AP Chemistry
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/82
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 9:43 PM on 10/17/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
83 Terms
1
New cards
isotope
element with a different number of neutrons
2
New cards
mass spectrometry
mass of elements
3
New cards
avogadros number
6.022 E23
4
New cards
? L/mol
22.4 L
5
New cards
empirical formula
simplest ratio of the molecules making up a compound
6
New cards
molecular formula
actual formula for a substance
7
New cards
coulombs law
the amount of energy that an electron has depends on its distance from the nucleus of an atom; e=k(q1*q20)/r
8
New cards
ionization energy
amount of energy necessary to remove electrons from an atom (electromagnetic energy exceeds binding energy)
9
New cards
shielding electrons
electrons between a valence electron and the nucleus that decreases the attraction between the nucleus and the valence electron
10
New cards
periodic trend: left to right
periodic trend: atomic radius decreases; protons are added to the nucleus so valence electrons are more strongly attracted
ionization energy increases (protons are added to the nucleus)
ionization energy increases (protons are added to the nucleus)
11
New cards
periodic trend: down a group
periodic trend: atomic radius increases; shells of electrons are added which shield the more distant shells and valence e- get farther away
ionization energy decreases (shells of e- added, each inner shell shields more and reduces the pull on valence e- so they are easier to remove)
ionization energy decreases (shells of e- added, each inner shell shields more and reduces the pull on valence e- so they are easier to remove)
12
New cards
ionic bond
bond between metal and nonmetal; electrons are NOT shared: the cation gives an e- up to the anion
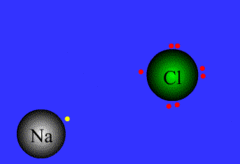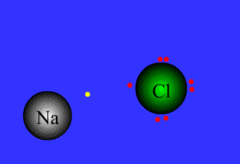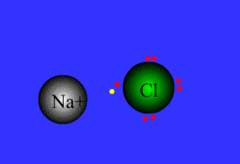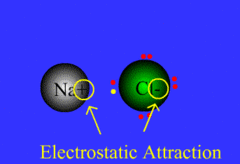
13
New cards
metallic bonding
bond between two metals; sea of electrons that make metals such good conductors; delocalized structure allows for malleability and ductility
14
New cards
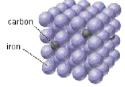
interstitial alloy
metal atoms with vastly different radii combine; ex. steel
15
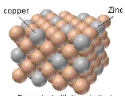
New cards
substitutional alloy
metal atoms with similar radii combine; ex. brass
16
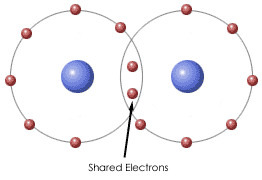
New cards
covalent bonds
bond in which two atoms share electrons; each atom counts the e- as a part of its valence shell
17
New cards
single bonds
one sigma bond, one e- pair; longest bond, least energy
18
New cards
double bonds
one sigma bond, one pi bond; two e- pairs
19
New cards
triple bonds
one sigma bond, two pi bonds; 3 e- pairs; shortest bond, most energy
20
New cards
network covalent bonds
lattice of covalent bonds; network solid (acts similar to one molecule); very hard, high melting/boiling points; poor conductors
21
New cards
the common network solids
SiO2,
22
New cards
doping
the addition of an impurity to an existing lattice
23
New cards
p-doping
create a hole (positively charged) that draws electrons through the substance (add a substance with one LESS valence e-) i.e. si + al
24
New cards
n-doping
add a substance with one MORE valence e- which leaves a free e- to travel freely
i.e. si + p
i.e. si + p
25
New cards
polarity
exists when a molecule has a clustering of negative charge on one side due to unequal sharing of electrons (e- are pulled to the more electronegative side); creates dipoles in molecules
26
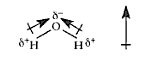
New cards
dipole moment
the measurement of the polarity of a molecule; the unit of measurement is a debye (D)
27
New cards
more polar molecule....
.... larger dipole moment
28
New cards
intermolecular forces (IMFs)
forces that exist between molecules in a covalently bonded substance; not bonds
29
New cards
dipole-dipole forces
the positive end of one polar molecule is attracted to the negative end of another molecule; relatively weak attraction force
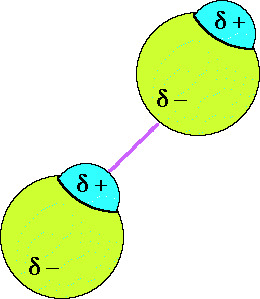
30
New cards
hydrogen bonding
strong IMF between two moelcules; F, O, N; have higher melting and boiling points than molecules with other IMFs
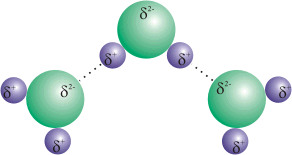
31
New cards
london dispersion forces
IMFs that occur between all molecules; occur because of the random motions of electrons on atoms within molecules to create instantaneous polarities; molecules with more e- will have greater _________________ forces
32
New cards
substances with only london dispersion forces usually...
... are gases at room temp, and boil/melt at extremely low temps
33
New cards
melting & boiling points of a covalent substance is almost always _____________ than that of ionic substances
lower
34
New cards
vapor pressure
the pressure exerted by a vapor over a liquid
35
New cards
resonance structures
structures that occur when it is possible to draw two or more valid lewis electron dot diagrams that have the same number of electron pairs for a molecule or ion
36
New cards
formal charge
used to find which structure is most likely to occur; valence - assigned
37
New cards
linear geometry
sp hybridization
0 lone pairs
ex. BeCl2 & CO2
0 lone pairs
ex. BeCl2 & CO2
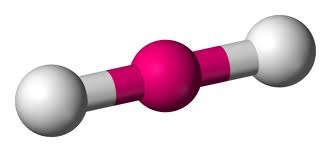
38
New cards
trigonal planar geometry
sp2 hybridization
bond angles 120
0 lone pairs: trigonal planar (three bonds)
1 lone pair: bent (two bonds)
bond angles 120
0 lone pairs: trigonal planar (three bonds)
1 lone pair: bent (two bonds)
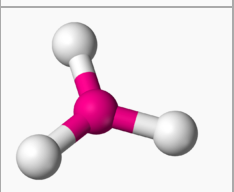
39
New cards
tetrahedral geometry
4 e- pairs, sp3 hybridization
angles 109.5
0 lone pairs: tetrahedral (four bonds) [CH4, NH4+, ClO4-, SO4 2-, PO4 3-]
1 lone pair: trigonal pyramidal (3 bonds) [NH3, PCl3, SO3 2-]
2 lone pairs: bent (2 bonds) [H2O, OF2, NH2-]
angles 109.5
0 lone pairs: tetrahedral (four bonds) [CH4, NH4+, ClO4-, SO4 2-, PO4 3-]
1 lone pair: trigonal pyramidal (3 bonds) [NH3, PCl3, SO3 2-]
2 lone pairs: bent (2 bonds) [H2O, OF2, NH2-]
![4 e- pairs, sp3 hybridization
angles 109.5
0 lone pairs: tetrahedral (four bonds) [CH4, NH4+, ClO4-, SO4 2-, PO4 3-]
1 lone pair: trigonal pyramidal (3 bonds) [NH3, PCl3, SO3 2-]
2 lone pairs: bent (2 bonds) [H2O, OF2, NH2-]](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/c60ffb1d2070420a84feef8c875e0691.jpg)
40
New cards
trigonal bipyramidal geometry
5 e- pairs, sp4 hybridization
0 lone pairs: trigonal bipyramidal (5 bonds) [PCl5, PF5]
1 lone pair: seesaw (4 bonds) [SF4, IF4+]
2 lone pairs: t-shaped (3 bonds) [ClF3, ICl3]
3 lone pairs: linear (2 bonds) [XeF2, I3-]
0 lone pairs: trigonal bipyramidal (5 bonds) [PCl5, PF5]
1 lone pair: seesaw (4 bonds) [SF4, IF4+]
2 lone pairs: t-shaped (3 bonds) [ClF3, ICl3]
3 lone pairs: linear (2 bonds) [XeF2, I3-]
![5 e- pairs, sp4 hybridization
0 lone pairs: trigonal bipyramidal (5 bonds) [PCl5, PF5]
1 lone pair: seesaw (4 bonds) [SF4, IF4+]
2 lone pairs: t-shaped (3 bonds) [ClF3, ICl3]
3 lone pairs: linear (2 bonds) [XeF2, I3-]](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/eccf6a9661fb4d658c8702446d94c12d.png)
41
New cards
octahedral geometry
6 e- pairs, sp5 hybridization
0 lone pairs: octahedral (6 bonds) [SF6]
1 lone pair: square pyramidal (5 bonds) [BrF5, IF5]
2 lone pairs: square planar (4 bonds) [XeF4]
0 lone pairs: octahedral (6 bonds) [SF6]
1 lone pair: square pyramidal (5 bonds) [BrF5, IF5]
2 lone pairs: square planar (4 bonds) [XeF4]
![6 e- pairs, sp5 hybridization
0 lone pairs: octahedral (6 bonds) [SF6]
1 lone pair: square pyramidal (5 bonds) [BrF5, IF5]
2 lone pairs: square planar (4 bonds) [XeF4]](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/2da31ca3a2754f7c9137b4007fd625d9.png)
42
New cards
maxwell-boltzmann diagrams
shows the range of velocities for molecules of a gas
43
New cards
effusion
the rate at which a gas will escape from a container through microscopic holes in the surface of the container
44
New cards
mole fraction
moles of substance/total moles in solution
45
New cards
dissociation
when ionic substances break up into ions into solution
46
New cards
electrolytes
free ions in solution that conduct electricity
47
New cards
paper chromatography
the separation of a mixture by passing it through a medium in which the components of the solution move at different rates
48
New cards
retention factor
stronger the attraction between the solute and the solvent front is, the larger the Rf value will be

49
New cards
column chromatography
a column is packed with stationary substance, then the solution to be separated (analyte) is injected into the column where it adheres to the stationary phase, then the eluent solution is injected into the column. as the eluent solution passes through the stationary phase the analyte molecules will be attracted to it with varying degrees of strength based on polarity
50
New cards
distillation
the process that separates the substances in a solution based on their boiling points
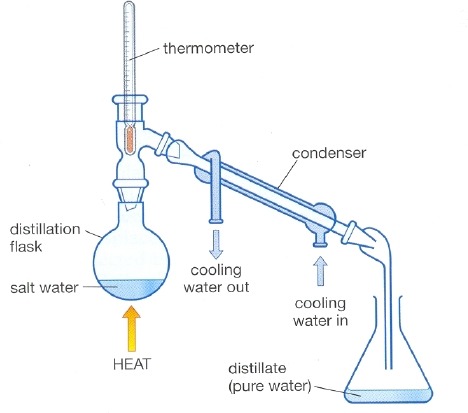
51
New cards
precipitation reaction
a reaction in which an insoluble substance (salt) forms and separates from the solution
52
New cards
net ionic equation
an equation for a reaction in solution showing only those particles that are directly involved in the chemical change
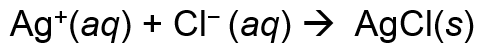
53
New cards
limiting reactant
the substance that controls the quantity of product that can form in a chemical reaction; moles of each reactant divided by moles used in reaction
54
New cards
gravimetric analysis
a type of quantitative analysis in which the amount of a species in a material is determined by converting the species to a precipitate that can be isolated completely and weighed
55
New cards
when bonds are formed
...energy is released
56
New cards
when bonds are broken
...energy is absorbed
57
New cards
exothermic
products have stronger bonds than the reactants; heat is released, - ΔH
58
New cards
endothermic
reactants have stronger bonds than the products; heat is absorbed, + ΔH
59
New cards
activation energy
the minimum amount of energy required to start a chemical reaction
60
New cards
catalyst
substance that speeds up a reaction by reducing the activation energy required by the reaction; provides an alternate reaction pathway; no effect on equilibrium conditions
61
New cards
oxidation number: H
+1
62
New cards
entropy
ΔS; a measure of the randomness or disorder of the system
63
New cards
enthalpy
ΔH; heat of a system at constant pressure
64
New cards
Gibbs free-energy
ΔG; a measure of whether or not a process will proceed without the input of outside energy
∆G=∆H-T∆S (T in degrees Kelvin)
when ΔG=0, the reaction is at equilibrium
∆G=∆H-T∆S (T in degrees Kelvin)
when ΔG=0, the reaction is at equilibrium
65
New cards
spontaneous
thermodynamically favored; -ΔG
66
New cards
nonspontaneous
thermodynamically unfavored; +ΔG
67
New cards
Arrhenius acids
a substance that ionizes in water and produces hydrogen ions
68
New cards
Arrhenius bases
a substance that ionizes in water and produces hydroxide ions
69
New cards
Brønsted-Lowry acids
a substance that is capable of donating a proton
70
New cards
Brønsted-Lowry bases
a substance that is capable of accepting a proton
71
New cards
pH
-log [H+]
72
New cards
pOH
-log [OH-]
73
New cards
pKa
-log [Ka]
74
New cards
pKb
-log [Kb]
75
New cards
amphoteric
a substance that can act as both an acid and a base; ex. H2O
76
New cards
strong acids
dissociate completely in water; reaction goes to completion and never reaches equilibrium
77
New cards
weak acid
most of the acid molecules remain in solution and very few dissociate
78
New cards
percent dissociation
the ratio of the amount of a substance that is dissociated at equilibrium to the initial concentration of the substance in a solution, multiplied by 100
79
New cards
oxoacids
acids that contain oxygen; the more oxygens, the stronger the acid
80
New cards
polyprotic acids
acids that can donate more than one H+
81
New cards
Kw
1.0x10^-14
82
New cards
henderson hasselbach
pH = pKa + log([A-]/[HA])
83
New cards
buffers
weak acids or bases that can react with strong acids or bases to prevent sharp, sudden changes in pH