Section 1- biological molecules
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 6:38 PM on 4/25/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
37 Terms
1
New cards
what is the basic unit and polymer of a carbohydrate called
sugar unit called monosaccharide and polymer called polysaccharide
2
New cards
monosaccharide
\-sweet tasting
\-general formula of (CH2O)n
\-general formula of (CH2O)n
3
New cards
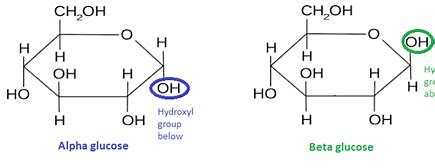
alpha and beta glucose
4
New cards
testing for reducing sugars
\-add 2cm3 of sample to test tube and grind it up
\-add equal volume of benedict’s solution to the test tube
\-gently heat solution for 5 minutes
\-if there is a colour change from blue to orange then reducing sugars are present
\-add equal volume of benedict’s solution to the test tube
\-gently heat solution for 5 minutes
\-if there is a colour change from blue to orange then reducing sugars are present
5
New cards
disaccharides - examples
glucose+glucose = maltose
glucose+fructose=sucrose
glucose+galactose=lactose
glucose+fructose=sucrose
glucose+galactose=lactose
6
New cards
disaccharides - bonding
form a condensation reaction resulting in a glyosidic bond and a side product of water
adding water will form the two original monosaccharides and this a hydrolysis reaction
adding water will form the two original monosaccharides and this a hydrolysis reaction
7
New cards
testing for nonreducing sugars
\-add 2cm3 of sample to test tube and grind it up
\-add equal volume of benedict’s solution to the test tube
\-gently heat solution for 5 minutes
\-if there is a colour change from blue to orange then reducing sugars are present
\-if no colour change add dilute hcl and heat for another 5 mins, then add sodium hydrogencarbonate and test for neutral using pH paper. test using benedicts again.
\-add equal volume of benedict’s solution to the test tube
\-gently heat solution for 5 minutes
\-if there is a colour change from blue to orange then reducing sugars are present
\-if no colour change add dilute hcl and heat for another 5 mins, then add sodium hydrogencarbonate and test for neutral using pH paper. test using benedicts again.
8
New cards
polysaccharides - starch and its forms
starch is a glucose used to store glucose in plants.
\-amylose is unbranched starch, with 1,4 bonds creating a helix chain
\-amylopectin in branched with 1,4 bonds and 1,6 bonds, also creating a helix shape, but one that can be hydrolysed more easily to release glucose quicker.
\
\-amylose is unbranched starch, with 1,4 bonds creating a helix chain
\-amylopectin in branched with 1,4 bonds and 1,6 bonds, also creating a helix shape, but one that can be hydrolysed more easily to release glucose quicker.
\
9
New cards
polysaccharides - starch and its properties
\-helix coiled structure so is compact and can store lots of glucose
\-insoluble so wont move out of the cell
\-doesn’t affect water potential of the cell
\-large structure so doesn’t diffuse out of the cell
\-insoluble so wont move out of the cell
\-doesn’t affect water potential of the cell
\-large structure so doesn’t diffuse out of the cell
10
New cards
testing for starch
add iodine to a 2cm3 sample
shake or stir
the orange iodine will change to blue-black if the starch is present inside the sample
shake or stir
the orange iodine will change to blue-black if the starch is present inside the sample
11
New cards
polysaccharides - glycogen form and properties
\-known as animal starch, stores a glucose within animals
\-very highly branched so can hydrolyse lots of glucose quickly.
\-insoluble so doesn’t affect the water potential of the cell
\-large molecule so doesn’t diffuse out of the cell
\-compact so easily stored
\-more branched than starch
\-very highly branched so can hydrolyse lots of glucose quickly.
\-insoluble so doesn’t affect the water potential of the cell
\-large molecule so doesn’t diffuse out of the cell
\-compact so easily stored
\-more branched than starch
12
New cards
cellulose - forms and properties
\-cellulose is b glucose and used in cell walls.
\-forms straight ,unbranched chains and then the layers are joined together y hydrogen bonds
\-hydrogen bonds help to strengthen the cellulose making it god for its function of cell walls.
\-forms straight ,unbranched chains and then the layers are joined together y hydrogen bonds
\-hydrogen bonds help to strengthen the cellulose making it god for its function of cell walls.
13
New cards
lipids - roles and properties
* insulation as they’re not god heat conductors
* waterproofing as they’re insoluble
* energy sources
* protection around vital organs
\
* only carbon hydrogen and oxygen
* insoluble in water but soluble in organic solvents
* waterproofing as they’re insoluble
* energy sources
* protection around vital organs
\
* only carbon hydrogen and oxygen
* insoluble in water but soluble in organic solvents
14
New cards
triglycerides
* made from three fatty acids (COOH) and one glycerol molecule (CH2OH)
* fatty acids and glycerol form a glyosidic bond with condensation reaction
* fatty acids and glycerol form a glyosidic bond with condensation reaction
15
New cards
structure of triglycerides related to function
* high ratio of carbon to hydrogen bonds to carbon atoms so they produce lots of energy
* low mass to energy ration so good storage molecule
* insoluble so don’t affect water potential of the cells
* release water when oxidised so a good water source
* low mass to energy ration so good storage molecule
* insoluble so don’t affect water potential of the cells
* release water when oxidised so a good water source
16
New cards
phospholipids structure
* the same as triglycerides but with a phosphate molecule instead of a fatty acid
* hydrophobic tail of fatty acids
* hydrophilic phosphate head
* used in cell membranes
* hydrophobic tail of fatty acids
* hydrophilic phosphate head
* used in cell membranes
17
New cards
lipids test
* add the sample to test tube
* add ethanol to same along with water
* shake the test tube
* milky white emulsion at the top of the tube means lipid is present in the sample
* add ethanol to same along with water
* shake the test tube
* milky white emulsion at the top of the tube means lipid is present in the sample
18
New cards
proteins monomer and its structure
* the monomer for the protein is amino acid
* the amino acid has a H group, a COOH group, a NH3 group and an R group
* the amino acid has a H group, a COOH group, a NH3 group and an R group
19
New cards
bonding in protein/poly peptide
* the bonds between amino acids are condensation
* they remove a molecule of water and form a peptide bond
* they remove a molecule of water and form a peptide bond
20
New cards
Primary structure of proteins
* amino acids react to form polypeptide chains
* these are determined by the DNA sequence coded for
* primary protein structure determines the overall function and structure
* these are determined by the DNA sequence coded for
* primary protein structure determines the overall function and structure
21
New cards
secondary structure in proteins
* the polypeptide chains fold and form hydrogen bonds
* the hydrogen bonds start to form a coil or pleated beta sheet structure within the polypeptide chains
* the hydrogen bonds start to form a coil or pleated beta sheet structure within the polypeptide chains
22
New cards
tertiary structure in proteins
* tertiary structure is when the 3D structure begins to form
* there are three main bonds which cause this:
* disulphide bridges - fairly strong so not easily broken
* hydrogen bonds- lots of these but easily broken
* ionic bonds - form between the COOH and NH3 groups not involved in the reaction. these are weaker than disulphide and easily broken by changes in pH
* there are three main bonds which cause this:
* disulphide bridges - fairly strong so not easily broken
* hydrogen bonds- lots of these but easily broken
* ionic bonds - form between the COOH and NH3 groups not involved in the reaction. these are weaker than disulphide and easily broken by changes in pH
23
New cards
Quaternary structure of proteins
* these are when many polypeptide chains join together and form more complex structures.
24
New cards
test for proteins
* add biuret to a warmed sample of proteins
* if present, the solution will turn from blue to purple
* if present, the solution will turn from blue to purple
25
New cards
nucleotide structure and bonding
* a nucleotide is made up of a pentose sugar, a phosphate group and nitrogen bases: CTUAG
* the components of a nucleotide join together through a condensation reaction to form a mononucleotide
* mononucleotides join together to form a phosphodiester bonds, resulting in a dinucleotide or polynucleotide
* the components of a nucleotide join together through a condensation reaction to form a mononucleotide
* mononucleotides join together to form a phosphodiester bonds, resulting in a dinucleotide or polynucleotide
26
New cards
RNA
* called ribonucleic acid
* pentose sugar is a ribose sugar
* bases are CGUA
* used to transfer genetic info from DNA to ribosomes
* used for protein synthesis
* used in ribosomes along with proteins
* pentose sugar is a ribose sugar
* bases are CGUA
* used to transfer genetic info from DNA to ribosomes
* used for protein synthesis
* used in ribosomes along with proteins
27
New cards
DNA
* pentose sugar is a deoxyribose sugar
* bases are ATCG
* double stranded with hydrogen bonds connecting the complimentary bases
* double helix twisted structure
* bases are ATCG
* double stranded with hydrogen bonds connecting the complimentary bases
* double helix twisted structure
28
New cards
stability of DNA
* the cytosine and guanine bonds have a triple hydrogen bond so the more C-G bonds there are, the more stable
* the phosphodiester bonds acts as a backbone for the helix and protects more chemically reactive bases
* the phosphodiester bonds acts as a backbone for the helix and protects more chemically reactive bases
29
New cards
function of DNA
* stable structure so limited number of mutations occur
* two separate strands only joined by hydrogen bonds so easy to separate for DNA replication
* large molecule carrying lots of info but the helix coil means it is compact
* base pairing allows for DNA replication
* strong phosphodiester backbone protects DNA from outside forces
* two separate strands only joined by hydrogen bonds so easy to separate for DNA replication
* large molecule carrying lots of info but the helix coil means it is compact
* base pairing allows for DNA replication
* strong phosphodiester backbone protects DNA from outside forces
30
New cards
two types of cell division
* nuclear division which is the nucleus dividing (mitosis and meiosis)
* cytokinesis is the division of the cell
* cytokinesis is the division of the cell
31
New cards
semi conservative replication
* the enzymes DNA helicase works its way through the strand, hydrolysing the hydrogen bonds and unwinding DNA
* the free nucleotides use complimentary base pairing to match up and form new strands.
* DNA polymerase works to join the new strands from the nucleotides connected to the original strand
* the 2 new strands consist of one original strand and one new strand, meaning the strands are semi conserved
* the free nucleotides use complimentary base pairing to match up and form new strands.
* DNA polymerase works to join the new strands from the nucleotides connected to the original strand
* the 2 new strands consist of one original strand and one new strand, meaning the strands are semi conserved
32
New cards
equation for ATP to store energy
ATP + H2O → ADP + Pi + Energy
33
New cards
synthesis of ATP
* production of atp is a reversible reaction.
* the atp molecule can be condensed to form adp again
* atp has a low activation energy so energy can quickly and easily be released from this process
* the atp molecule can be condensed to form adp again
* atp has a low activation energy so energy can quickly and easily be released from this process
34
New cards
roles of ATP
* immediate energy source, each ATP molecule releases less energy than a glucose molecule so the energy is being released in more manageable loads. it is also a lot quicker than hydrolysing all the ends of the glucose storage
* metabolic processes to build up molecules from their monomers such as starch and cellulose
* movement in muscle contraction
* active transport of substances in processes such as digestion
* activation of molecules as ATP is used to overcome the activation energy of a reaction
* metabolic processes to build up molecules from their monomers such as starch and cellulose
* movement in muscle contraction
* active transport of substances in processes such as digestion
* activation of molecules as ATP is used to overcome the activation energy of a reaction
35
New cards
Water and its functions
* polar molecule
* hydrogen and oxygen in the water bond so the molecule ‘stick’ together and form unusual properties
* the specific heat capacity of water is high as the bonds require lots of energy in order to break them
* same with latent heat of vaporisation
* high surface tension
\
* hydrogen and oxygen in the water bond so the molecule ‘stick’ together and form unusual properties
* the specific heat capacity of water is high as the bonds require lots of energy in order to break them
* same with latent heat of vaporisation
* high surface tension
\
36
New cards
water in living organisms
* used in metabolic processes to do hydrolysis
* a solvent for gases and enzymes
* evaporates to cool organisms
* a solvent for gases and enzymes
* evaporates to cool organisms
37
New cards
inorganic ions
* phosphate molecules in DNA and lipids
* hydrogen ions for determining the pH of solutions and therefore the use of enzymes
* sodium ions are important in the cotransport of glucose and amino acids
* hydrogen ions for determining the pH of solutions and therefore the use of enzymes
* sodium ions are important in the cotransport of glucose and amino acids