section 2 - Cell structure
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 11:32 AM on 5/7/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
1
New cards
magnification
how many times larger an image is when compared to the object
magnification = image / actual
magnification = image / actual
2
New cards
resolution
the smallest distance between two objects under the microscope that they are distinguisable
3
New cards
cell fractionation
* before place cells in a buffer with same water potential, same pH and a cool temperature
* then blend cells in step called homogentation, remove large pieces of debris
* then slowly spin cells in centrifuge in step called ultracentrifugation
* collect the heaviest collected organelle (nucleus). collect supernatant and then repeat spinning supernatant until all the organelles are collected
* then blend cells in step called homogentation, remove large pieces of debris
* then slowly spin cells in centrifuge in step called ultracentrifugation
* collect the heaviest collected organelle (nucleus). collect supernatant and then repeat spinning supernatant until all the organelles are collected
4
New cards
order for cell fractionation
→nucleus and whole cells
→lysosomes and mitochondria
→microsomes
→ribosomes and viruses
→lysosomes and mitochondria
→microsomes
→ribosomes and viruses
5
New cards
the nucleus
* nuclear envelope
→double membrane surrounding the nucleus controlling the entry and exit of substances. often extension of the rough endoplasmic reticulum, with ribosomes
* nuclear pores
→around 3000 in a nuclear envelope, control the entry and exit of very large molecules (messenger RNA)
* nucleoplasm
→ jelly like substance which occupies majority of the nucleus
* chromosomes
→linear DNA
* nucleolus
→small sphere where the manufacture of messenger RNA is synthesised
→double membrane surrounding the nucleus controlling the entry and exit of substances. often extension of the rough endoplasmic reticulum, with ribosomes
* nuclear pores
→around 3000 in a nuclear envelope, control the entry and exit of very large molecules (messenger RNA)
* nucleoplasm
→ jelly like substance which occupies majority of the nucleus
* chromosomes
→linear DNA
* nucleolus
→small sphere where the manufacture of messenger RNA is synthesised
6
New cards
mitochondrion
* surrounded by a double membrane to control entry and exit of the material. folded into cristae
* cristae is an extension of membrane to provide large surface area for the use of enzymes
* matrix makes up remainder of mitochondria. contains enzymes, DNA, proteins ,lipids
* mitochondria are used to produce energy aerobically. they produce ATP which is used in metabolic reactions and other important processes around the body
* cristae is an extension of membrane to provide large surface area for the use of enzymes
* matrix makes up remainder of mitochondria. contains enzymes, DNA, proteins ,lipids
* mitochondria are used to produce energy aerobically. they produce ATP which is used in metabolic reactions and other important processes around the body
7
New cards
chloroplasts
* chloroplast double membrane which is highly selective of which substances it will allow in and out.
* chloroplasts contains stacks of thylakoids called grana. these contain the chlorophyll and have bridges connecting the stacks. first stage of photosynthesis takes place here (light absorption)
* stroma is the matrix filled fluid which is where second stage of photosynthesis occurs (synthesis of sugars)
* has DNA and RNA to quickly make proteins for photosynthesis
* large surface area in grana so lots of light can be absorbed
* chloroplasts contains stacks of thylakoids called grana. these contain the chlorophyll and have bridges connecting the stacks. first stage of photosynthesis takes place here (light absorption)
* stroma is the matrix filled fluid which is where second stage of photosynthesis occurs (synthesis of sugars)
* has DNA and RNA to quickly make proteins for photosynthesis
* large surface area in grana so lots of light can be absorbed
8
New cards
Endoplasmic reticulum
* 3D sheet continuous from the nuclear envelope
* smooth endoplasmic reticulum
* no ribosomes
* synthesise store and transport lipids
* synthesise store and transport carbohydrates
* rough endoplasmic reticulum
* has ribosomes
* large surface area for glycoprotein synthesis and protein synthesis
* smooth endoplasmic reticulum
* no ribosomes
* synthesise store and transport lipids
* synthesise store and transport carbohydrates
* rough endoplasmic reticulum
* has ribosomes
* large surface area for glycoprotein synthesis and protein synthesis
9
New cards
Golgi appartatus
* occurs in all eukaryotic cells
* functions
* add carbs to proteins to form glycoproteins
* produce secretory enzymes such as enzymes secreted by the pancreas
* transport modify and store lipids
* form lysosomes
* structure
* stack of membranes that make up flattened stacks
* small round hollow vesicles
* functions
* add carbs to proteins to form glycoproteins
* produce secretory enzymes such as enzymes secreted by the pancreas
* transport modify and store lipids
* form lysosomes
* structure
* stack of membranes that make up flattened stacks
* small round hollow vesicles
10
New cards
lysosomes
* hydrolysis material ingested by the phagocytic cells
* releases enzymes
* completely breaks down cells once they’ve been destroyed
* releases enzymes
* completely breaks down cells once they’ve been destroyed
11
New cards
ribosomes
* free or connected to the RER
* 80s in eukaryotes
* 70s in prokaryotes
* 80s in eukaryotes
* 70s in prokaryotes
12
New cards
cell wall
* consist of polysaccharides such as cellulose
* thin layer called lamella which marks the boundary between adjacent cells
* provide strength to cell and plant as a whole
* allow water to pass in through cell wall
* thin layer called lamella which marks the boundary between adjacent cells
* provide strength to cell and plant as a whole
* allow water to pass in through cell wall
13
New cards
vacuole
* fluid filled sack bounded by a single membrane
* sugar and amino acid storage
* pigments are attractive to pollenating insects
* sugar and amino acid storage
* pigments are attractive to pollenating insects
14
New cards
cell specialisation
* tissues
* group of similar cells working together to perform a similar
* epithelial tissues are in animals and they line surfaces of organs.
* organs
* group of similar tissues together to form an organ to perform a specific function
* examples:
* muscles to turn food
* spongy mesophyll for gaseous diffusion
* xylem to transport water an ions
* phloem to transport organic material
* organ systems
* organs that work together as a single unit
* examples:
* digestive systems to digest and process food
* respiratory system for breathing and gas exchange
* circulatory system to circulate blood
\
* group of similar cells working together to perform a similar
* epithelial tissues are in animals and they line surfaces of organs.
* organs
* group of similar tissues together to form an organ to perform a specific function
* examples:
* muscles to turn food
* spongy mesophyll for gaseous diffusion
* xylem to transport water an ions
* phloem to transport organic material
* organ systems
* organs that work together as a single unit
* examples:
* digestive systems to digest and process food
* respiratory system for breathing and gas exchange
* circulatory system to circulate blood
\
15
New cards
prokaryotic cells
* cell wall and capsule are made up of mixture of polypeptides and polysaccharides
* cell wall is a physical barrier that excludes certain substances from entry
* capsule protects bacteria from other cells and sticks other bacteria cells together in order to gain more protection
* cell surface membrane controls the entry and exit of substances from between cell and external environment
* circular DNA contains genetic information for replication and cells and coding for proteins
* plasmids are small circular sections of DNA containing gene that aid bacteria to survive in certain conditions
* flagella for species in need to move. some species may have more than one.
* cell wall is a physical barrier that excludes certain substances from entry
* capsule protects bacteria from other cells and sticks other bacteria cells together in order to gain more protection
* cell surface membrane controls the entry and exit of substances from between cell and external environment
* circular DNA contains genetic information for replication and cells and coding for proteins
* plasmids are small circular sections of DNA containing gene that aid bacteria to survive in certain conditions
* flagella for species in need to move. some species may have more than one.
16
New cards
virus structure drawing
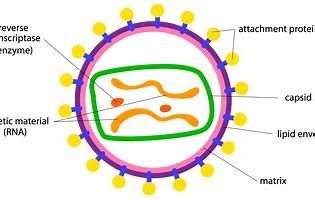
17
New cards
main features of virus molecule
* capsid - protective protein coat to provide protection for genetic material
* genetic material - virus consists of a core which contains RNA and DNA. has a reduced genome and only produces the proteins which it cannot obtain for host cells
* attachment proteins - allows the virus to attach to the host cell
* genetic material - virus consists of a core which contains RNA and DNA. has a reduced genome and only produces the proteins which it cannot obtain for host cells
* attachment proteins - allows the virus to attach to the host cell