Chapter 7 - Transport of Ions and Small Molecules Across Cell Membranes
- The plasma membrane is a selectively permeable barrier between the cell and the extracellular environment
- Its permeability properties ensure that essential molecules such as ions, glucose, amino acids, and lipids readily enter the cell, metabolic intermediates remain in the cell, and waste compounds leave the cell
- The movement of virtually all molecules and ions across cellular membranes is mediated by selective membrane transport proteins embedded in the phospholipid bilayer
7.1 - Overview of Membrane Transport
- The phospholipid bilayer, the basic structural unit of biomembranes, is essentially impermeable to most water-soluble molecules, ions, and water itself
Few Molecules Cross Membranes by Passive Diffusion
- Gases, such as O2 and CO2, and small, uncharged polar molecules, such as urea and ethanol, can readily move by passive (simple) diffusion across an artificial membrane composed of pure phospholipid or of phospholipid and cholesterol
- The relative diffusion rate of any substance across a pure phospholipid bilayer is proportional to its concentration gradient across the layer and to its hydrophobicity and size
- Charged molecules are also affected by any electric potential across the membrane
- The hydrophobicity of a substance is measured by its partition coefficient K, the equilibrium constant for its partition between oil and water
- The higher a substance’s partition coefficient, the more lipid-soluble it is
- The first and rate-limiting step in transport by passive diffusion is the movement of a molecule from the aqueous solution into the hydrophobic interior of the phospholipid bilayer, which resembles oil in its chemical properties
- If a transported substance carries a net charge, its movement is influenced by both its concentration gradient and the membrane potential, the electric potential (voltage) across the membrane
- The combination of these two forces, called the electrochemical gradient, determines the energetically favorable direction of transport of a charged molecule across a membrane
Membrane Proteins Mediate Transport of Most Molecules and All Ions Across Biomembranes
- Very few molecules and no ions can cross a pure phospholipid bilayer at appreciable rates by passive diffusion
- All transport proteins are transmembrane proteins containing multiple membrane-spanning segments that generally are ox helices
- ATP-powered pumps (or simply pumps) are ATPases that use the energy of ATP hydrolysis to move ions or small molecules across a membrane against a chemical concentration gradient or electric potential or both
- This process is referred to as active transport
- Channel proteins transport water or specific types of ions and hydrophilic small molecules down their concentration or electric potential gradients
- Such protein-assisted transport sometimes is referred to as facilitated diffusion
- Transporters (also called carriers) move a wide variety of ions and molecules across cell membranes
- Three types of transporters have been identified
- Uniporters transport a single type of molecule down its concentration gradient via facilitated diffusion
- Glucose and amino acids cross the plasma membrane into most mammalian cells with the aid of uniporters
- Like ATP pumps, cotransporters mediate coupled reactions in which an energetically unfavorable reaction (i.e., uphill movement of molecules) is coupled to an energetically favorable reaction
- ATP-powered pumps and transporters undergo a cycle of conformational change exposing a binding site (or sites) to one side of the membrane in one conformation and to the other side in a second conformation
Several Features Distinguish Uniport Transport from Passive Diffusion
- The protein-mediated movement of glucose and other small hydrophilic molecules across a membrane, known as uniport transport, exhibits the following distinguishing properties:
The rate of facilitated diffusion by uniporters is far higher than passive diffusion through a pure phospholipid bilayer.
Because the transported molecules never enter the hydrophobic core of the phospholipid bilayer, the partition coefficient K is irrelevant
Transport occurs via a limited number of uniporter molecules, rather than throughout the phospholipid bilayer
- Consequently, there is a maximum transport rate Vmax that is achieved when the concentration gradient across the membrane is very large and each uniporter is working at its maximal rate
Transport is specific. Each uniporter transports only a single species of a molecule or a single group of closely related molecules
- A measure of the affinity of a transporter for its substrate is Km, which is the concentration of substrate at which transport is half-maximal
- One of the best-understood uniporters is the glucose transporter GLUT1 found in the plasma membrane of erythrocytes
- The properties of GLUT1 and many other transport proteins from mature erythrocytes have been extensively studied
- These cells, which have no nucleus or other internal organelles, are essentially, “bags” of hemoglobin containing relatively few other intracellular proteins and a single membrane, the plasma membrane
GLUT1 Uniporter Transports Glucose into Most Mammalian Cells
- Most mammalian cells use blood glucose as the major source of cellular energy and express GLUT1
- Since the glucose concentration usually is higher in the extracellular medium (blood in the case of erythrocytes) than in the cell
- GLUT1 generally catalyzes the net import of glucose from the extracellular medium into the cell
- GLUT1 alternates between two conformational states: in one, a glucose-binding site faces the outside of the membrane; in the other, a glucose-binding site faces the inside
- The kinetics of the unidirectional transport of glucose from the outside of a cell inward via GLUT1 can be described by the same type of equation used to describe a simple enzyme-catalyzed chemical reaction
- For GLUT1 in the erythrocyte membrane, the Km for glucose transport is 1.5 millimolar (mM); at this concentration, roughly half the transporters with outward-facing binding sites would have bound glucose, and transport would occur at 50 percent of the maximal rate
- The isomeric sugars D-mannose and D-galactose, which differ from D-glucose in the configuration at only one carbon atom, are transported by GLUT1 at measurable rates
- The Km for glucose (1.5 mM) is much lower than the Km for D-mannose (20 mM) or D-galactose (30 mM)
- GLUT1 accounts for 2 percent of the protein in the plasma membrane of erythrocytes
- After glucose is transported into the erythrocyte, it is rapidly phosphorylated, forming glucose 6-phosphate, which cannot leave the cell
The Human Genome Encodes a Family of Sugar-Transporting GLUT Proteins
- The human genome encodes 12 proteins, GLUT1–GLUT12, that are highly homologous in sequence, and all are thought to contain 12 membrane-spanning helices
- Detailed studies on GLUT1 have shown that the amino acid residues in the transmembrane helices are predominantly hydrophobic; several helices
- The structures of all GLUT isoforms are quite similar, and all transport sugars
- Nonetheless, their differential expression in various cell types and isoform-specific functional properties enable different body cells to regulate glucose metabolism independently and at the same time maintain a constant concentration of glucose in the blood
Transport Proteins Can Be Enriched within Artificial Membranes and Cells
- Transport proteins can be isolated from membranes and purified, the functional properties of these proteins can be studied only when they are associated with a membrane
- Most cellular membranes contain many different types of transport proteins but a relatively low concentration of any particular one, making functional studies of a single protein difficult
7.2 - ATP-Powered Pumps and the Intracellular Ionic Environment
- All ATP-powered pumps are transmembrane proteins with one or more binding sites for ATP located on the cytosolic face of the membrane
- Although these proteins commonly are called ATPases, they normally do not hydrolyze ATP into ADP and Pi unless ions or other molecules are simultaneously transported
Different Classes of Pumps Exhibit Characteristic Structural and Functional Properties
- All P-class ion pumps possess two identical catalytic ox subunits that contain an ATP-binding site
- Most also have two smaller B subunits that usually have regulatory functions
- During the transport process, at least one of the ox subunits is phosphorylated (hence the name “P” class), and the transported ions are thought to move through the phosphorylated subunit
- The structures of F-class and V-class ion pumps are similar to one another but unrelated to and more complicated than P-class pumps
- F- and V-class pumps contain several different transmembrane and cytosolic subunits
ATP-Powered Ion Pumps Generate and Maintain Ionic Gradients Across Cellular Membranes
- The specific ionic composition of the cytosol usually differs greatly from that of the surrounding extracellular fluid
- In virtually all cells—including microbial, plant, and animal cells—the cytosolic pH is kept near 7.2 regardless of the extracellular pH
- The ion pumps discussed in this section are largely responsible for establishing and maintaining the usual ionic gradients across the plasma and intracellular membranes
- In carrying out this task, cells expend considerable energy
- In cells treated with poisons that inhibit the aerobic production of ATP (e.g., 2,4-dinitrophenol in aerobic cells), the ion concentrations inside the cell gradually approach those of the exterior environment as ions move through channels in the plasma membrane down their electrochemical gradients
Muscle Ca2+ ATPase Pumps Ca2+ Ions from the Cytosol into the Sarcoplasmic Reticulum
- In the cytosol of muscle cells, the free Ca2+ concentration ranges from 10-7M (resting cells) to more than 10-6M (contracting cells), whereas the total Ca2 concentration in the SR lumen can be as high as 102 M
- The current model for the mechanism of action of the Ca2+ ATPase in the SR membrane involves two conformational states of the protein termed E1 and E2
- Cryoelectron microscopy and x-ray crystallography of the protein in different conformational states also revealed that the bulk of the catalytic subunit
- Consists of cytosolic globular domains that are involved in ATP binding, phosphorylation of aspartate, and transduction of the energy released by hydrolysis of the aspartyl phosphate into conformational changes in the protein
Calmodulin-Mediated Activation of Plasma-Membrane Ca2+ ATPase Leads to Rapid Ca2+ Export
- Small increases in the concentration of free Ca2 ions in the cytosol trigger a variety of cellular responses
- In order for Ca2 to function in intracellular signaling, the concentration of Ca2 ions free in the cytosol usually must be kept below 0.1 – 0.2 μM
Na+/K+ ATPase Maintains the Intracellular Na+ and K+ Concentrations in Animal Cells
- P-class ion pump present in the plasma membrane of all animal cells is the Na+/K+ ATPase
- This ion pump is a tetramer of subunit composition ox2B2
- The three Na+ ions, transported outward through the protein and now bound to the low-affinity Na+ sites exposed to the ectoplasmic face, dissociate one at a time into the extracellular medium despite the high extracellular Na concentration
- Transition to the E2 conformation also generates two high-affinity K+ sites accessible to the ectoplasmic face. Because the Km for K+ binding to these sites (0.2 mM) is lower than the extracellular K+ concentration (4 mM), these sites will fill with K+ ions
- Similarly, during the E2 → E1 transition, the two bound K ions are transported inward and then released into the cytosol
V-Class H+ ATPases Pump Protons Across Lysosomal and Vacuolar Membranes
- All V-class ATPases transport only H+ ions
- These proton pumps, present in the membranes of lysosomes, endosomes, and plant vacuoles, function to acidify the lumen of these organelles
- The pH of the lysosomal lumen can be measured precisely in living cells by the use of particles labeled with a pH-sensitive fluorescent dye
- Pumping of relatively few protons is required to acidify an intracellular vesicle
- By themselves ATP-powered proton pumps cannot acidify the lumen of an organelle (or the extracellular space) because these pumps are electrogenic; that is, a net movement of electric charge occurs during transport
- Pumping of just a few protons causes a buildup of positively charged H ions on the ectoplasmic (inside) face of the organelle membrane
- In order for an organelle lumen or an extracellular space (e.g., the lumen of the stomach) to become acidic
- Movement of protons must be accompanied either by (1) movement of an equal number of anions (e.g., Cl-) in the same direction or by (2) movement of equal numbers of a different cation in the opposite direction
Bacterial Permeases Are ABC Proteins That Import a Variety of Nutrients from the Environment
- The T domains, each built of six membrane-spanning helices, form the pathway through which the transported substance (substrate) crosses the membrane and determine the substrate specificity of each ABC protein
- The plasma membrane of many bacteria contains numerous permeases that belong to the ABC superfamily
- In E. coli histidine permease, a typical bacterial ABC protein, the two transmembrane domains, and two cytosolic ATP-binding domains are formed by four separate subunits
About 50 ABC Small-Molecule Pumps Are Known in Mammals
- The discovery of the first eukaryotic ABC protein to be recognized came from studies on tumour cells and cultured cells that exhibited resistance to several drugs with unrelated chemical structures
- Most drugs transported by MDR1 are small hydrophobic molecules that diffuse from the medium across the plasma membrane, unaided by transport proteins, into the cell cytosol, where they block various cellular functions
- Substrates for these ABC proteins include sugars, amino acids, cholesterol, peptides, proteins, toxins, and xenobiotics
- So the normal function of MDR1 most likely is to transport various natural and metabolic toxins into the bile, intestinal lumen, or forming urine
ABC Proteins That Transport Lipid-Soluble Substances May Operate by a Flippase Mechanism
- In contrast to bacterial ABC proteins, all four domains of MDR1 are fused into a single 170,000-MW protein
- The mechanism of transport by MDR1 and similar ABC proteins has not been definitively demonstrated, a likely candidate is the flippase model
- Support for the flippase model of transport by MDR1 comes from MDR2, a homologous protein present in the region of the liver cell plasma membrane that faces the bile duct
7.3 - Non-Gated Ion Channels and the Resting Membrane Potential
- Ion concentration gradients generated by pumps and selective movements of ions through channels constitute the principal mechanism by which a difference in voltage, or electric potential, is generated across the plasma membrane
- The magnitude of this electric potential generally is ≈70 millivolts (mV) with the inside of the cell always negative with respect to the outside
- The ionic gradients and electric potential across the plasma membrane play a role in many biological processes
- In many animal cells, the combined force of the Na concentration gradient and membrane electric potential drives the uptake of amino acids and other molecules against their concentration gradient by ion-linked symport and antiport proteins
Selective Movement of Ions Creates a Transmembrane Electric Potential Difference
- Na+-channel proteins that accommodate Na ions but exclude K+ and Cl- ions
- As more and more Na+ ions move through channels across the membrane, the magnitude of this charge difference (i.e., voltage) increases
The Membrane Potential in Animal Cells Depends Largely on Resting K+ Channels
- The plasma membranes of animal cells contain many open K+ channels but few open Na+, Cl-, or Ca2+ channels
- As a result, the major ionic movement across the plasma membrane is that of K+ from the inside outward
- Powered by the K+ concentration gradient, leaving an excess of negative charge on the inside and creating an excess of positive charge on the outside, similar to the experimental system
- Quantitatively, the usual resting membrane potential of 70 mV is close to but lower in magnitude than that of the potassium equilibrium potential calculated from the Nernst equation because of the presence of a few open Na+ channels
- Resting K channels play the dominant role in generating the electric potential across the plasma membrane of animal cells, this is not the case in plant and fungal cells
- The potential across the plasma membrane of large cells can be measured with a microelectrode inserted inside the cell and a reference electrode placed in the extracellular fluid
- The two are connected to a potentiometer capable of measuring small potential differences
Ion Channels Contain a Selectivity Filter Formed from Conserved Transmembrane ox Helices and P segments
- All ion channels exhibit specificity for particular ions: K+ channels allow K but not closely related Na+ ions to enter, whereas Na+ channels admit Na+ but not K+
- Determination of the three-dimensional structure of a bacterial K+ channel first revealed how this exquisite ion selectivity is achieved
- Several types of evidence support the role of P segments in ion selection
- The amino acid sequence of the P segment is highly homologous in all known K+ channels and different from that in other ion channels
- Mutation of amino acids in this segment alters the ability of a K+ channel to distinguish Na+ from K+
- Replacing the P segment of a bacterial K+ channel with the homologous segment from a mammalian K+ channel yields a chimeric protein that exhibits normal selectivity for K+ over other ions
- Recent x-ray crystallographic studies reveal that the channel contains K ions within the selectivity filter even when it is closed; without these ions, the channel probably would collapse
- Although the amino acid sequences of the P segment in Na+ and K+ channels differ somewhat
- They are similar enough to suggest that the general structure of the ion-selectivity filters are comparable in both types of channels
Patch Clamps Permit Measurement of Ion Movements Through Single Channels
- The technique of patch clamping enables workers to investigate the opening, closing, regulation, and ion conductance of a single ion channel
- The inward or outward movement of ions across a patch of membrane is quantified from the amount of electric current needed to maintain the membrane potential at a particular “clamped” value
- Patches of the muscle membrane, each containing one Na+ channel, were clamped at a voltage slightly less than the resting membrane potential
- Under circumstances, transient pulses of current cross the membrane as individual Na+ channels open and then close
Novel Ion Channels Can Be Characterized by a Combination of Oocyte Expression and Patch Clamping
- Cloning of human disease-causing genes and sequencing of the human genome have identified many genes encoding putative channel proteins, including 67 putative K+ channel proteins
Na+ Entry into Mammalian Cells Has a Negative Change in Free Energy (△G)
- Two forces govern the movement of ions across selectively permeable membranes: the voltage and the ion concentration gradient across the membrane
- The sum of these forces, which may act in the same direction or in opposite directions, constitutes the electrochemical gradient
- To calculate the free-energy change △G corresponding to the transport of an ion across a membrane, consider the independent contributions from each of the forces to the electrochemical gradient
7.4 - Cotransport by Symporters and Antipoters
- Besides ATP-powered pumps, cells have a second, discrete class of proteins that transport ions and small molecules, such as glucose and amino acids, against a concentration gradient
- Cotransporters use the energy stored in the electrochemical gradient of Na+ or H+ ions to power the uphill movement of another substance, which may be a small organic molecule or a different ion
- Cotransporters share some features with uniporters such as the GLUT proteins
- The two types of transporters exhibit certain structural similarities, operate at equivalent rates, and undergo cyclical conformational changes during the transport of their substrates
- When the transported molecule and cotransported ion move in the same direction, the process is called symport; when they move in opposite directions, the process is called antiport
Na+-Linked Symporters Import Amino Acids and Glucose into Animal Cells Against High Concentration Gradients
- Most body cells import glucose from the blood down its concentration gradient, utilizing one or another GLUT protein to facilitate this transport
- The two-Na/glucose symporter is thought to contain 14 transmembrane helices with both its N- and C-termini extending into the cytosol
- A truncated recombinant protein consisting of only the five C-terminal transmembrane helices can transport glucose independently of Na across the plasma membrane, down its concentration gradient
Na-Linked Antiporter Exports Ca2 from Cardiac Muscle Cells
- In cardiac muscle cells a three-Na+/one-Ca2+ antiporter, rather than the plasma membrane Ca2 ATPase discussed earlier, plays the principal role in maintaining a low concentration of Ca2 in the cytosol
Several Cotransporters Regulate Cytosolic pH
- The anaerobic metabolism of glucose yields lactic acid, and aerobic metabolism yields CO2, which adds water to form carbonic acid (H2CO3)
- These weak acids dissociate, yielding H ions (protons); if these excess protons were not removed from cells, the cytosolic pH would drop precipitously, endangering cellular functions
- The CO2 diffuses out of the cell, and the OH- ions combine with intracellular protons, forming water
- Under certain circumstances, the cytosolic pH can rise beyond the normal range of 7.2–7.5
- To cope with the excess OH- ions associated with elevated pH, many animal cells utilize an anion antiporter that catalyzes the one-for-one exchange of HCO3 and Cl across the plasma membrane
Numerous Transport Proteins Enable Plant Vacuoles to Accumulate Metabolites and Ions
- The lumen of plant vacuoles is much more acidic (pH 3 to 6) than is the cytosol (pH 7.5)
- The acidity of vacuoles is maintained by a V-class ATP-powered proton pump and by a PPi-powered pump that is unique to plants
- The proton electrochemical gradient across the plant vacuole membrane is used in much the same way as the Na+ electrochemical gradient across the animal-cell plasma membrane
- To power the selective uptake or extrusion of ions and small molecules by various antiporters
7.5 - Movement of Water
Osmotic Pressure Causes Water to Move Across Membranes
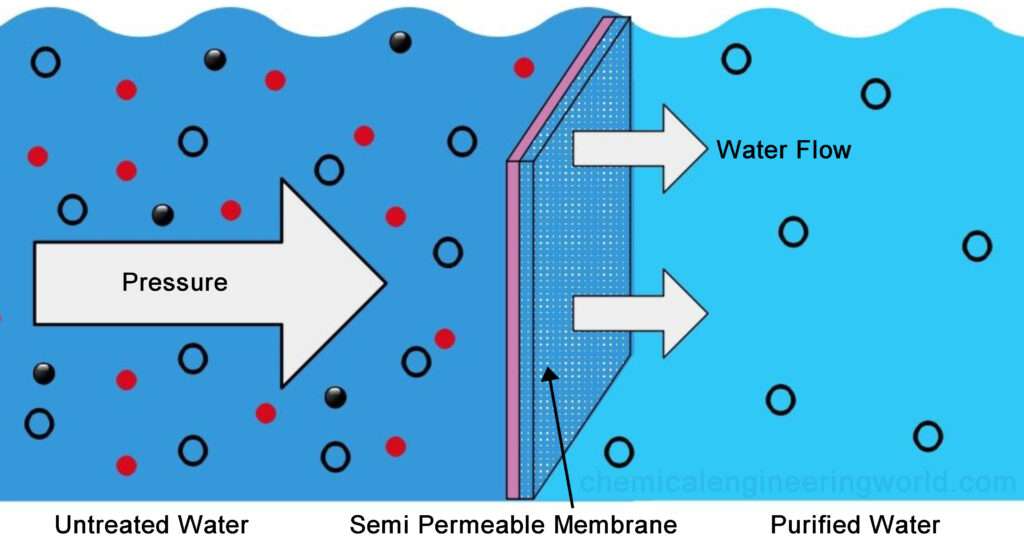
Water tends to move across a semipermeable membrane from a solution of low solute concentration to one of high concentration, a process termed osmosis or osmotic flow
Osmotic pressure is defined as the hydrostatic pressure required to stop the net flow of water across a membrane separating solutions of different compositions
Pure phospholipid bilayers are essentially impermeable to water, but most cellular membranes contain water-channel proteins that facilitate the rapid movement of water in and out of cells
Such movement of water across the epithelial layer lining the kidney tubules of vertebrates is responsible for concentrating the urine
Different Cells Have Various Mechanisms for Controlling Cell Volume
- When placed in a hypotonic solution (i.e., one in which the concentration of solutes is lower than in the cytosol), animal cells swell owing to the osmotic flow of water inward
- Conversely, when placed in a hypertonic solution (i.e., one in which the concentration of solutes is higher than in the cytosol)
- Animal cells shrink as cytosolic water leaves the cell by osmotic flow
- Even in an isotonic environment, however, animal cells face a problem in maintaining their cell volume within a limited range, thereby avoiding lysis
- In the absence of some countervailing mechanism, the osmolarity of the cytosol would increase beyond that of the surrounding fluid, causing an osmotic influx of water and eventual cell lysis
- Most protozoans (like animal cells) do not have a rigid cell wall, many contain a contractile vacuole that permits them to avoid osmotic lysis
- A contractile vacuole takes up water from the cytosol and, unlike a plant vacuole, periodically discharges its contents through fusion with the plasma membrane
Aquaporins Increase the Water Permeability of Cell Membranes
- Small changes in extracellular osmotic strength cause most animal cells to swell or shrink rapidly
- In its functional form, aquaporin is a tetramer of identical 28-kDa subunits
- Each subunit contains six membrane-spanning ox helices that form a central pore through which water moves
- At its center, the ≈2-nm-long water-selective gate, or pore, is only 0.28 nm in diameter, which is only slightly larger than the diameter of a water molecule
- The molecular sieving properties of the constriction are determined by several conserved hydrophilic amino acid residues whose side-chain and carbonyl groups extend into the middle of the channel
7.6 - Transepithelial Transport
Multiple Transport Proteins Are Needed to Move Glucose and Amino Acids Across Epithelia
- In the first stage of this process, a two-Na+/one-glucose symporter located in microvillar membranes imports glucose
- Against its concentration gradient, from the intestinal lumen across the apical surface of the epithelial cells
- In the second stage, glucose and amino acids concentrated inside intestinal cells by symporters are exported down their concentration gradients into the blood via uniport proteins in the basolateral membrane
- The net result of this two-stage process is a movement of Na+ ions, glucose, and amino acids from the intestinal lumen across the intestinal epithelium into the extracellular medium that surrounds the basolateral surface of intestinal epithelial cells
- Tight junctions between the epithelial cells prevent these molecules from diffusing back into the intestinal lumen, and eventually, they move into the blood
Parietal Cells Acidify the Stomach Contents While Maintaining a Neutral Cytosolic pH
- The mammalian stomach contains a 0.1 M solution of hydrochloric acid (HCl)
- This strongly acidic medium kills many ingested pathogens and denatures many ingested proteins before they are degraded by proteolytic enzymes (e.g., pepsin) that function at acidic pH
- Hydrochloric acid is secreted into the stomach by specialized epithelial cells called parietal cells (also known as oxyntic cells) in the gastric lining
- If parietal cells simply exported H+ ions in exchange for K+ ions, the loss of protons would lead to a rise in the concentration of OH ions in the cytosol and thus a marked increase in cytosolic pH
7.7 - Voltage-Gated Ion Channels and the Propagation of Action Potentials in Nerve Cells
- Neurons (nerve cells) and certain muscle cells are specialized to generate and conduct a particular type of electric impulse, the action potential
- This alteration of the electric potential across the cell membrane is caused by the opening and closing of certain voltage-gated ion channels
Specialized Regions of Neurons Carry Out Different Functions
- The cell body contains the nucleus and is the site of synthesis of virtually all neuronal proteins and membranes
- Some proteins are synthesized in dendrites, but none are made in axons or axon terminals
- Special transport processes involving microtubules move proteins and membranes from their sites of synthesis in the cell body down the length of the axon to the terminals
- Axons, whose diameter varies from a micrometer in certain nerves of the human brain to a millimeter in the giant fiber of the squid, are specialized for the conduction of action potentials
- Action potentials move at speeds up to 100 meters per second
- It takes about 0.5 milliseconds (ms) for neurotransmitters to diffuse across the synaptic cleft and bind to a receptor on the postsynaptic cells
- The binding of neurotransmitters triggers the opening or closing of specific ion channels in the plasma membrane of postsynaptic cells
- Leading to changes in the membrane potential at this point
- Most neurons have multiple dendrites, which extend outward from the cell body and are specialized to receive chemical signals from the axon termini of other neurons
- Neurons use changes in the membrane potential, the action potentials, to conduct signals along their length, and small molecules, the neurotransmitters, to send signals from cell to cell
The Magnitude of the Action Potential Is Close to ENa
- The subsequent outward movement of K+ ions through non-gated K+ channels is driven by the K+ concentration gradient, generating the resting membrane potential
- The entry of Na+ ions into the cytosol from the medium also is thermodynamically favored, driven by the Na concentration gradient and the inside-negative membrane potential
- The magnitude of the membrane potential at the peak of depolarization in an action potential is very close to the Na+ equilibrium potential ENa given by the Nernst equation
Sequential Opening and Closing of Voltage-Gated Na and K Channels Generate Action Potentials
- The cycle of membrane depolarization, hyperpolarization, and return to the resting value that constitutes an action potential lasts 1–2 milliseconds and can occur hundreds of times a second in a typical neuron
- Voltage-Gated Na Channels: Voltage-gated Na+ channels are closed in resting neurons
- A small depolarization of the membrane causes a conformational change in these channel proteins that opens a gate on the cytosolic surface of the pore
- Permitting Na+ ions to pass through the pore into the cell
- As Na+ ions flow inward through opened channels, the excess positive charges on the cytosolic face and negative charges on the ectoplasmic face diffuse a short distance away from the initial site of depolarization
- Voltage-Gated K Channels: The repolarization of the membrane that occurs during the refractory period is due largely to the opening of voltage-gated K channels
- The subsequently increased efflux of K from the cytosol removes the excess positive charges from the cytosolic face of the plasma membrane (i.e., makes it more negative), thereby restoring the inside-negative resting potential
- Opening of the voltage-gated K channels is induced by the large depolarization of the action potential
- Unlike voltage-gated Na channels, most types of voltage-gated K+ channels remain open as long as the membrane is depolarized and close only when the membrane potential has returned to an inside-negative value
Action Potentials Are Propagated Unidirectionally Without Diminution
- The generation of an action potential just described relates to the changes that occur in a small patch of the neuronal plasma membrane
- At the peak of the action potential, the passive spread of the membrane depolarization is sufficient to depolarize a neighboring segment of the membrane
Nerve Cells Can Conduct Many Action Potentials in the Absence of ATP
- It is important to note that the depolarization of the membrane characteristic of an action potential results from the movement of just a small number of Na+ ions into a neuron and does not significantly affect the intracellular Na concentration gradient
- Because so few Na and K ions move across the plasma membrane during each action potential, the Na+/K+ pump that maintains the usual ion gradients plays no direct role in impulse conduction
- When this pump is experimentally inhibited by dinitrophenol or another inhibitor of ATP production, the concentrations of Na+ and K+ gradually become the same inside and outside the cell, and the membrane potential falls to zero
All Voltage-Gated Ion Channels Have Similar Structures
- The initial breakthrough in understanding voltage-gated ion channels came from the analysis of fruit flies (Drosophila melanogaster) carrying the shaker mutation
- These flies shake vigorously under ether anesthesia, reflecting a loss of motor control and a defect in certain motor neurons that have an abnormally prolonged action potential
- The Shaker K+ channel and most other voltage-gated K+ channels that have been identified are tetrameric proteins composed of four identical subunits arranged in the membrane around a central pore
- Voltage-gated Na channels and Ca2 channels are monomeric proteins organized into four homologous domains, I–IV
Voltage-Sensing S4 Helices Move in Response to Membrane Depolarization
- Sensitive electric measurements suggest that the opening of a voltage-gated Na+ or K+ channel is accompanied by the movement of 10 to 12 protein-bound positive charges from the cytosolic to the axoplasmic surface of the membrane
- Alternatively, a larger number of charges may move a shorter distance across the membrane
- Studies with mutant Shaker K channels support this model for the operation of the S4 helix in voltage sensing
Movement of the Channel-Inactivating Segment into the Open Pore Blocks Ion Flow
- An important characteristic of most voltage-gated channels is inactivation; that is, soon after opening they close spontaneously, forming an inactive channel that will not reopen until the membrane is repolarized
- The single channel-inactivating segment in voltage-gated Na+ channels contains a conserved hydrophobic motif composed of isoleucine, phenylalanine, methionine, and threonine
Myelination Increases the Velocity of Impulse Conduction
- Action potentials can move down an axon without diminution at speeds up to 1 meter per second
- But even such fast speeds are insufficient to permit the complex movements typical of animals
- In non-myelinated neurons, the conduction velocity of an action potential is roughly proportional to the diameter of the axon
- Because a thicker axon will have a greater number of ions that can diffuse
Action Potentials “Jump” from Node to Node in Myelinated Axons
- The myelin sheath surrounding an axon is formed from many glial cells
- Each region of myelin formed by an individual glial cell is separated from the next region by an unmyelinated area of axonal membrane about 1 μm in length called the node of Ranvier (or simply, node)
7.8 - Neurotransmitters and Receptor and Transport Proteins in Signal Transmission at Synapses
- Neurotransmitter receptors fall into two broad classes: ligand-gated ion channels, which open immediately upon neurotransmitter binding, and G protein-coupled receptors
- Neurotransmitter binding to a G protein-coupled receptor induces the opening or closing of a separate ion channel protein over a period of seconds to minutes
Neurotransmitters Are Transported into Synaptic Vesicles by H-Linked Antiport Proteins
- Numerous small molecules function as neurotransmitters at various synapses
- With the exception of acetylcholine
- All the “classic” neurotransmitters are synthesized in the cytosol and imported into membrane-bound synaptic vesicles within axon terminals, where they are stored
- These vesicles are 40–50 nm in diameter, and their lumen has a low pH, generated by the operation of a V-class proton pump in the vesicle membrane
- Synaptic vesicles take up and concentrate acetylcholine from the cytosol against a steep concentration gradient, using an H+/acetylcholine antiporter in the vesicle membrane
The Influx of Ca2 Through Voltage-Gated Ca2 Channels Triggers Release of Neurotransmitters
- Neurotransmitters are released by exocytosis, a process in which neurotransmitter-filled synaptic vesicles fuse with the axonal membrane
- Releasing their contents into the synaptic cleft
- Depolarization of the plasma membrane cannot, by itself, cause synaptic vesicles to fuse with the plasma membrane
- In order to trigger vesicle fusion, an action potential must be converted into a chemical signal—namely, a localized rise in the cytosolic Ca2+ concentration
- A simple experiment demonstrates the importance of voltage-gated Ca2+ channels in the release of neurotransmitters
- A preparation of neurons in a Ca2+-containing medium is treated with tetrodotoxin, a drug that blocks voltage-gated Na+ channels and thus prevents conduction of action
- Two pools of neurotransmitter-filled synaptic vesicles are present in axon terminals: those “docked” at the plasma membrane, which can be readily exocytosed, and those in reserve in the active zone near the plasma membrane
- Each rise in Ca2+ triggers exocytosis of about 10 percent of the docked vesicles
Signaling at Synapses Usually Is Terminated by Degradation or Reuptake of Neurotransmitters
- Following their release from a presynaptic cell, neurotransmitters must be removed or destroyed to prevent continued stimulation of the postsynaptic cell
- Signaling can be terminated by diffusion of a transmitter away from the synaptic cleft, but this is a slow process
- Signaling by acetylcholine is terminated when it is hydrolyzed to acetate and choline by acetylcholinesterase, an enzyme localized to the synaptic cleft
Opening of Acetylcholine-Gated Cation Channels Leads to Muscle Contraction
- Acetylcholine is the neurotransmitter at synapses between motor neurons and muscle cells, often called neuromuscular junctions
- A single axon terminus of a frog motor neuron may contain a million or more synaptic vesicles, each containing 1000–10,000 molecules of acetylcholine
- These vesicles often accumulate in rows in the active zone
- The nicotinic acetylcholine receptor, which is expressed in muscle cells, is a ligand-gated channel that admits both K+ and Na+
- The acetylcholine receptor from skeletal muscle is a pentameric protein with a subunit composition of ox2ByoS
- The ox, B, y, and oS subunits have considerable sequence homology; on average, about 35–40 percent of the residues in any two subunits are similar
- The channel opens when the receptor cooperatively binds two acetylcholine molecules to sites located at the interfaces of the oxoS and oxy subunits
- Once acetylcholine is bound to a receptor, the channel is opened within a few microseconds
- Although the structure of the central ion channel is not known in molecular detail, much evidence indicates that it is lined by five homologous transmembrane M2 ox helices, one from each of the five subunits
- The two acetylcholine binding sites in the extracellular domain of the receptor lie ≈4 to 5 nm from the center of the pore
- The binding of acetylcholine thus must trigger conformational changes in the receptor subunits that can cause channel opening at some distance from the binding sites
Nerve Cells Make an All-or-None Decision to Generate an Action Potential
- At the neuromuscular junction, virtually every action potential in the presynaptic motor neuron triggers an action potential in the postsynaptic muscle cell
- The situation at synapses between neurons, especially those in the brain, is much more complex because the postsynaptic neuron commonly receives signals from many presynaptic neurons
- A single neuron can be affected simultaneously by signals received at multiple excitatory and inhibitory synapses
- The neuron continuously integrates these signals and determines whether or not to generate an action potential
The Nervous System Uses Signaling Circuits Composed of Multiple Neurons
- In complex multicellular animals, such as insects and mammals, various types of neurons form signaling circuits
- In the simple type of circuit, called a reflex arc, interneurons connect multiple sensory and motor neurons allowing one sensory neuron to affect multiple motor neurons and one motor neuron to be affected by multiple sensory neurons; in this way, interneurons integrate and enhance reflexes
- These simple signaling circuits, however, do not directly explain higher-order brain functions such as reasoning, computation, and memory development
- Typical neurons in the brain receive signals from up to a thousand other neurons and, in turn, can direct chemical signals to many other neurons