in-so plant root hair cells use active transport to absorb mineral ions from soil
59
New cards
When is active transport used in the gut?
When there is a lower concentration of nutrients in the gut but a higher concentration of nutrients in the blood
60
New cards
how do u calculate surface area to volume ratio?
1)calculate the area of each surface and add them together
2)calculate volume
3)show as simplified ratio of total surface area to volume
2)calculate volume
3)show as simplified ratio of total surface area to volume
61
New cards
whats an exchange surface?
a specialised area of an organism that efficiently transfers substances between the organism and its environment
62
New cards
why don't single celled organisms need exchange surfaces ?
single celled organisms have relatively large surface area to volume ratio.
this means substances can diffuse over their cell membranes at. rate thats high enough to keep them alive.
this means single celled organisms don't need exchange surfaces
this means substances can diffuse over their cell membranes at. rate thats high enough to keep them alive.
this means single celled organisms don't need exchange surfaces
63
New cards
why do multicellular organisms need exchange surfaces?
multicellular organisms have relatively small surface are to volume ratio .
substances can't diffuse over their surfaces at a level thats high enough to keep all of their cells alive.
this means that multi cellular organism need exchange surfaces to transfer substances efficiently.
substances can't diffuse over their surfaces at a level thats high enough to keep all of their cells alive.
this means that multi cellular organism need exchange surfaces to transfer substances efficiently.
64
New cards
give 4 adaptations of exchange surfaces to increase they effectiveness
-Large surface area(lets more substances diffuse at once)
-Thin membrane (speeds up diffusion because diffusion distance is short)
-Rich blood supply in animals.(takes things to and from exchange surface efficiently )
-gas exchange surfaces are exposed to the air(in animals)
-Thin membrane (speeds up diffusion because diffusion distance is short)
-Rich blood supply in animals.(takes things to and from exchange surface efficiently )
-gas exchange surfaces are exposed to the air(in animals)
65
New cards
give 3 ways that the small intestine is adapted for exchanging surfaces
-walls are folded and have millions of projections called Villi to give a massive surface area
-Villi have very thin walls
-Villi have a rich blood supply
-Villi have very thin walls
-Villi have a rich blood supply
66
New cards
give 3 ways that alveoli in the lungs are adapted for gas exchange
-thin walls
-a rich blood supply
-large surface area
-a rich blood supply
-large surface area
67
New cards
give 2 ways that plant leaves are adapted for gas exchange
-opening in epidermal tissue called stomata let gases in and out of the leaf
-air spaces inside leaf tissues allow gases to diffuse in and out of cells
-air spaces inside leaf tissues allow gases to diffuse in and out of cells
68
New cards
how does the structure of fish gills help it exchange gases with water
A fishes gills are made up of lots of gill filaments, which are covered in lots of folds called lamellae
this gives the gills a large surface area, which increases rate of diffusion of gases between the fish's blood and water
this gives the gills a large surface area, which increases rate of diffusion of gases between the fish's blood and water
69
New cards
give 3 ways that the lamellae in a fish's gills are adapted for exchanging gases with water
-thin walls
-a rich blood supply
-blood flows through them in the opposite direction to water flowing over them
-a rich blood supply
-blood flows through them in the opposite direction to water flowing over them
70
New cards
what is a tissue?
A group of cells that act together to perform a specific function.
71
New cards
what Is an organ
A group of different tissues that work together to perform a certain function.
72
New cards
what is an organ system?
A group of organs working together to perform a particular function
73
New cards
put these in order (smallest to largest):organ, tissue, organ system, cell
1)Cell
2)Tissue
3)organ
4)Organ system
2)Tissue
3)organ
4)Organ system
74
New cards
wha are enzymes?
proteins that catalyse chemical reactions in an organism
75
New cards
whats an enzymes active site?
the part of an enzyme that a substrate blinds with
76
New cards
why do enzymes only catalyse specific reactions?
an enzymes active site is a specific shape
Only certain substrates fit the active, so an enzyme can only catalyse specific reactions
Only certain substrates fit the active, so an enzyme can only catalyse specific reactions
77
New cards
describe the lock and key model of enzyme action
Only a substrate that exactly fits an enzymes active site can bind to the enzyme.
once a substrate binds, the enzyme catalyse the reaction
once a substrate binds, the enzyme catalyse the reaction
78
New cards
what does it mean when an enzyme is denatured?
When an enzyme is denatured, its active site changes shape.
This means the substrates won't fit the active site any more, so the enzyme can't catalyse any more reactions.
This means the substrates won't fit the active site any more, so the enzyme can't catalyse any more reactions.
79
New cards
how does changing temp affect the rate of a enzyme catalysed reaction?
as temp increases, the rate of enzyme catalysed reaction increases.
But of the temp gets too high enzymes get denatured and the rate of reaction decreases.
But of the temp gets too high enzymes get denatured and the rate of reaction decreases.
80
New cards
Enzyme's optimum pH and temp, what's it meant by this?
The PH and temp at which an enzyme works best are the enzymes optimum temp and PH
81
New cards
Give the two things that causes enzymes to denature
-High temperatures
a ph value thats too high to too low
a ph value thats too high to too low
82
New cards
outline how the effect or PH on amylase activity can be investigated
the effect of PH on amylase activity can be investigated by comparing how long it takes amylase to fully break down a sample of starch solution at different PH levels
83
New cards
Give a brief method for investigating the effector PH on amylase activity
1)Put a drop of iodine solution in each well of a spotting tile
2)Add 2cm^3 starch solution and add 2cm^3 of PH5 buffer solution to a test tube in a water bath at 35*C
3)After 10 mins, stir in 2cm^3 of amylase solution and start timing
4)Take a drop from the test tube every 20 seconds and put it in well- repeat until the iodine solution stays orangey and record the time passed.
5)Repeat the experiment with a range of PH buffer solutions
2)Add 2cm^3 starch solution and add 2cm^3 of PH5 buffer solution to a test tube in a water bath at 35*C
3)After 10 mins, stir in 2cm^3 of amylase solution and start timing
4)Take a drop from the test tube every 20 seconds and put it in well- repeat until the iodine solution stays orangey and record the time passed.
5)Repeat the experiment with a range of PH buffer solutions
84
New cards
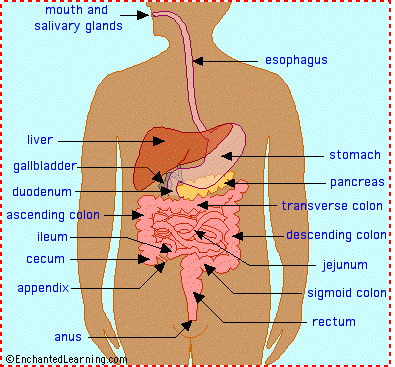
Organs of the digestive system
Salivary glands,Oesophagus,Stomach,Liver,Gall blader,Pancreas,Small intestine and large intestine
85
New cards
what do digestive enzymes do?
break down big molecules into smaller ones that will be absorbed into the blood
86
New cards
What are carboghydrases
Digestive enzyme that catalyse the break down of carbohydrates into simple sugars
87
New cards
what does amylase catalyse?
Amylase catalyses the breakdown of starch into simple sugars
88
New cards
give 2 places in the body where amylase is produced
-Salivary glands
-Pancreas
-Pancreas
89
New cards
What do proteases catalyse?
Proteases catalyse the breakdown of proteins into Amino acids
90
New cards
give 2 places in the body where proteases are produced
-stomach
-pancreas
-pancreas
91
New cards
what do lipase catalyse?
lipases catalyse the breakdown of lipids into fatty acids by glycerol
92
New cards
give 3 places in the body where lipase are produced
-mouth
-stomach
-pancreas
-stomach
-pancreas
93
New cards
where is bile produced and where is it stored?
produced in the liver and stored in the gallbladder
94
New cards
Bile is an alkaline substance
Explain why this is important for digestion
Explain why this is important for digestion
During digestion, food that's mixed with hydrochloric acid passes from the stomach into the small intestine.
Bile is an alkaline substance that neutralises the acid so the digestive enzymes in the small intestine can function at their optimum PH
Bile is an alkaline substance that neutralises the acid so the digestive enzymes in the small intestine can function at their optimum PH
95
New cards
Bile emulsifies fats
what does this mean and why is it important for digestion?
what does this mean and why is it important for digestion?
This means it turns fat into very small droplets.
This creates a large surface area for lipase to act on, increasing the rate of lipid breakdown by lipase
This creates a large surface area for lipase to act on, increasing the rate of lipid breakdown by lipase
96
New cards
Describe how to test a food sample for sugars
1)Heat a water bath to 80*C
2)Put the food sample in a test tube and add a few drops of Benedict's solution
3)Put the test tube in the water bath for around 5 minutes
4)if sugars are present, the solution changes from blue to green(some sugar),yellow or brick-red (lots of sugar)
2)Put the food sample in a test tube and add a few drops of Benedict's solution
3)Put the test tube in the water bath for around 5 minutes
4)if sugars are present, the solution changes from blue to green(some sugar),yellow or brick-red (lots of sugar)
97
New cards
Describe how to test a food sample for starch
1)put the food sample in a test tube
2)Add a few drops of iodine solution to the test tube
3)if starch is present, the solution changes from orangey to blue-black.
2)Add a few drops of iodine solution to the test tube
3)if starch is present, the solution changes from orangey to blue-black.
98
New cards
Describe how to test a food sample for protein
1)put the food sample in a test tube
2)Add 2cm^3 of biuret solution
3)Gently shake the test tube
4)if protein is present, the solution changes from blue to violet or purple
2)Add 2cm^3 of biuret solution
3)Gently shake the test tube
4)if protein is present, the solution changes from blue to violet or purple
99
New cards
Describe how to test a food sample for lipids
1)Put the sample in
a test tube with some distilled water
2)Add a few drops of ethanol OR a few drops of Sudan III stain to the test tube
3)Gently shake the test tube
4)if lipids are present, a cloudy emulsion forms(ethanol)OR a separate red layer forms at the top (Sudan III stain)
a test tube with some distilled water
2)Add a few drops of ethanol OR a few drops of Sudan III stain to the test tube
3)Gently shake the test tube
4)if lipids are present, a cloudy emulsion forms(ethanol)OR a separate red layer forms at the top (Sudan III stain)
100
New cards
parts of the lung
Trachea, lung, bronchus, bronchioles and alveoli