AP Art History: Greek Art
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
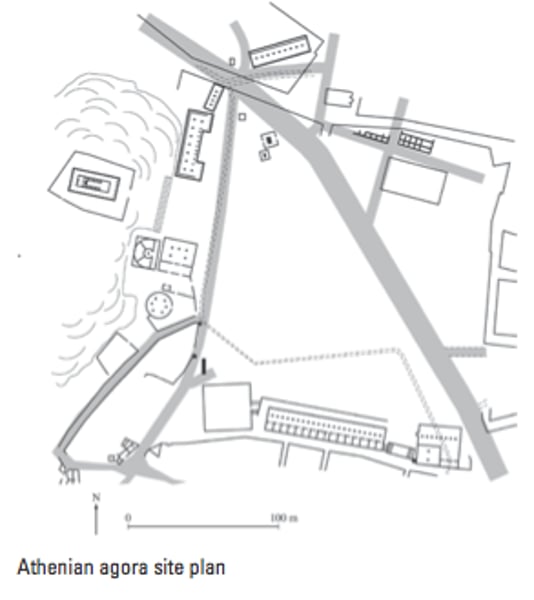
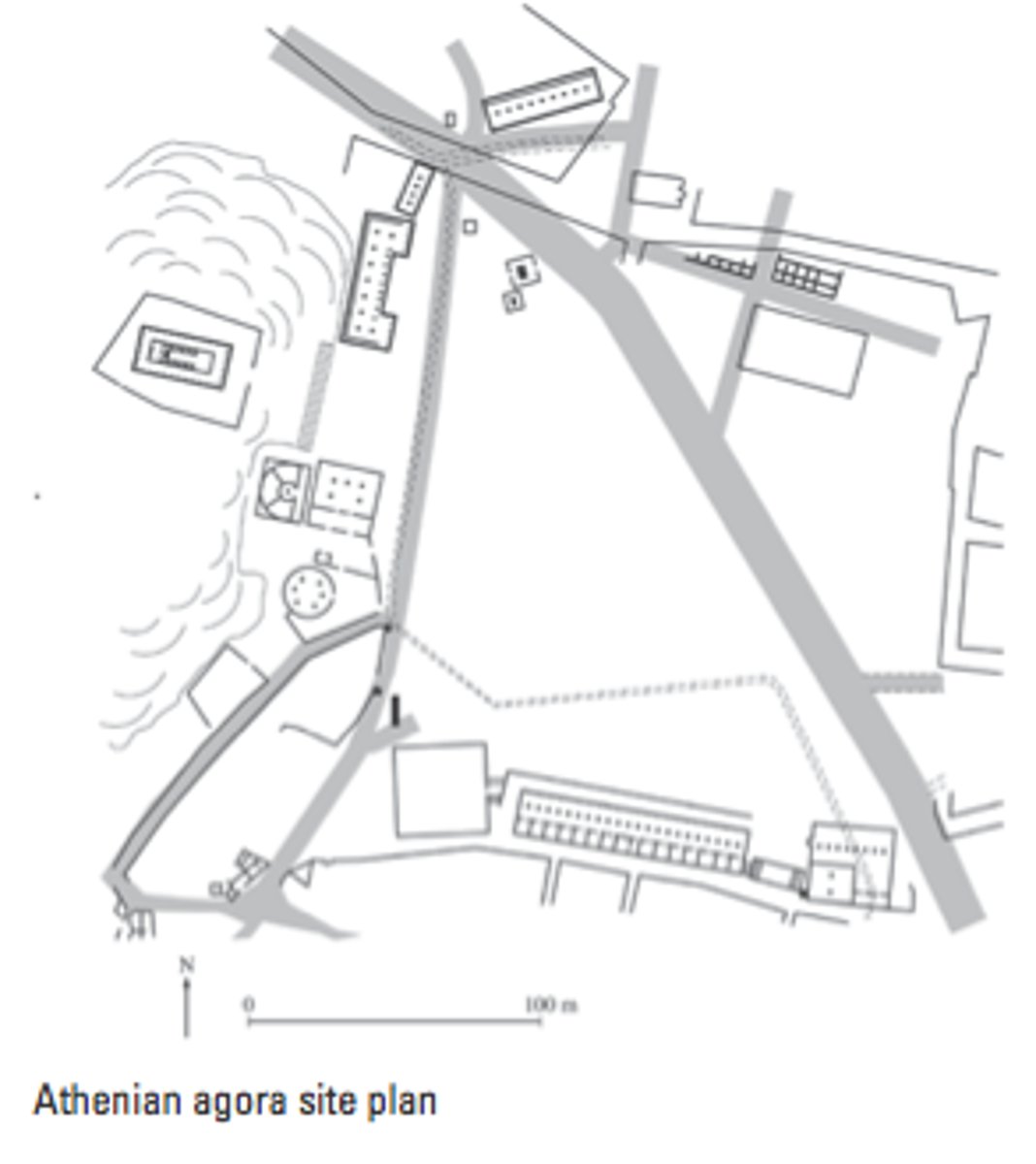
Athenian agora
Period: Archaic through Hellenistic
Function: Center of life for the Greeks
Content: Buildings for government and commerce. Links commercial, political, and religious aspects of life
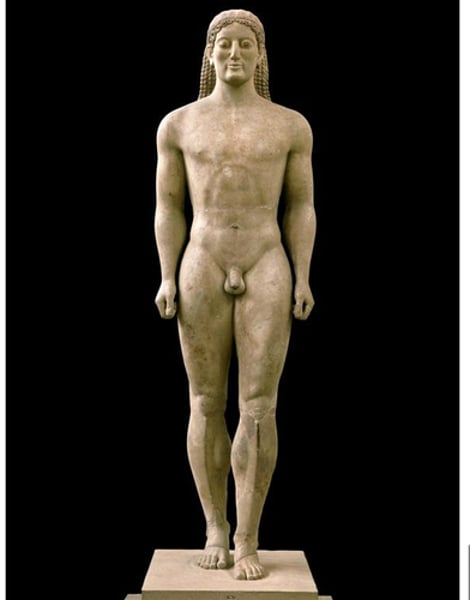
Anavyos Kouros
Period: Archaic c.530 B.C.E.
Form: Marble statue
Function: Funerary; welcomes mourners
Content: Man stands with an archaic smile, left leg forward. Better proportions. Perfect form. Rounder, softer.

Peplos Kore
Period: Archaic c.530 B.C.E.
Form: Marble statue
Function: Funerary; votive offering
Content: Goddess wears a peplos; natural, simple. Women always clothed. Buried at grave. Once held identity in left hand.

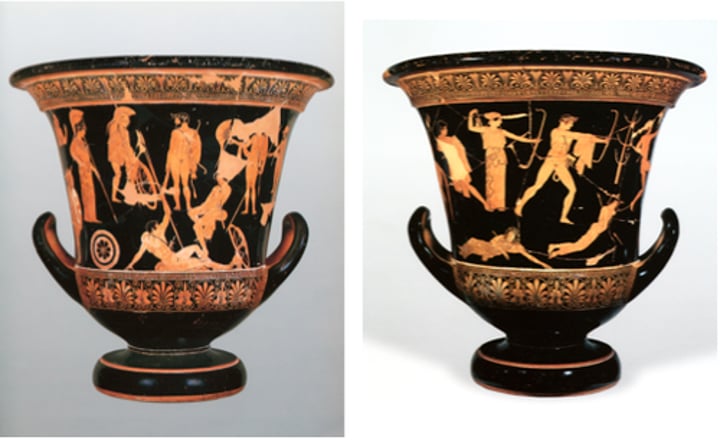
Niobides Krater
Period: Classical c.460-450 B.C.E.
Form: Black-figure vase
Function: Funerary, narrative
Content: Severe style is shown in serious faces. Niobe's kids are killed.

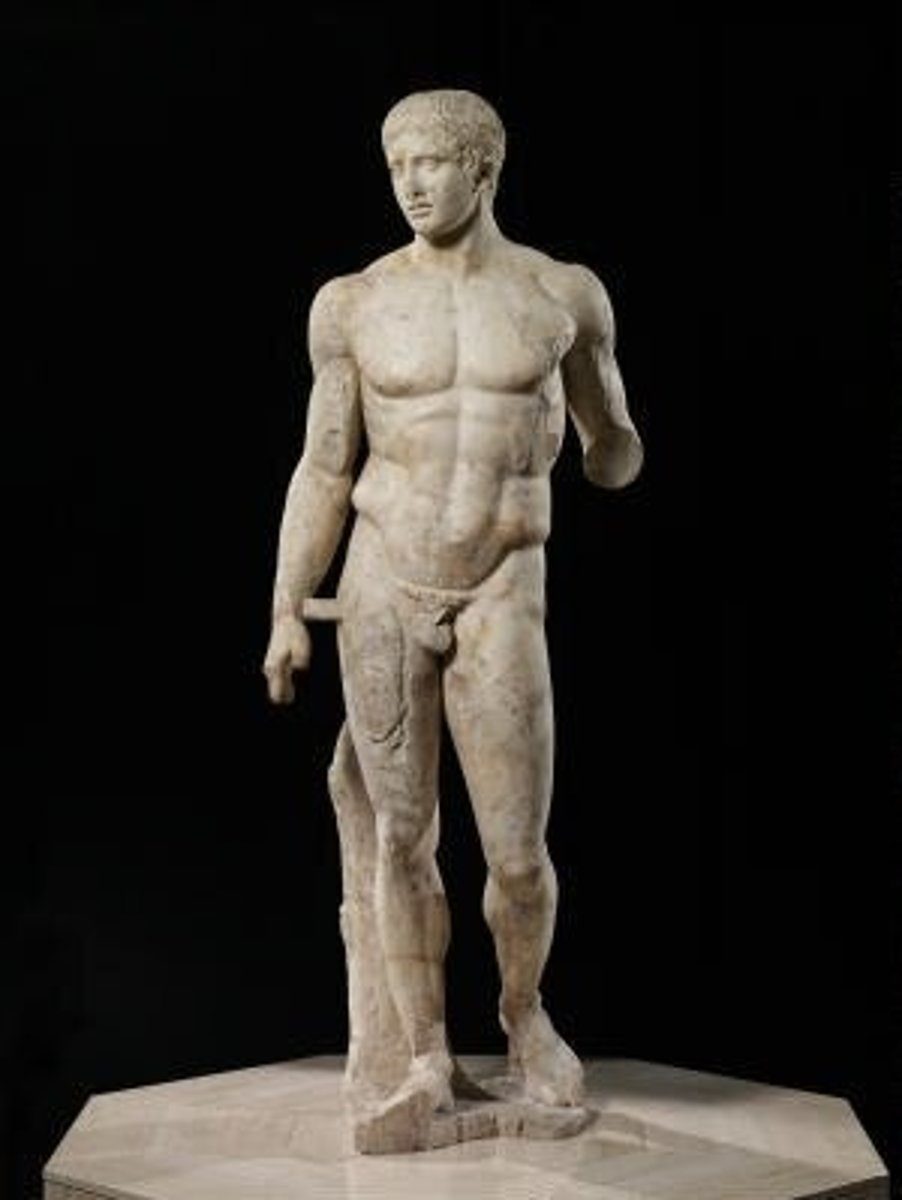
Doryphoros
Period: Early Classical c.450-440 B.C.E.
Artist: Polykleitos
Form: Marble copy of bronze original
Function: Decorative
Content: Perfect man is shown. Harmonic proportions balance. Weighted vs. relaxed. Canon is used. Contrapposto. Movement. Numerical ratios.

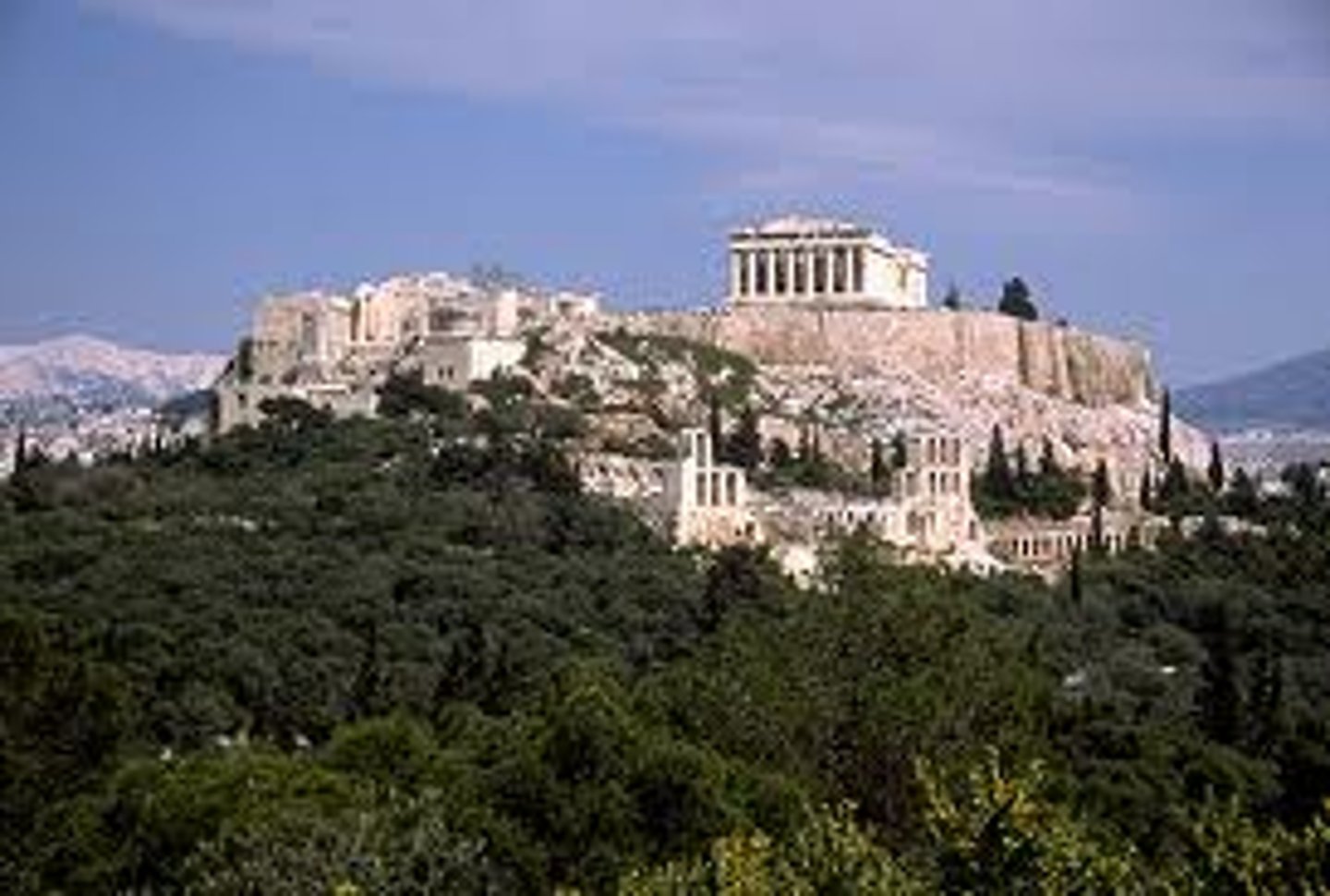
Athens Acropolis
Period: Early Classical c.447-410 B.C.E.
Architects: Iktinos and Kallikrates
Form: Marble
Function: Town center
Content: Pericles patroned art. Athens had to be rebuilt.
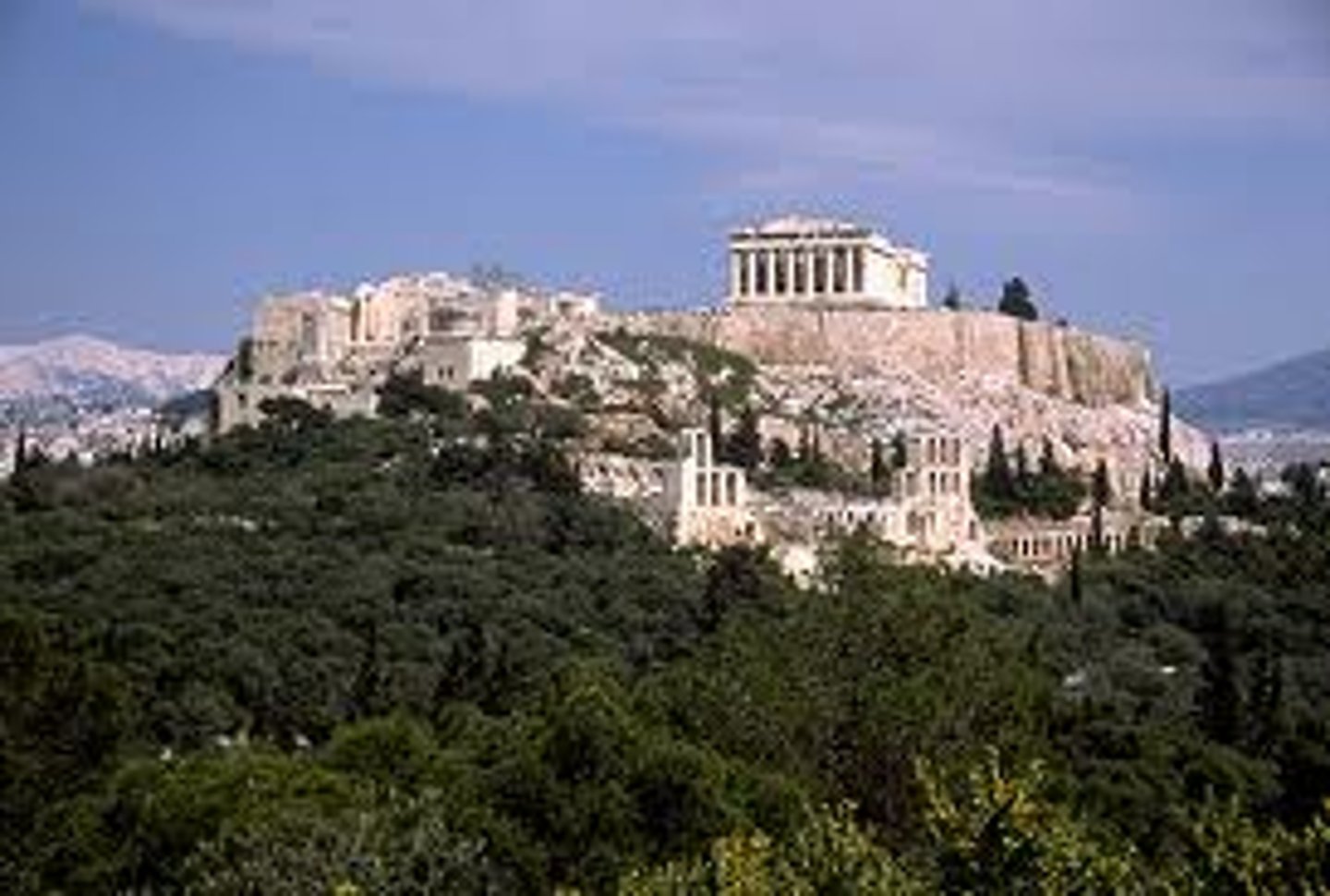

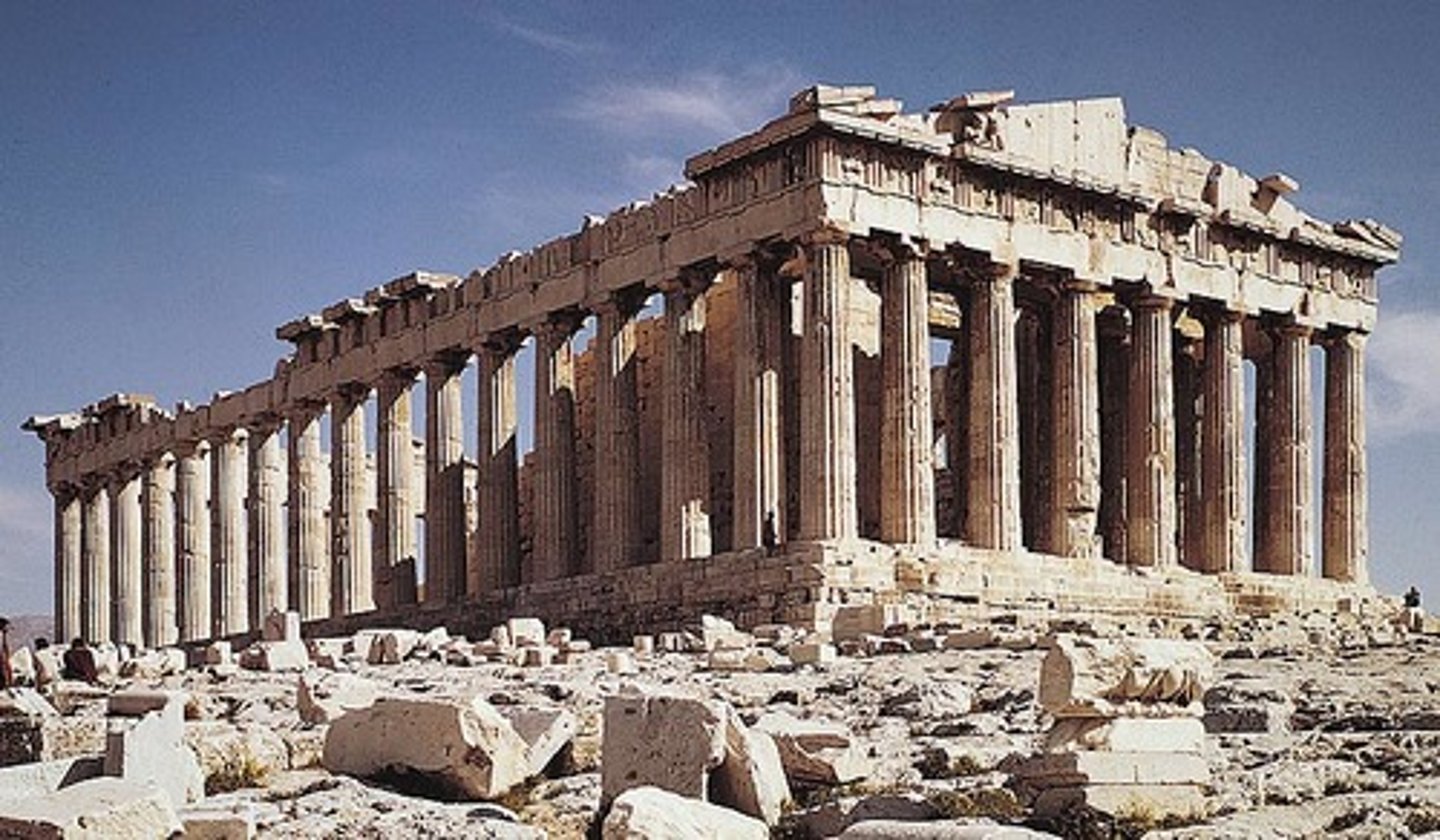
Parthenon
Period: Early Classical c.447-410 B.C.E.
Architects: Iktinos and Kallikrates
Form: Doric, stone
Function: Temple for Athena
Content: Doric structure with ionic interior. Mathematical proportions. Optical illusion. Looks southeast. Decorated under Phidias.

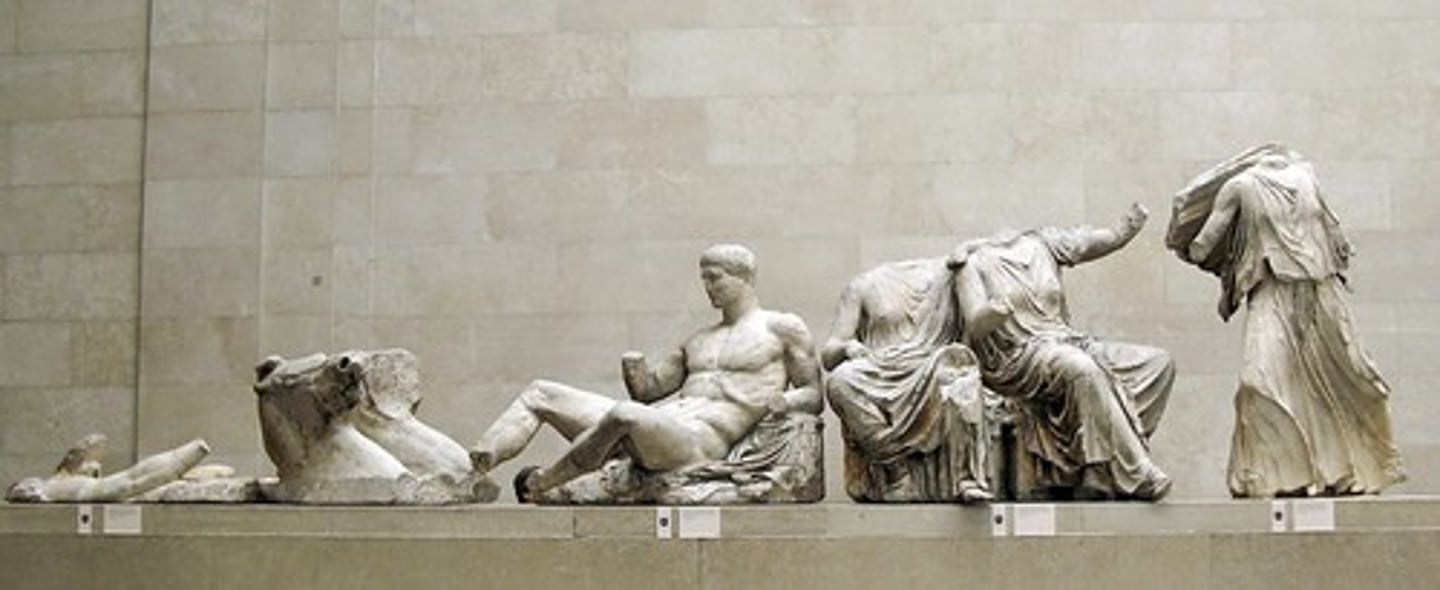
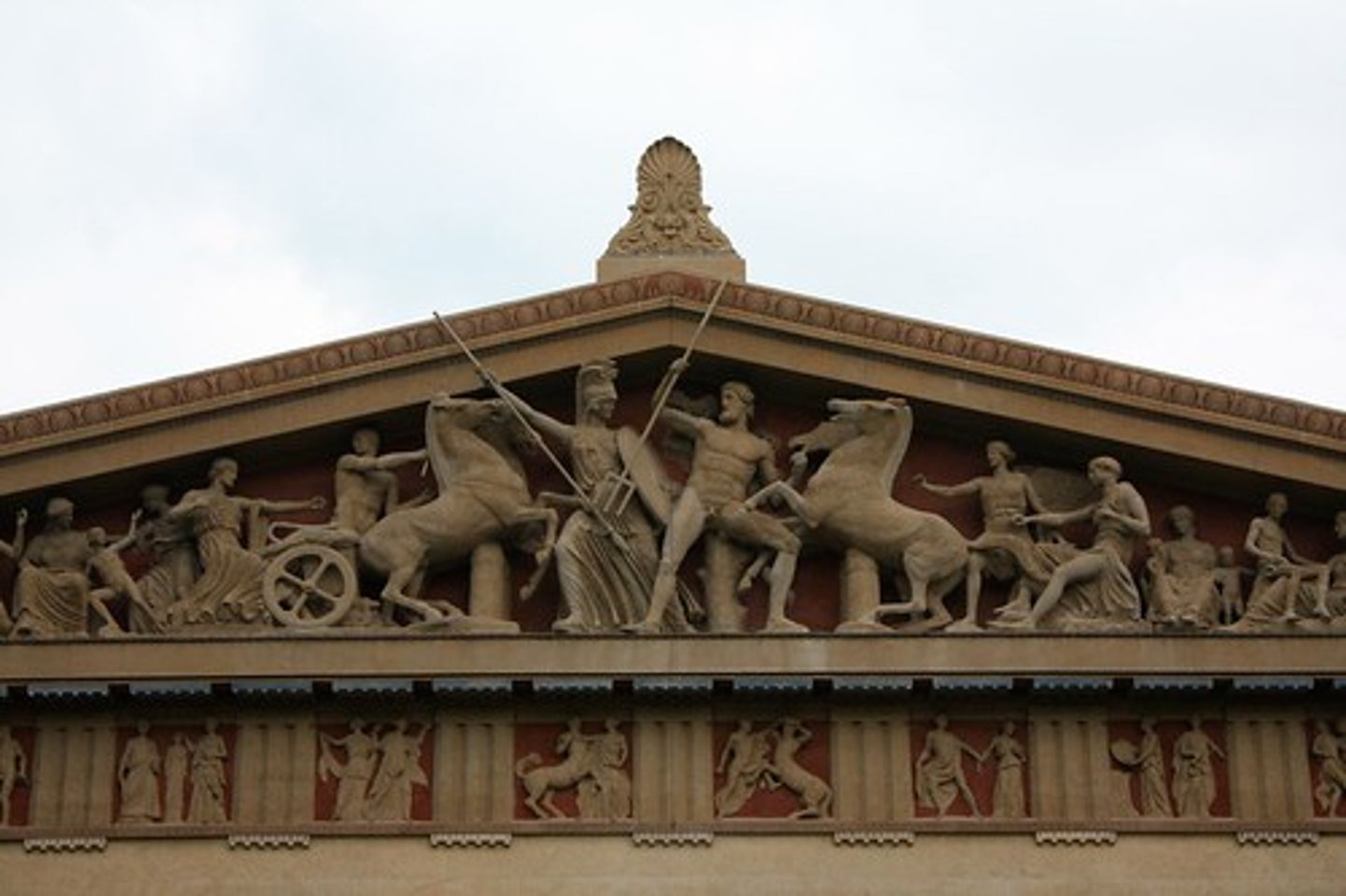
Helios, Horses, and Dionysus
Period: Early Classical 5th Century B.C.E.
Form: Marble statues from East Pediment
Function: Decorative
Content: Left- Helios' horses emerge from horizon. Cornice piece. Draped clothing. Man (Dionysus) entered realm of gods.

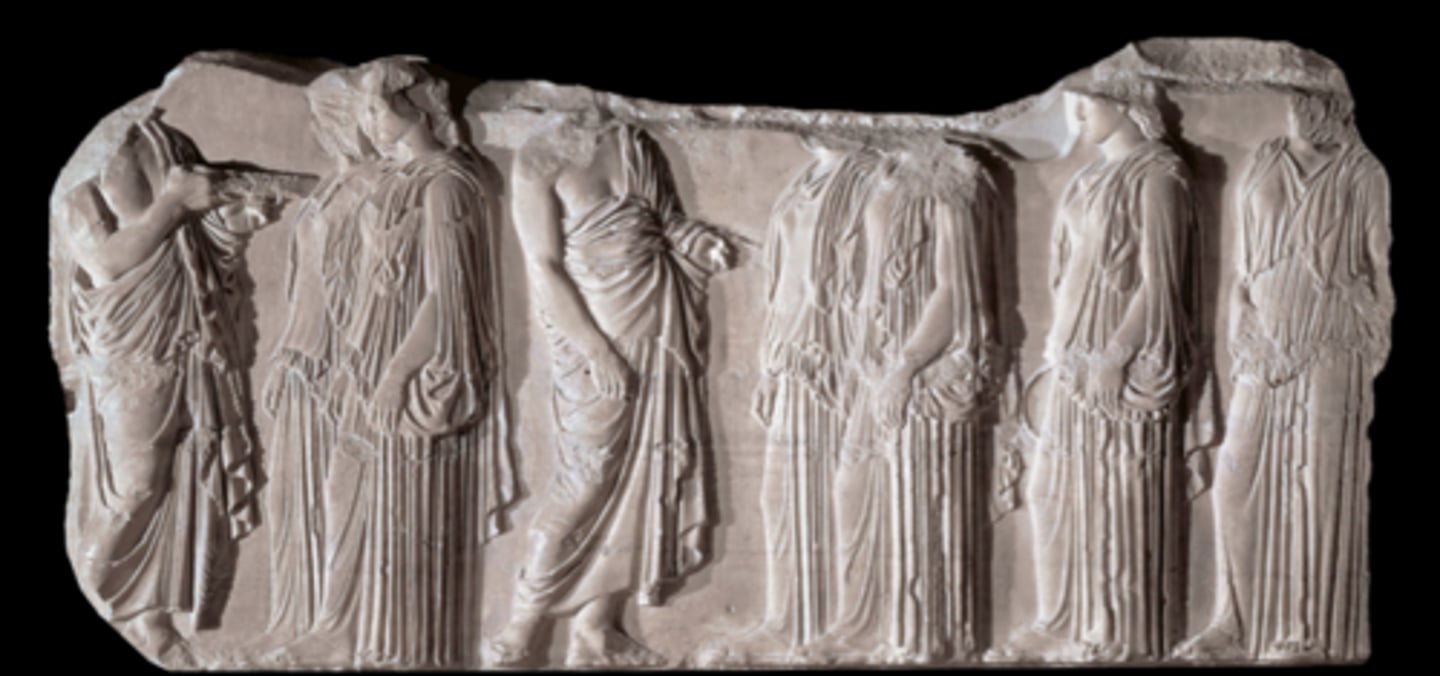
Plaque of the Ergustines
Period: Early Classical 5th Century B.C.E.
Form: Marble relief
Function: Narrative
Content: Panathenaic Procession takes place. Gods watch. Citizens look noble. Democracy, balanced time. Idealism. Column-like. Contrapposto.

Victory (Nike) Adjusting her Sandal
Period: Early Classical 5th Century B.C.E.
Form: Marble
Function: Decorative
Content: Athena is shown adjusting her sandal. Humanized. Temple of Athena. Nearly transparent garments. Folds form intricate linear patterns. Less ideal. Marks transition into Late Classical.
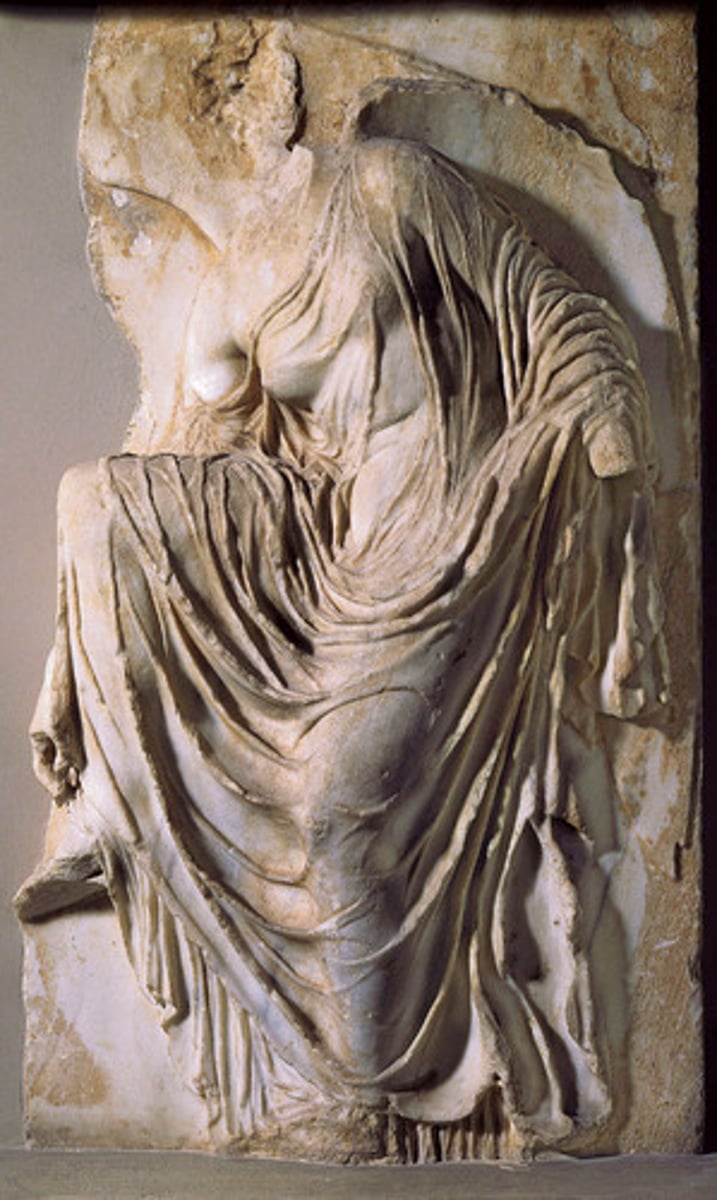

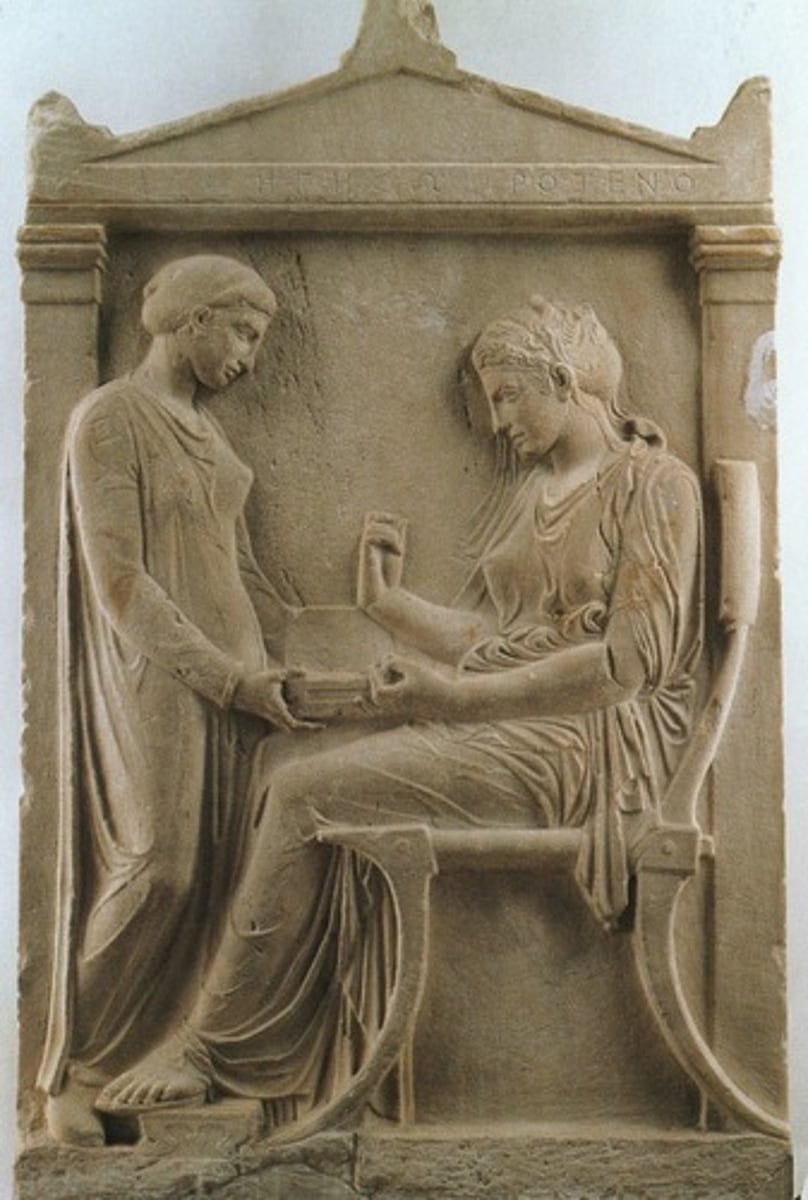
Grave Stele of Hegeso
Period: Late Classical c.410 B.C.E.
Form: Marble
Function: Funerary
Content: Hegeso examines jewels with servant. Daily life. Difference in clothing. Grave stele.
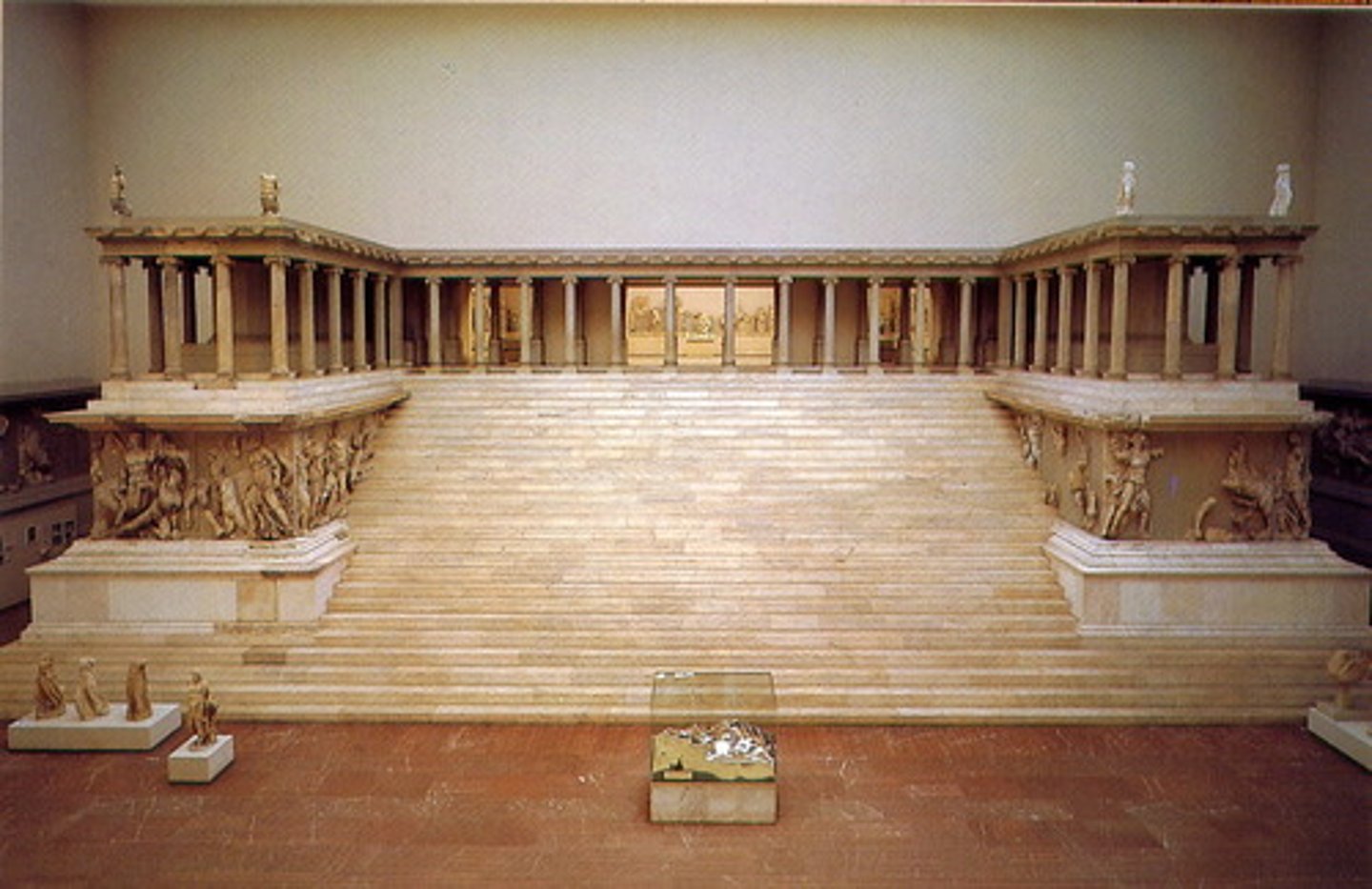
Great Altar of Zeus and Athena at Pergamon
Period: Hellenistic c.175 B.C.E.
Form: Marble with reliefs
Function: Honors Zeus
Content: Gigantomachy friezes. Ionic.

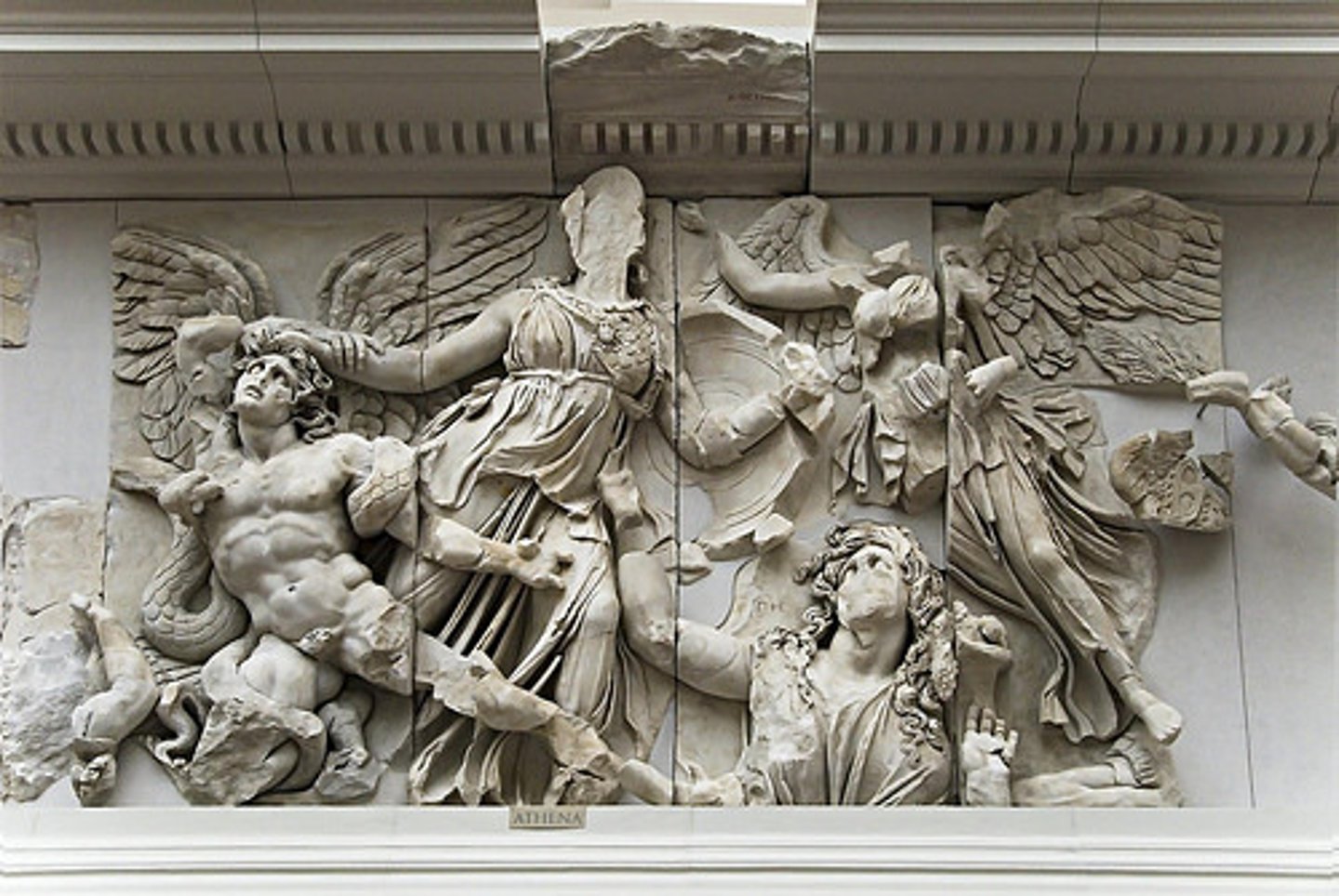
Athena Battling Alkyoneos
Period: Hellenistic c.175 B.C.E.
Form: Marble frieze
Function: Narrative; Altar of Zeus
Content: Athena battles Alkyoneos. Gigantomachy. Emotional. Violent movement; swirling drapery. Vivid depictions of suffering. Athena grabs Alkyoneos' hair; Nike flies to crown. High relief: dark shadows.

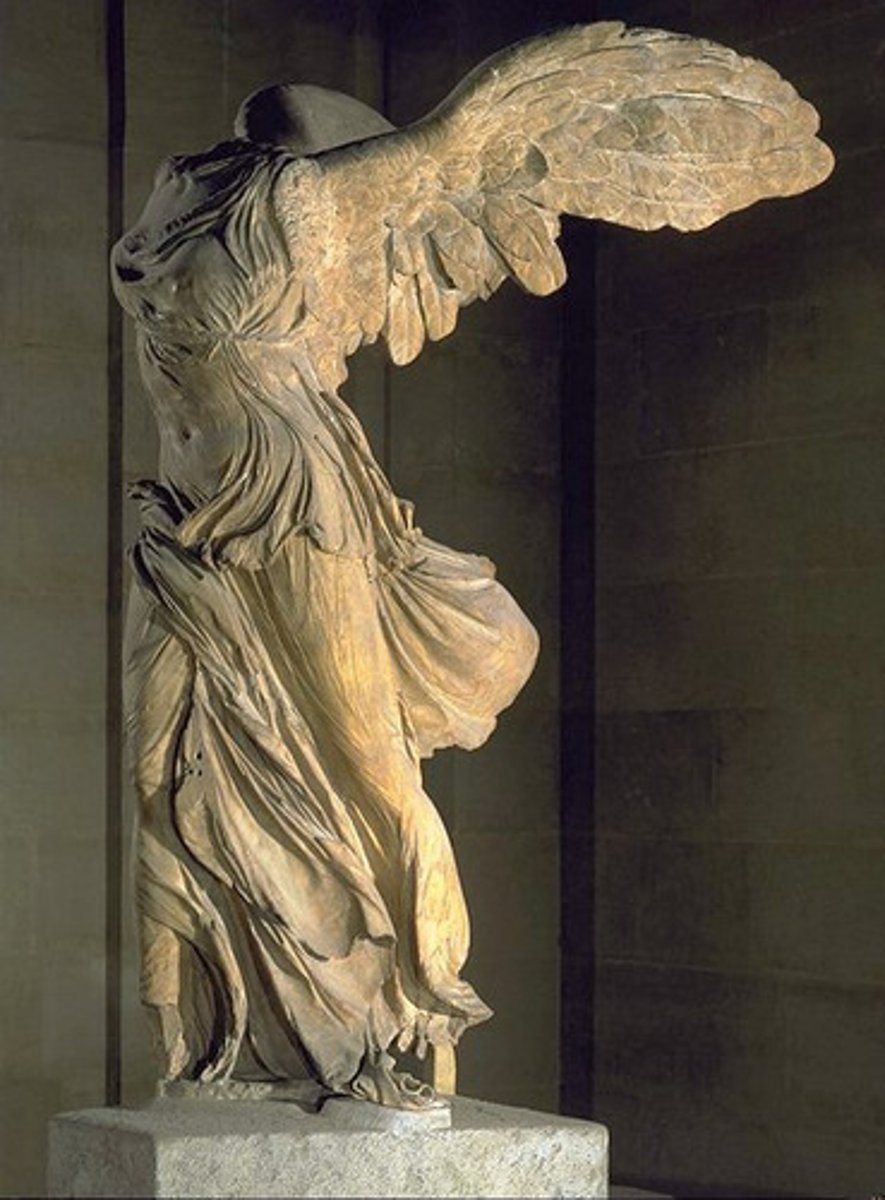
Winged Victory of Samothrace
Period: Hellenistic c.190 B.C.E.
Form: Marble
Function: Decorative
Content: Nike lands on ship's prow to crown victor at sea. Statue in fountain heightens dramatic effect. Wings still beat. Wind sweeps drapery.

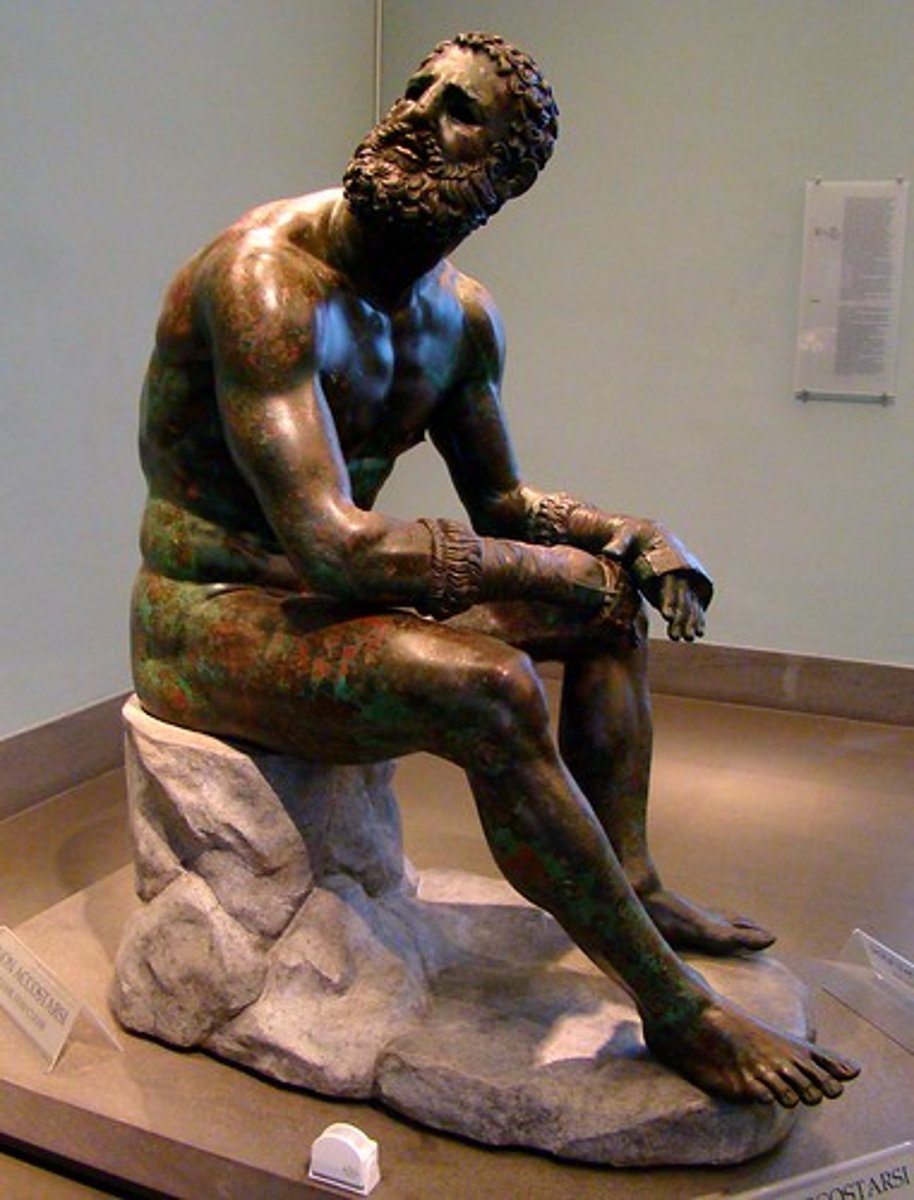
Seated Boxer
Period: Hellenistic c.100 B.C.E.
Form: Bronze statue
Function: Decorative
Content: Old, defeated boxer is shown with broken nose and battered eyes. Blood drips down forehead. Not as ideal. Emotion. Disappointed. Looking at opponent.

Acropolis
A fortified hilltop in an ancient Greek city

Agora
the marketplace in ancient Greece
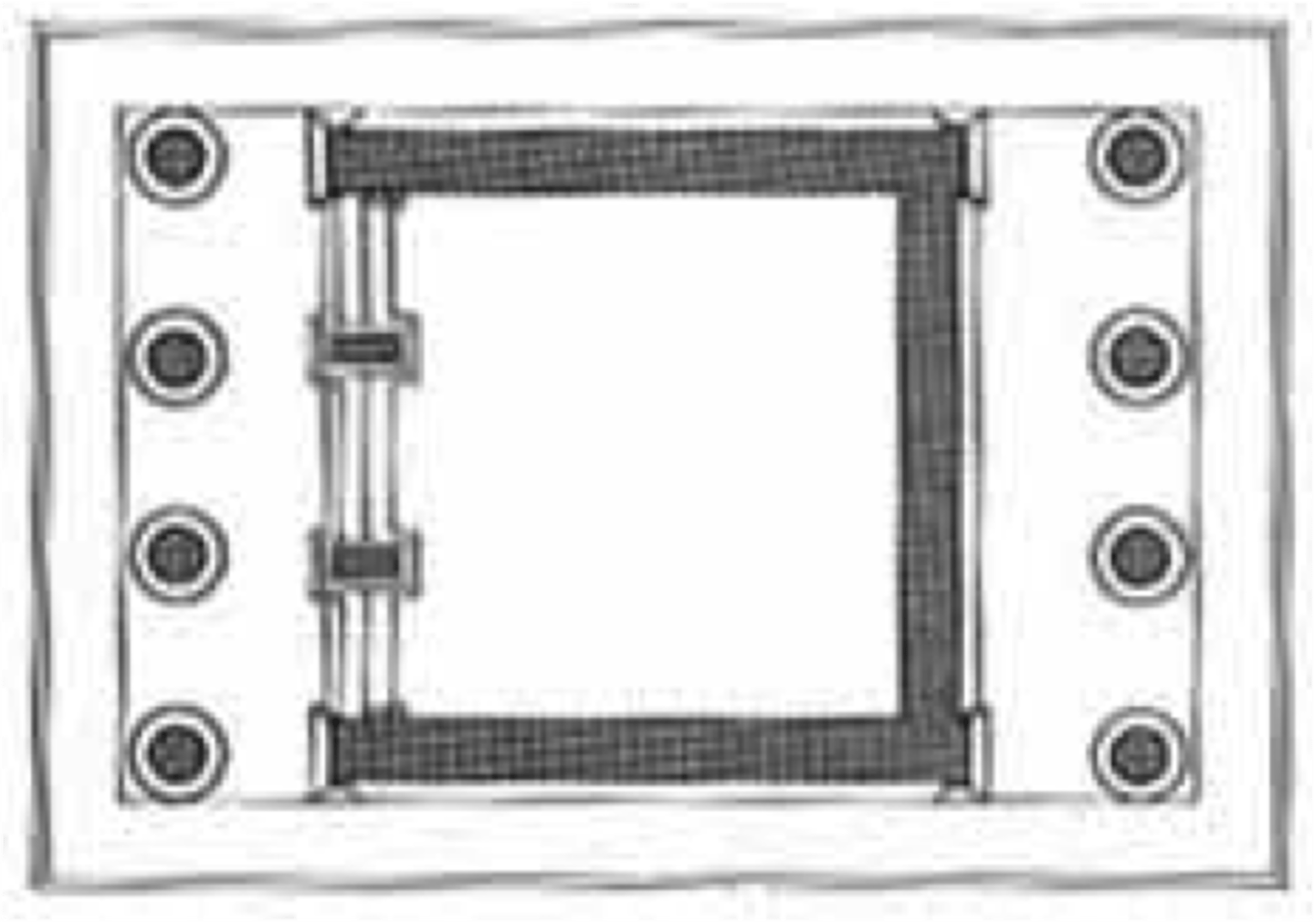
Amphiprostyle
having four columns in the front and rear of a temple
Amphora
a tall ancient Greek or Roman jar with two handles and a narrow neck.

Caryatid
a female figure that functions as a supporting column
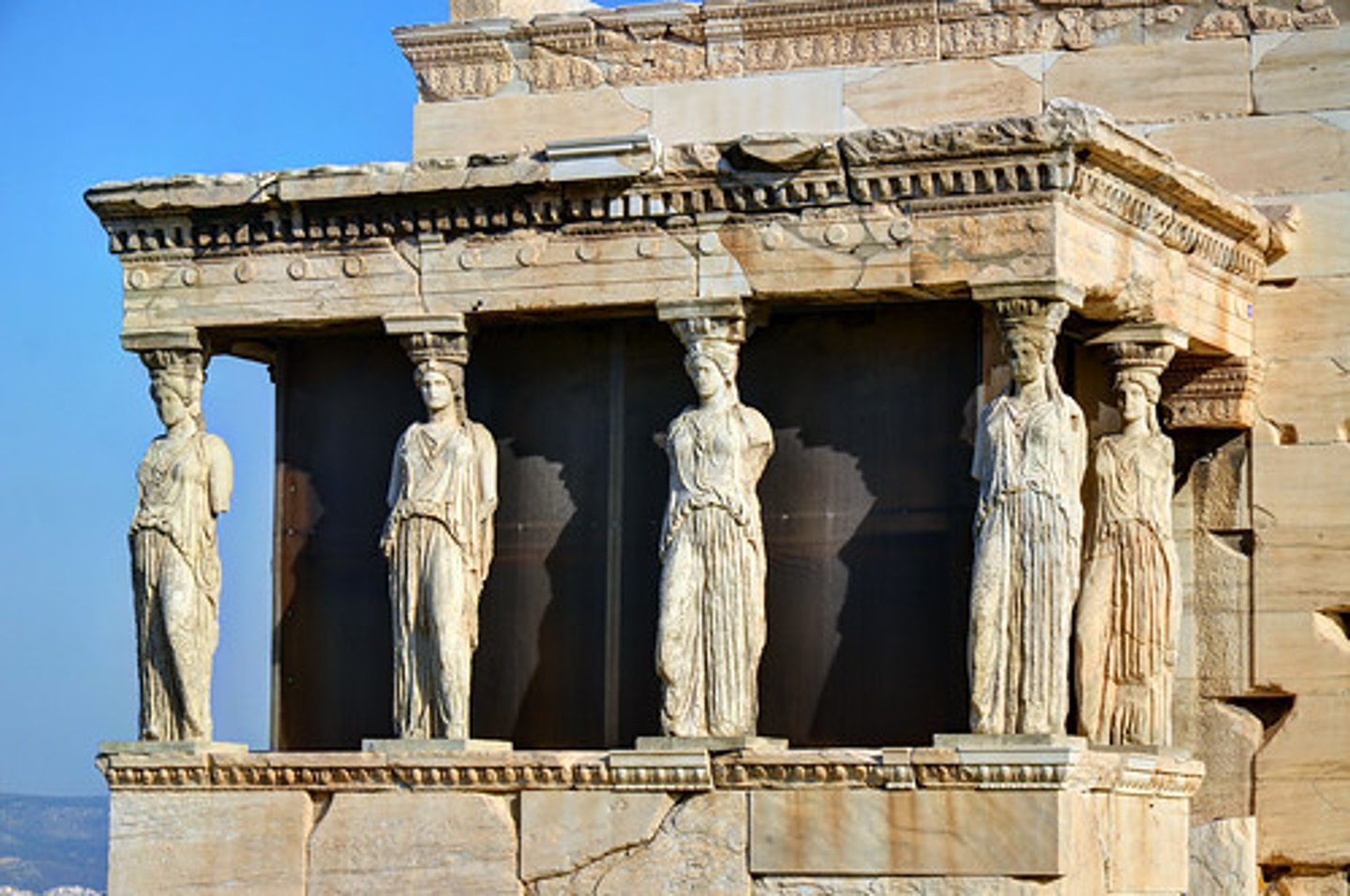

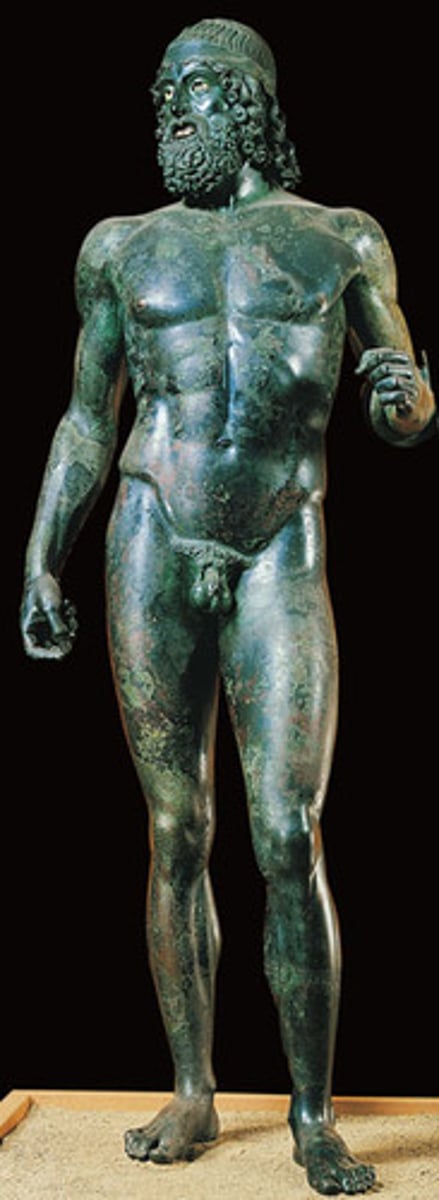
Contropposto
an asymmetrical arrangement of the human figure in which the line of the arms and shoulders contrasts with while balancing those of the hips and legs.

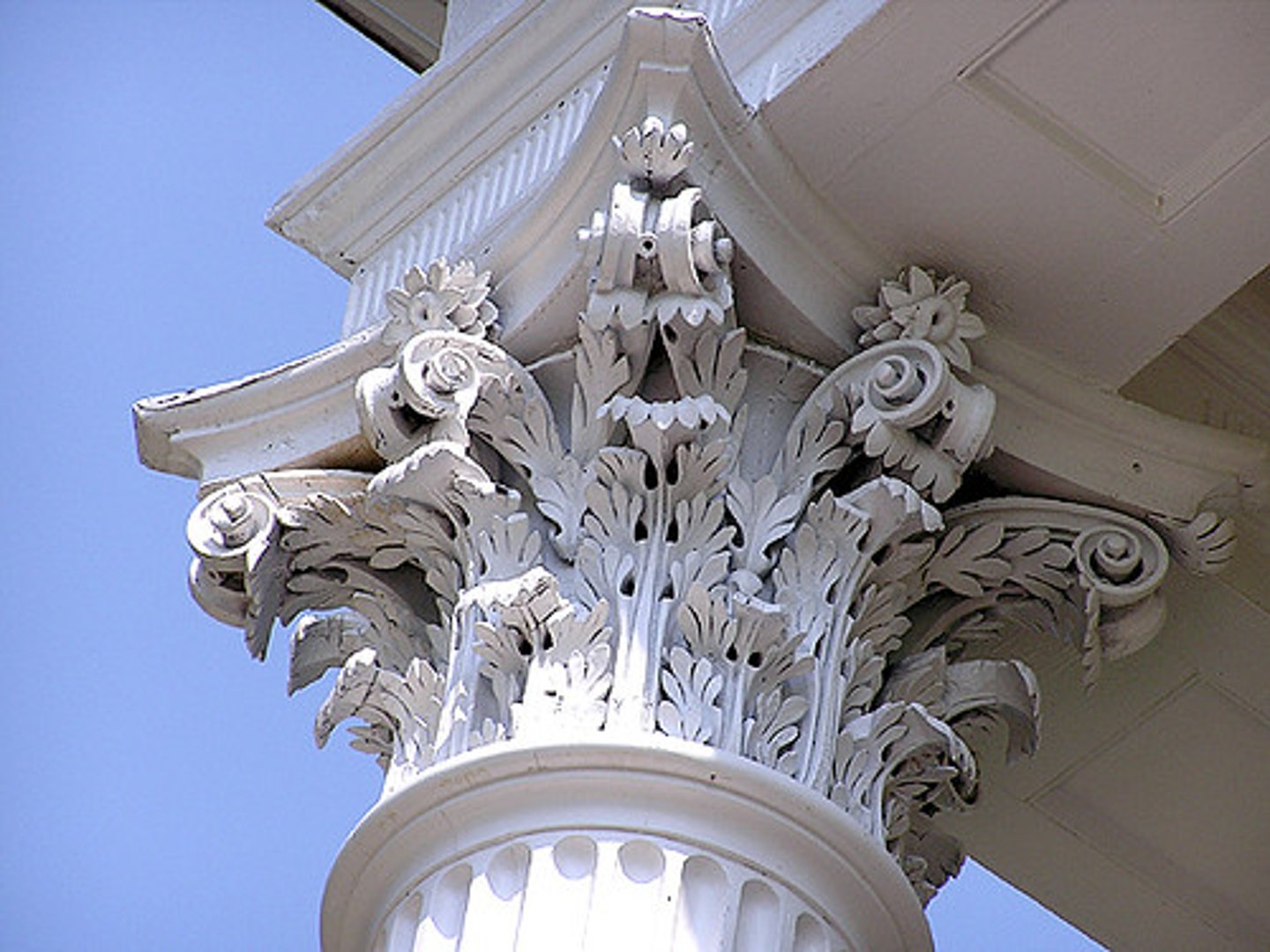
Corinthian
This style of column has elongated capitals that are decorated with leaves.

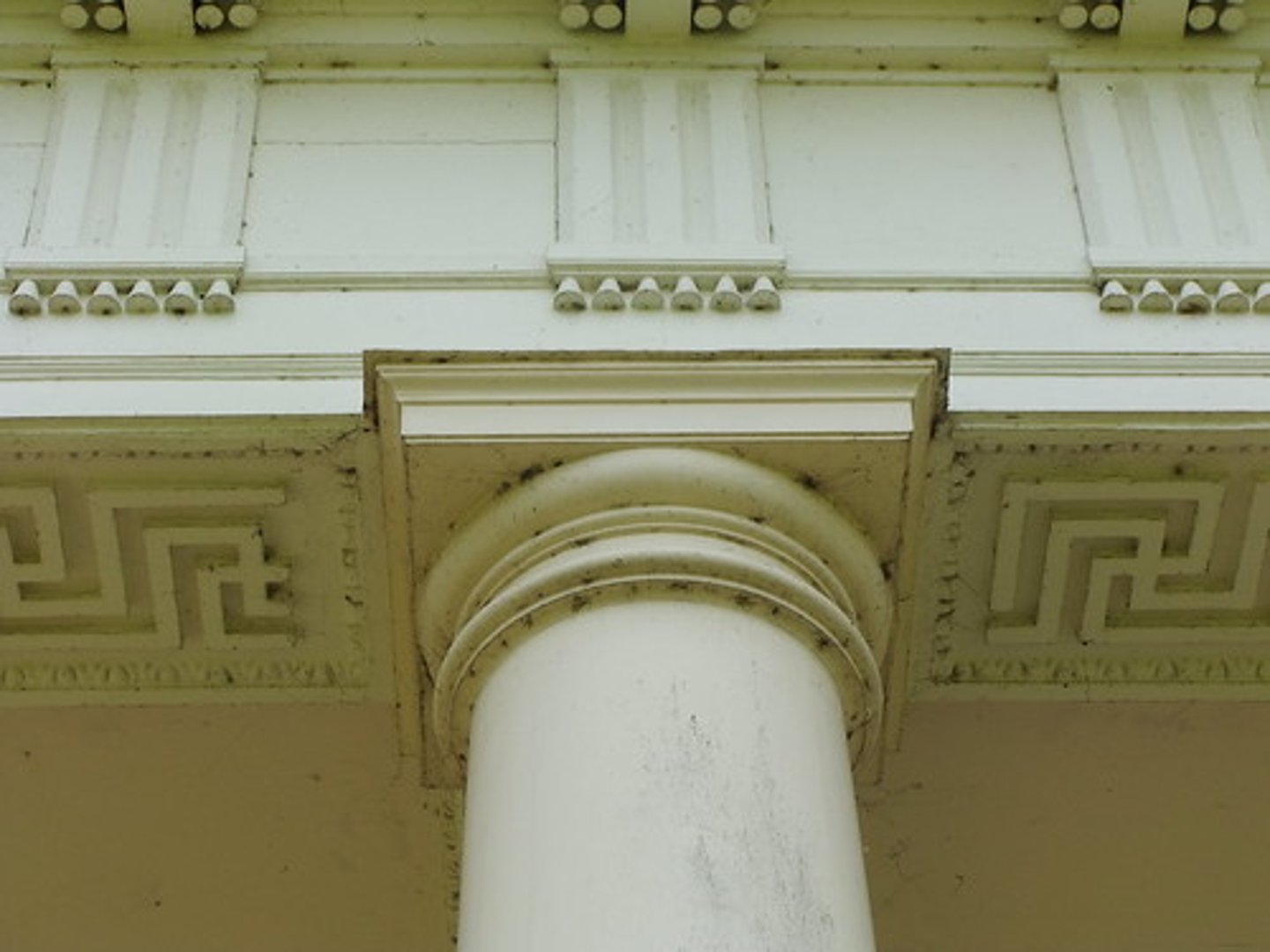
Doric
This style of column features simple, heavy columns without bases.

Entablature
a horizontal, continuous lintel on a classical building supported by columns or a wall, comprising the architrave, frieze, and cornice.
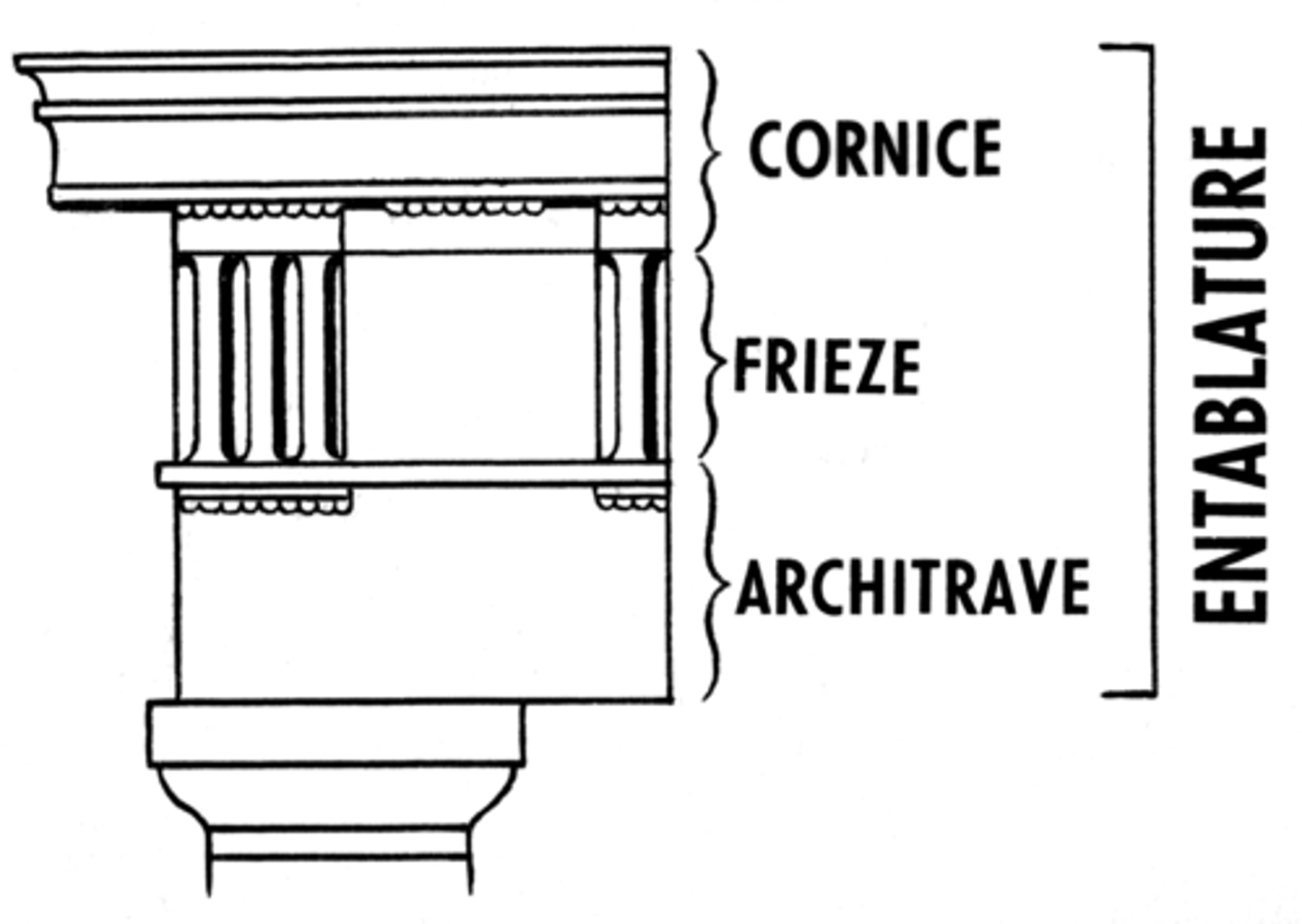
frieze
a broad horizontal band of sculpted or painted decoration, especially on a wall near the ceiling.

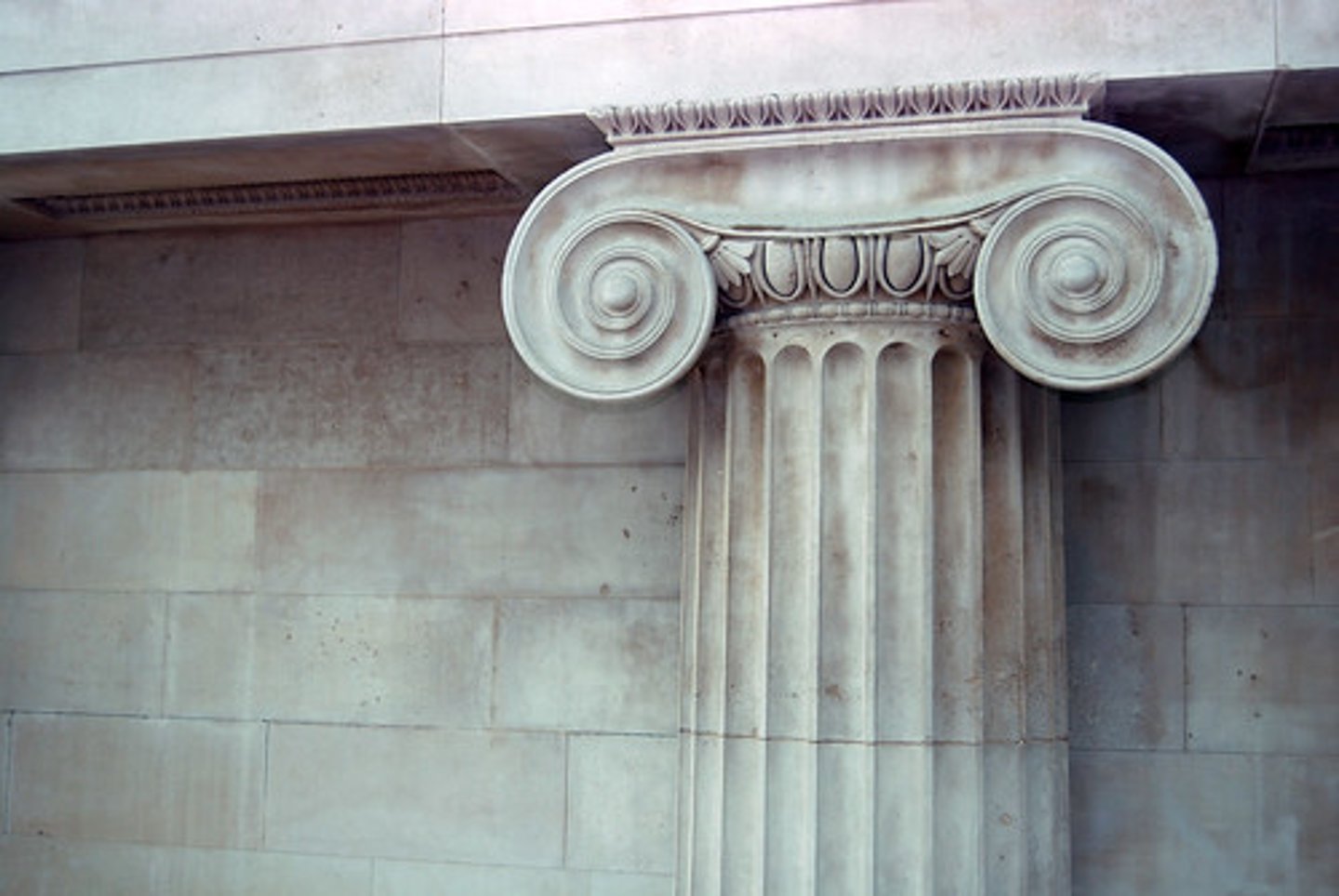
Ionic Column
This is a Greek column with short, fluted shafts and scroll-like decorations on its capital.

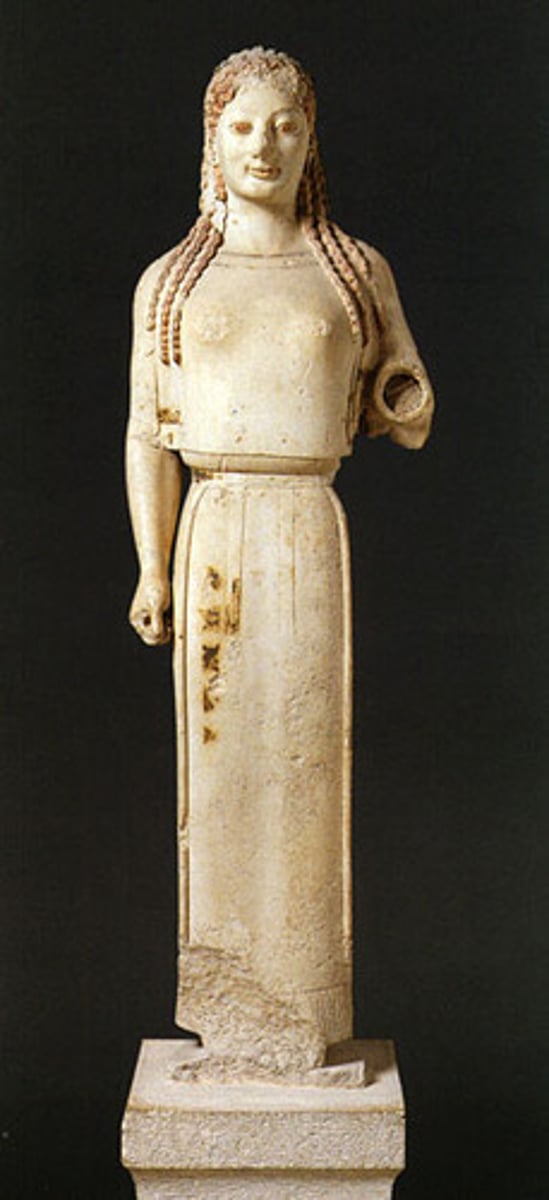
Kore
an archaic Greek statue of a young woman, standing and clothed in long loose robes.

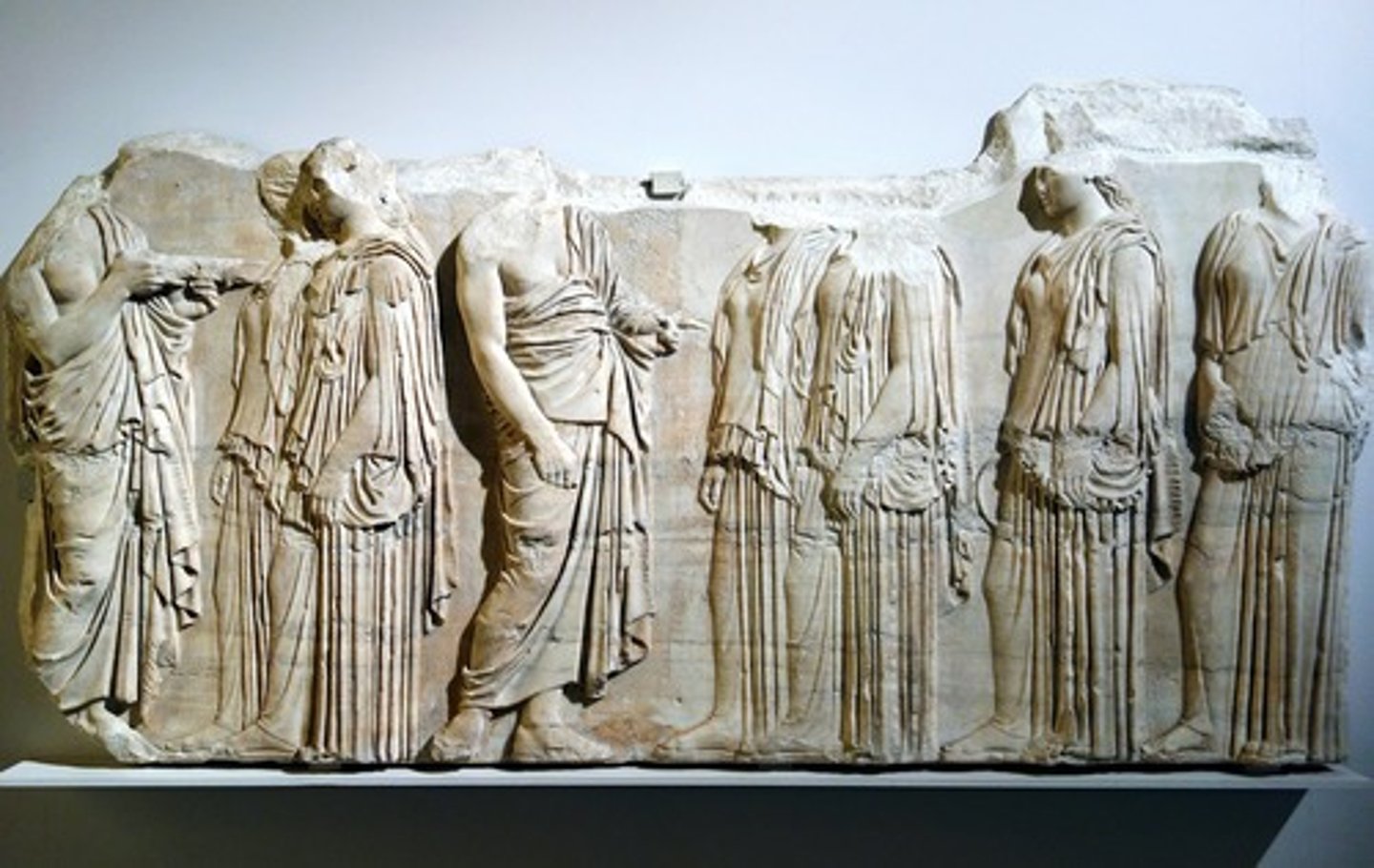
Isocephalism
the tradition of depicting heads of figures on the same level

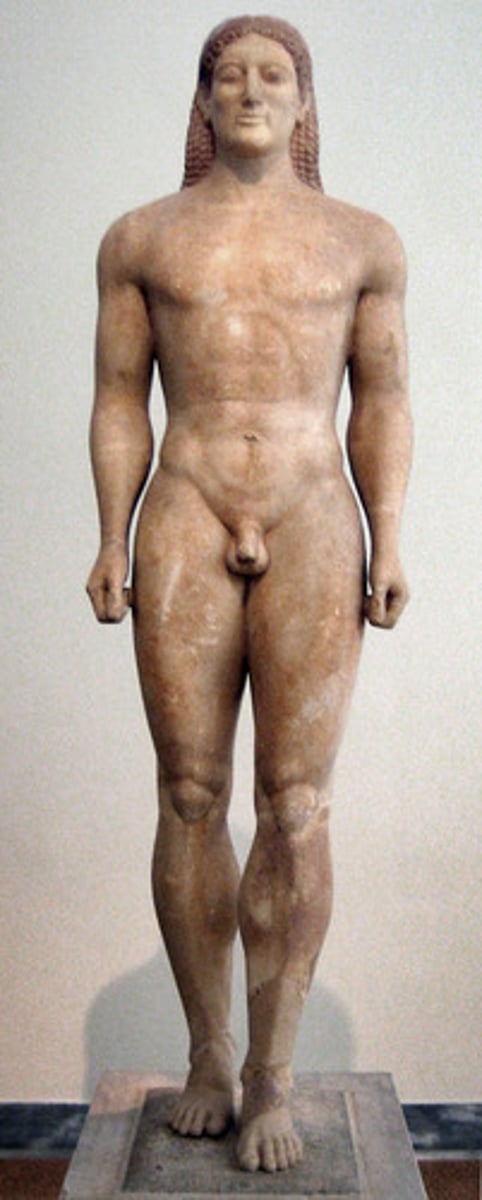
Kouros
Greek word for "male youth." An Archaic Greek statue of a standing, nude youth.

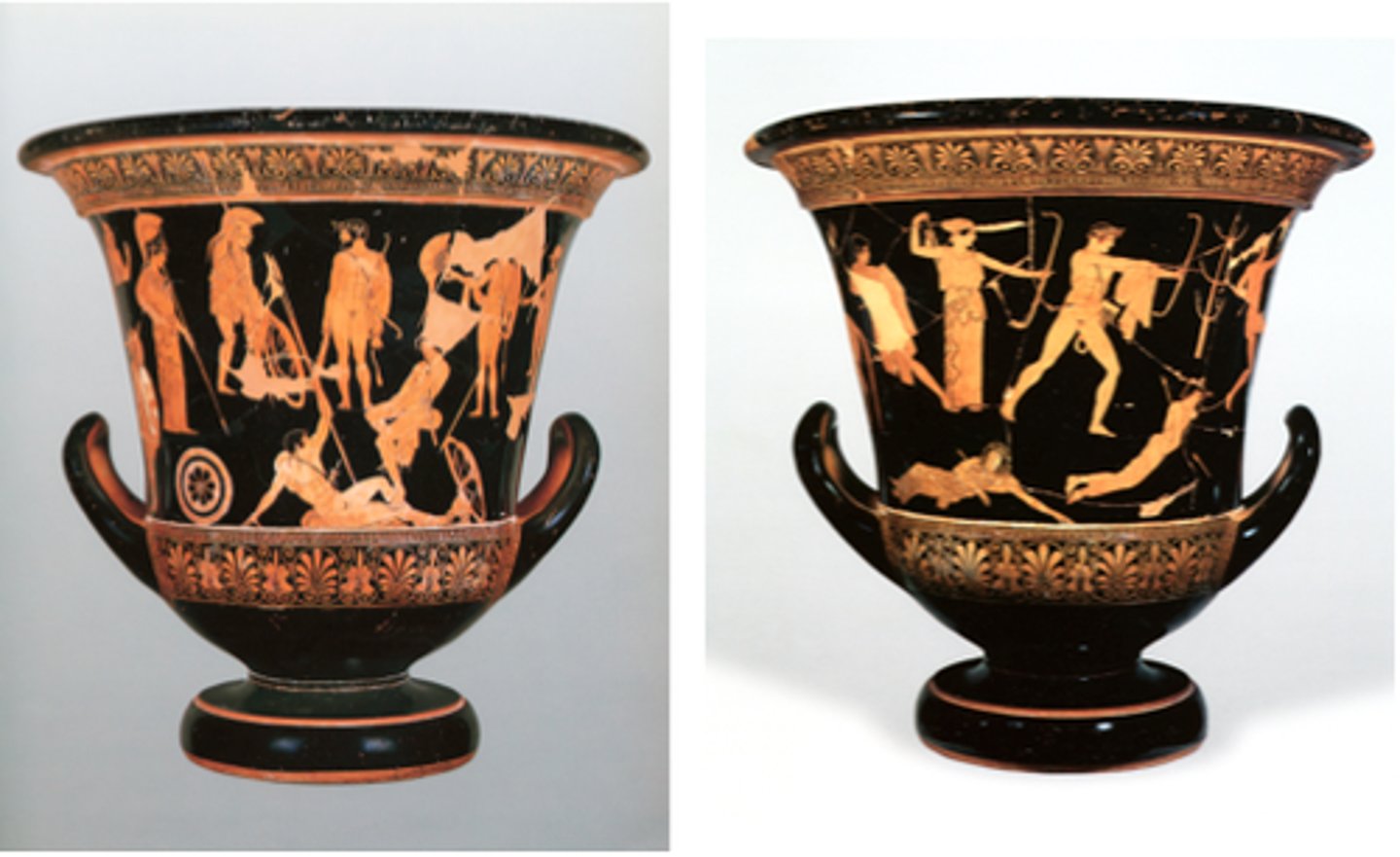
Krater
An ancient Greek wide-mouthed bowl for mixing wine and water.

Metope
a square space between triglyphs in a Doric frieze.
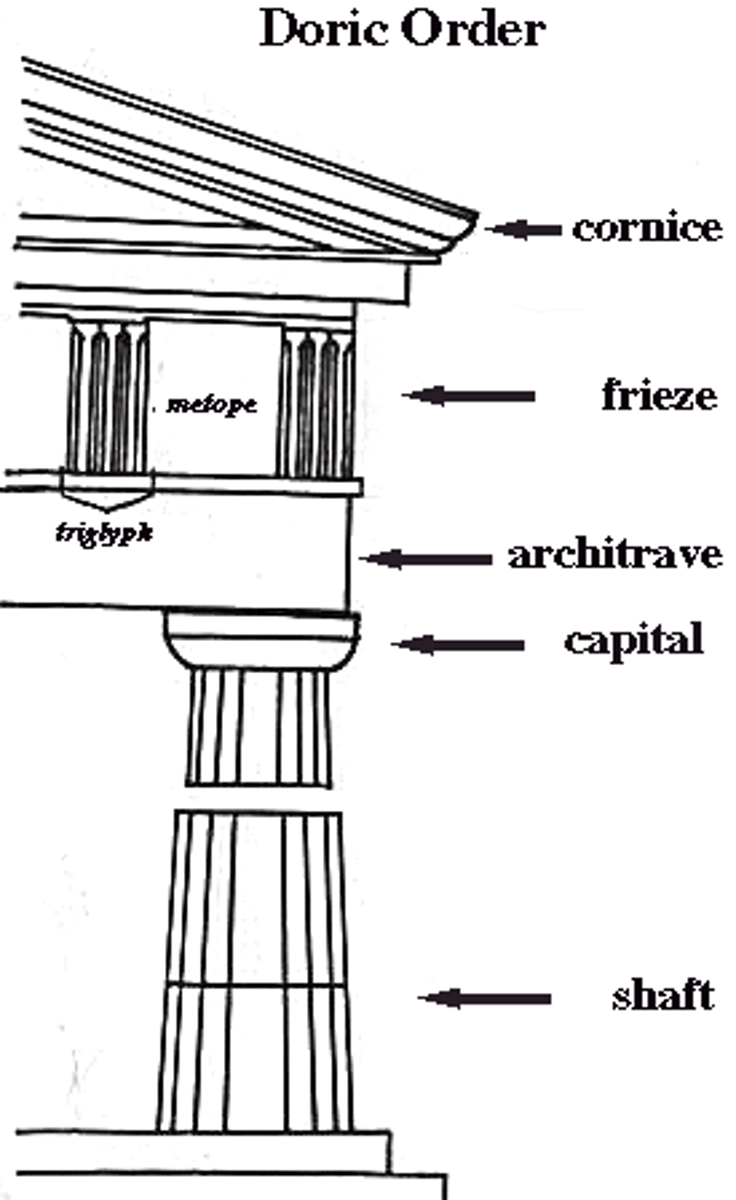
Pediment
the triangular top of a temple that contains sculpture

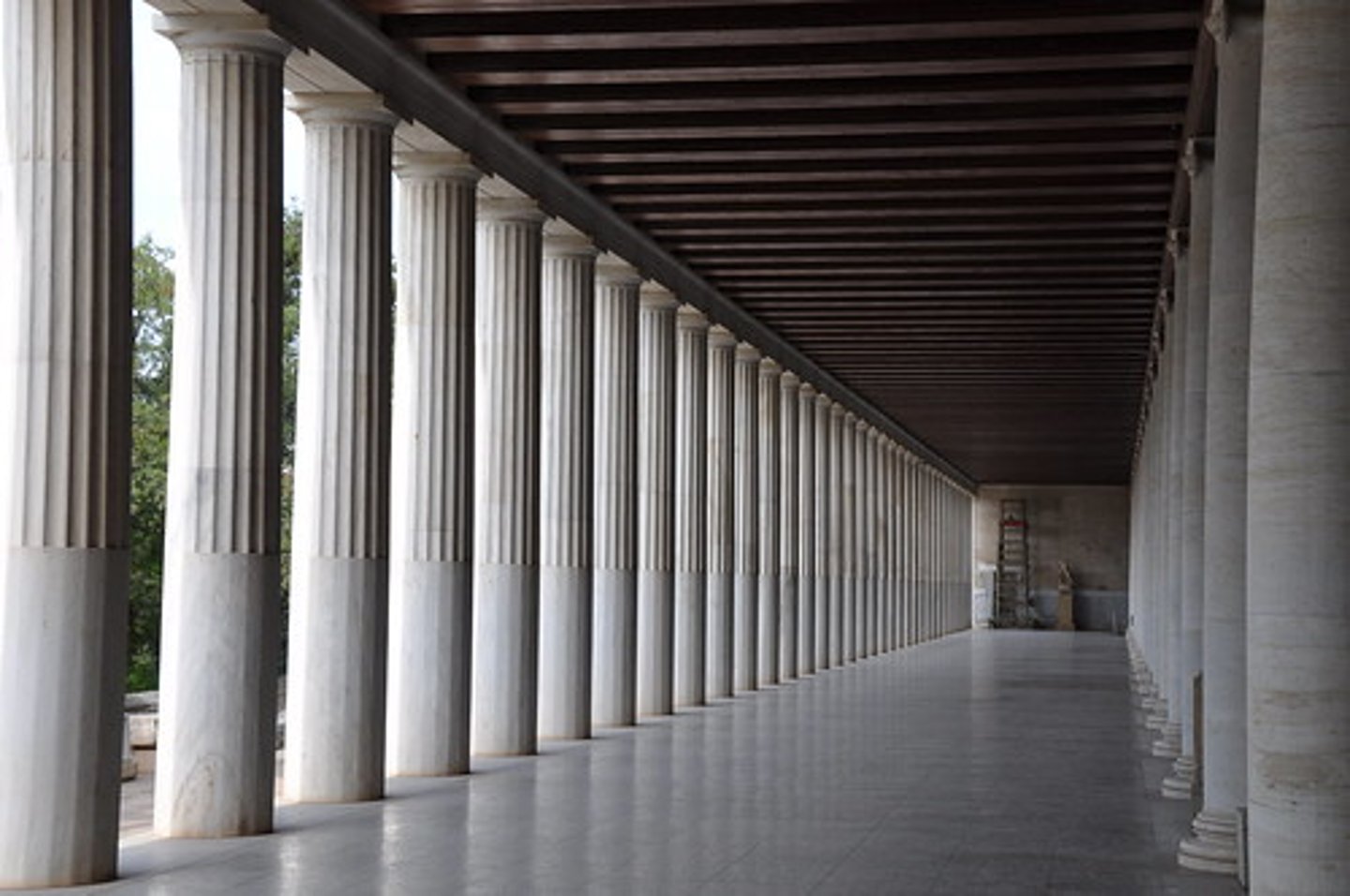
Stoa
an ancient Greek covered walkway having columns on one side and a wall on the other

Tholos
an ancient Greek circular shrine
Essay Question
The work shown is a copy of Doryphoros (Spear Bearer). Describe at least two visual characteristics of this representation of the male nude.
Using specific visual evidence, explain how Doryphoros (Spear Bearer) continued Greek traditions in terms of the representations of the male nude.
Using specific visual evidence, explain how Doryphoros (Spear Bearer) demonstrates changes from Greek traditions in terms of the representations of the male nude.
Using specific contextual evidence, explain why the artist deviated from previous traditions in terms of his choices with his representation of the human body.
