diagrams
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/108
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 1:22 AM on 11/4/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
109 Terms
1
New cards
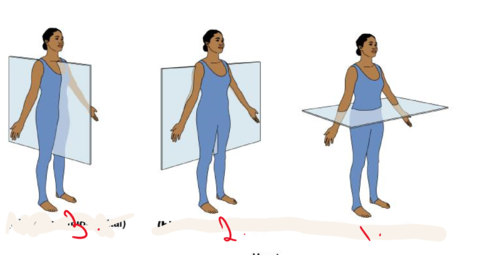
1. transverse plane
2. Frontal ( coronal) plane
3. median ( midsagittal)
2. Frontal ( coronal) plane
3. median ( midsagittal)
anatomical planes
1.
2.
3
1.
2.
3
2
New cards
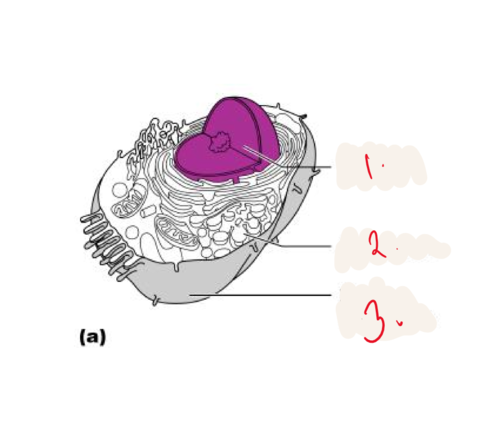
1. nucleus
2. cytoplasm
3. plasma membrane
2. cytoplasm
3. plasma membrane
Cell diagram
1.
2.
3.
1.
2.
3.
3
New cards
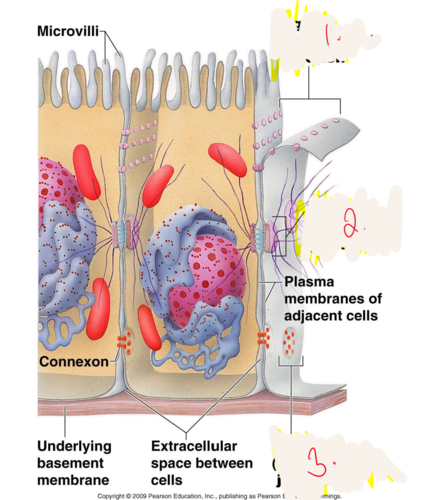
1. tight junctions
2. desmosome
3. tight junctions
2. desmosome
3. tight junctions
1.
2.
3.
2.
3.
4
New cards
simple columnar epithelium
Made up of a single layer of tall cells that fit closely together
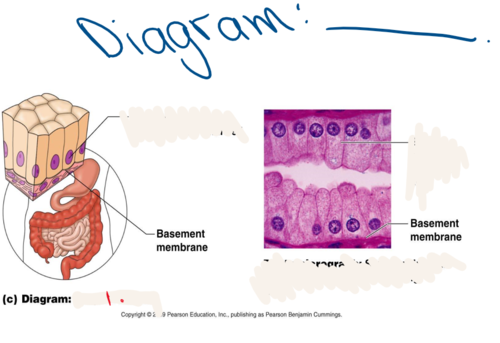
5
New cards
simple squamous epithelium
single layer of flattened cells
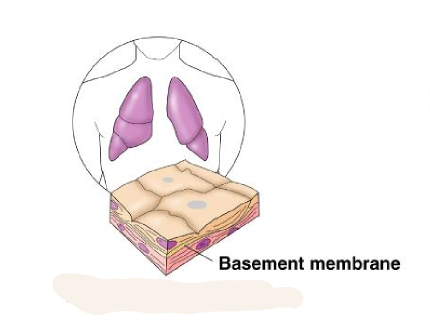
6
New cards
simple cuboidal
single layer of cube shaped cells
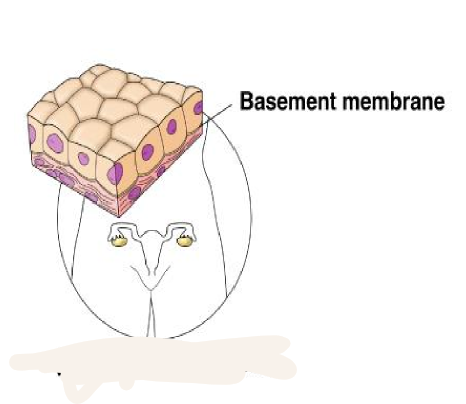
7
New cards
pseudostratified columnar epithelium
tissue that consists of a single layer of irregularly shaped and sized cells that give the appearance of multiple layers; found in ducts of certain glands and the upper respiratory tract
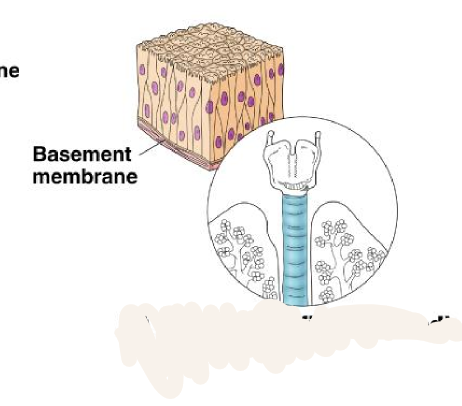
8
New cards
straified squamous
thick membrane
protects underlying tissues in areas subjected to abrasion
protects underlying tissues in areas subjected to abrasion
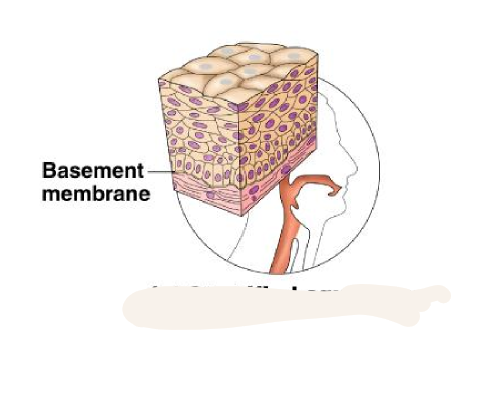
9
New cards
Transitions striated
shapes of cells that sketch lines organ of the urinary system
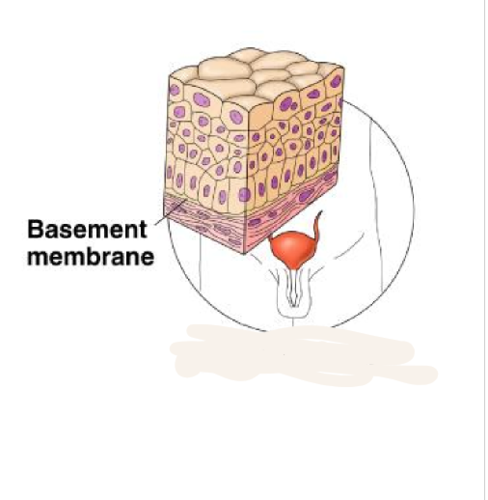
10
New cards
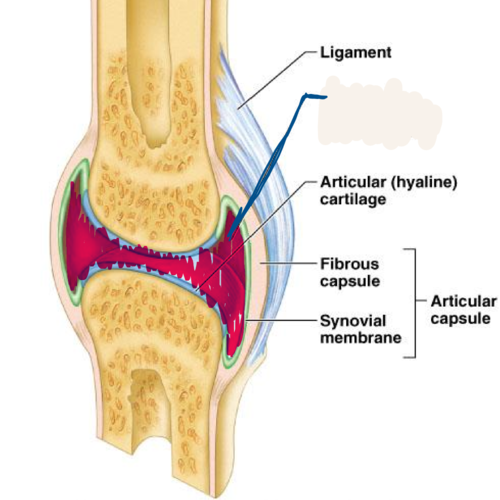
articular capsule
sleevelike structure around a synovical joint composed of a fibrous capsule and synovial membrane
this is called
this is called
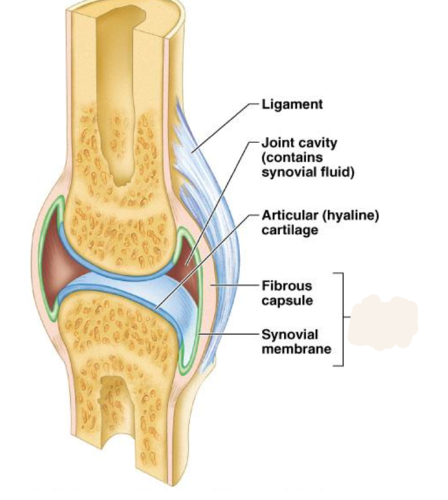
11
New cards
synovial membrane
membrane lining the capsule of a joint
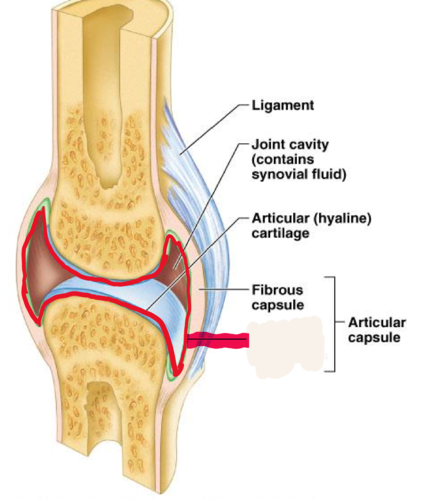
12
New cards
joint cavity
contains synovial fluid is called
13
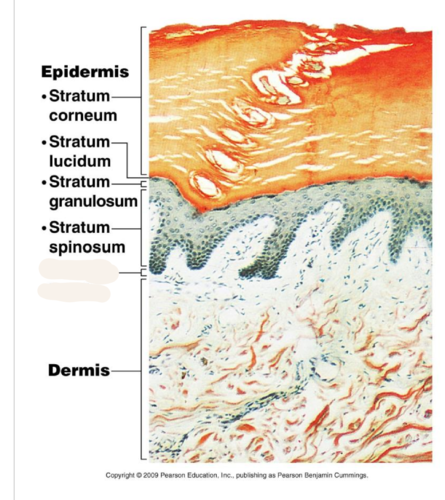
New cards
stratum basale
deepest layer of epidermis
14
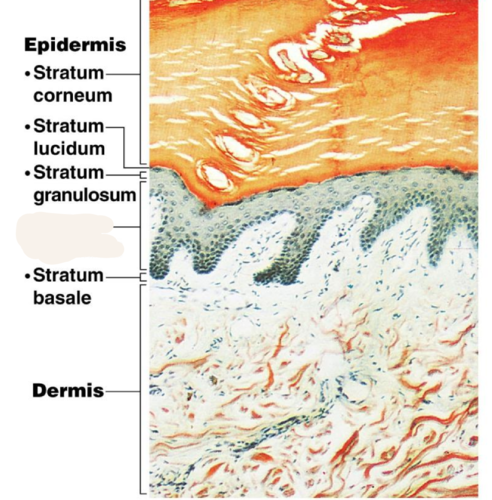
New cards
stratum spinosum
a layer of the epidermis that provides strength and flexibility to the skin
is called
is called
15
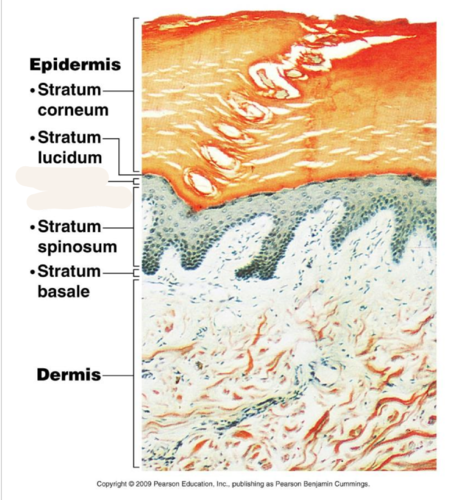
New cards
stratum granulosum (granular layer)
Layer of epidermis composed of cells that look like granules and are filled with keratin; replaces cells shed from stratum corneum
16
New cards
Stratum lucidum (clear layer)
Only in thick skin
Thin, translucent band superficial to the stratum granulosum
A few rows of flat, dead keratinocytes
Thin, translucent band superficial to the stratum granulosum
A few rows of flat, dead keratinocytes
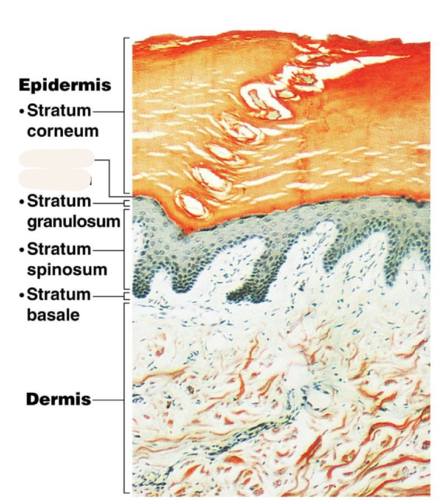
17
New cards
stratum corneum
outermost layer of epidermis
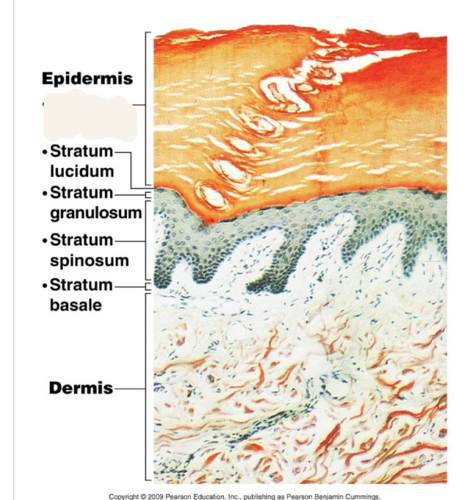
18
New cards
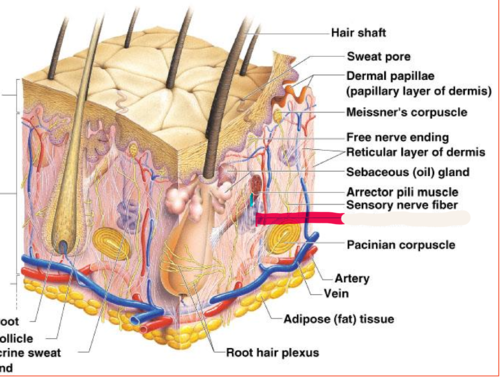
arrector pili muscle
An involuntary muscle fiber attached to the underside & base of the hair follicle
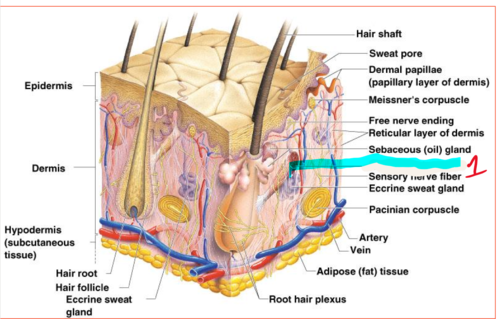
19
New cards
Meissner's corpuscles
sensitive touch receptors in the dermis
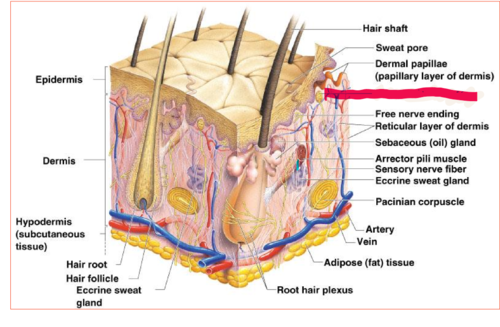
20
New cards
eccrine sweat glands
found in palms, soles of the feet, and forehead
21
New cards
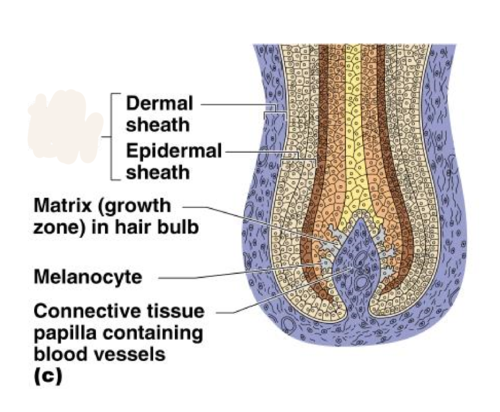
Melanocytes
cells that produce melanin
22
New cards
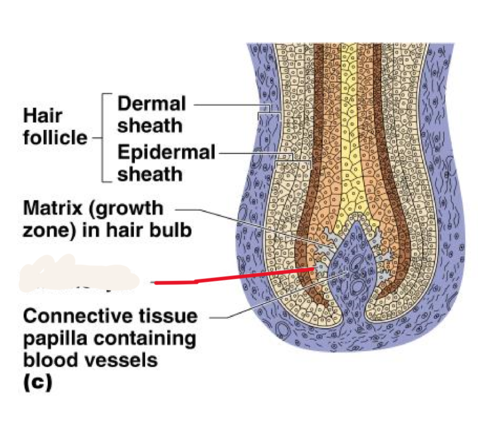
hair follicle
sac within which each hair grows
23
New cards
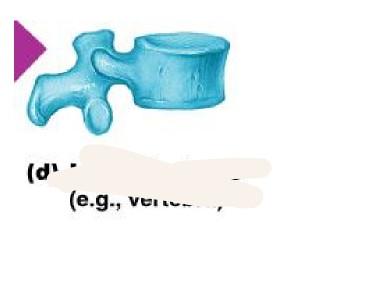
irregular bones
bones of the vertebrae and face
24
New cards
flat bones
bones of the ribs, shoulder blades, pelvis, and skull
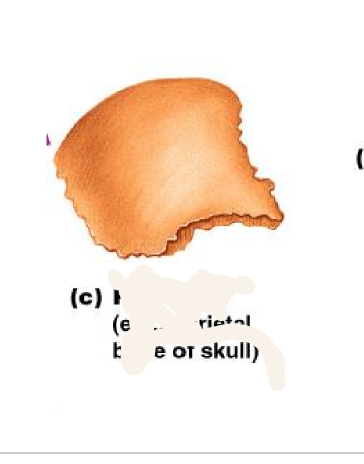
25
New cards
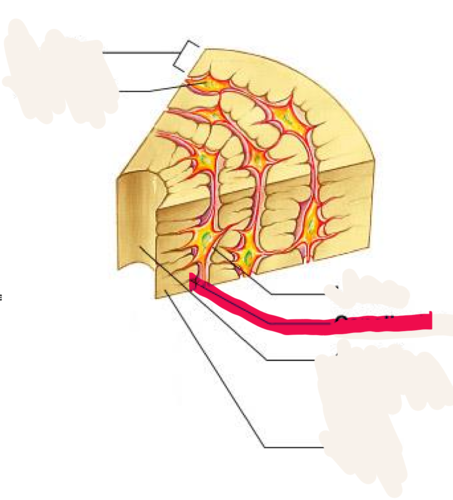
Central (Haversian) Canal
opening in the center of an osteon, carries blood vessels and nerves
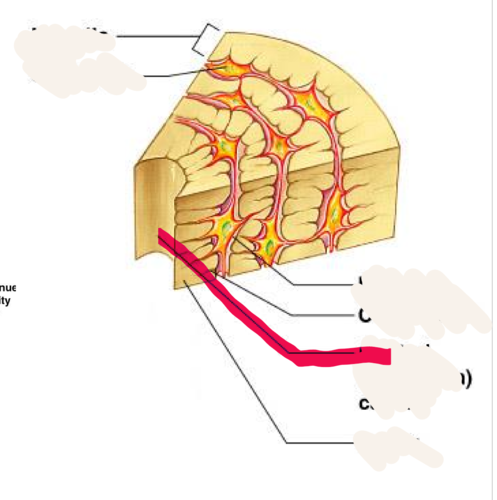
26
New cards
Canaliculus/canaliculi
tiny canals radiating outward from central canal
27
New cards
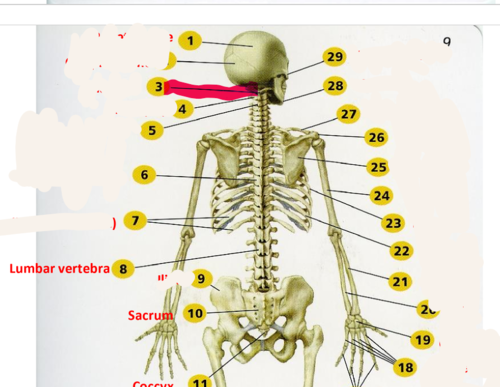
Axis (C2)
second cervical vertebrae
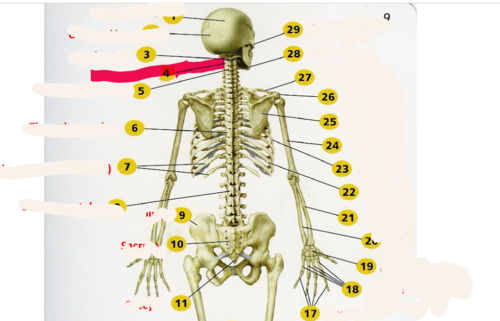
28
New cards
Atlas (C1)
supports the head
29
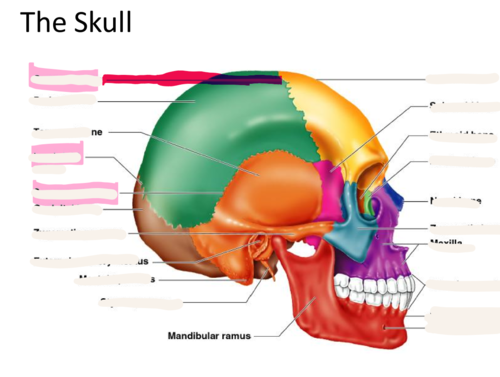
New cards
coronal suture
the suture between the parietal and frontal bones of the skull
30
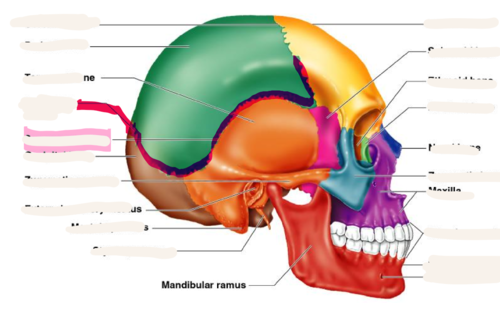
New cards
lambdoid suture
between parietal bones and occipital bone
31
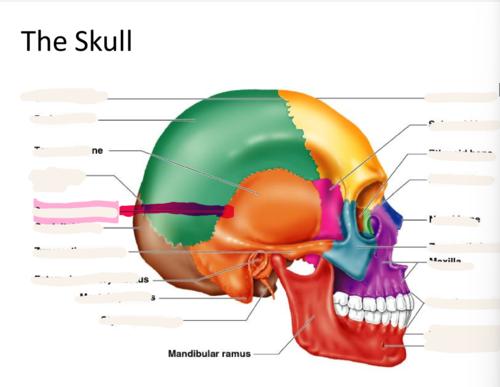
New cards
squamous suture
Between parietal and temporal bones
32
New cards
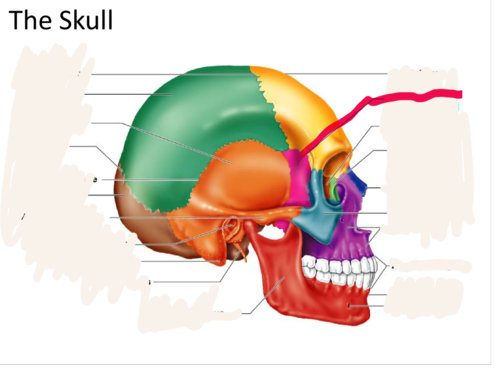
sphenoid bone
forms part of the base of the skull and parts of the floor and sides of the orbit
33
New cards
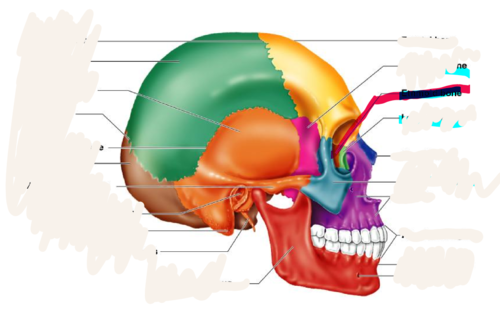
ethmoid bone
forms part of the posterior portion of the nose, the orbit, and the floor of the cranium
34
New cards
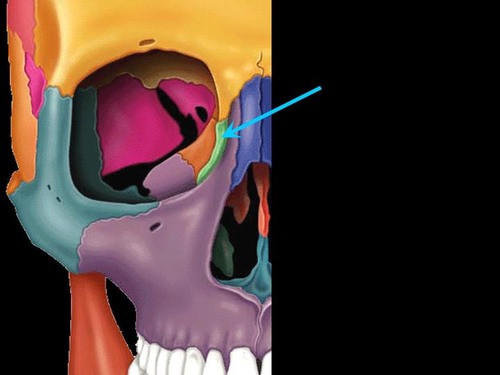
lacrimal bone
small fragile bone making up part of the front inner walls of each eye socket and providing room for the passage of the lacrimal ducts
35
New cards
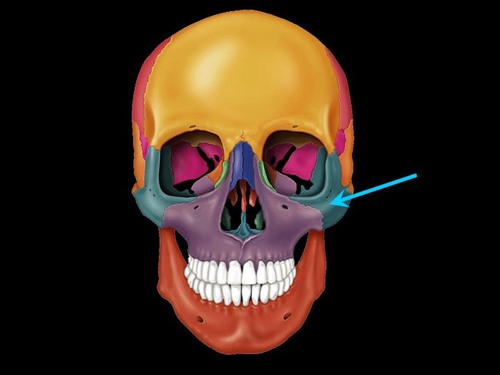
Zygomatic bone
cheek bone
36
New cards
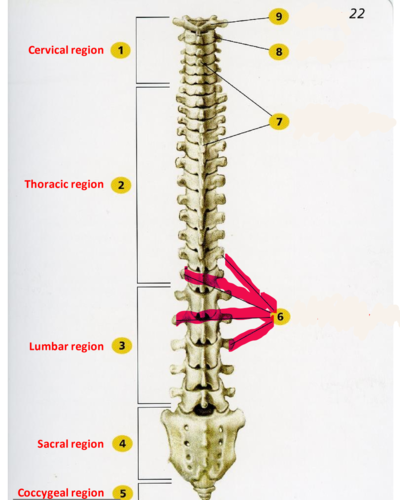
Transverse process of vertebra
forms joint with ribs in thoracic region, site for muscle attachment in lumbar region
37
New cards
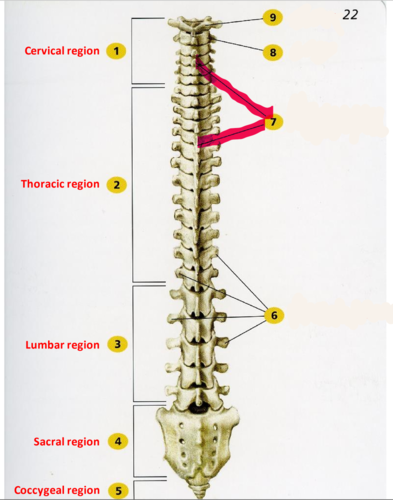
spinous process
sharp, slender projection
38
New cards
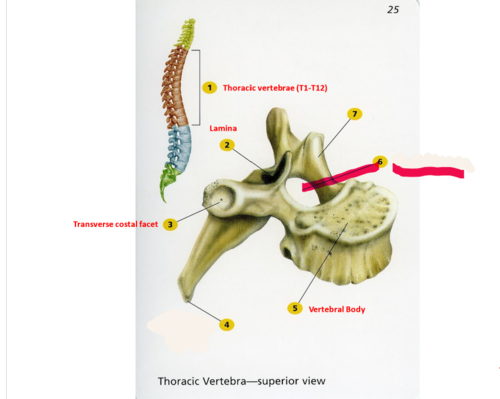
vertebral foramen
canal through which spinal cord passes
39
New cards
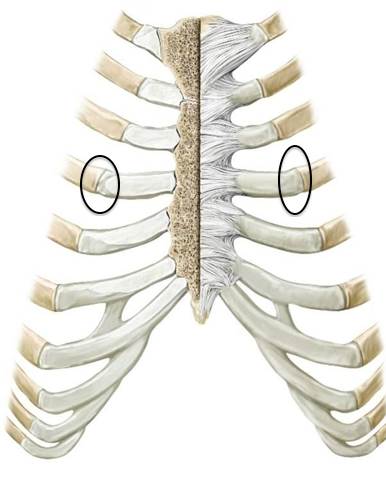
costochondral joint
where the cartilage meets the rib
40
New cards
sternoclavicular joint
Articulation between the clavicle and the sternum
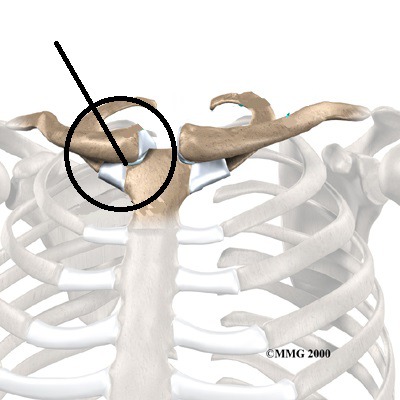
41
New cards
Acromion
Outward extension of the shoulder blade forming the point of the shoulder.
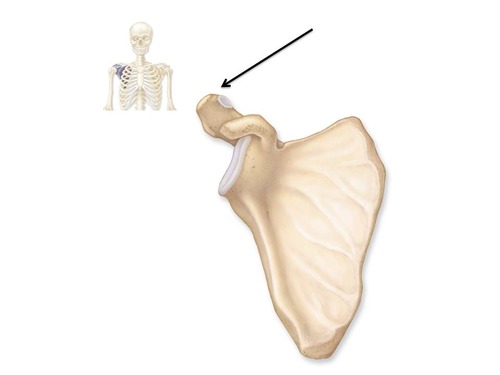
42
New cards
coracoid process
process above the glenoid cavity that permits muscle attachment
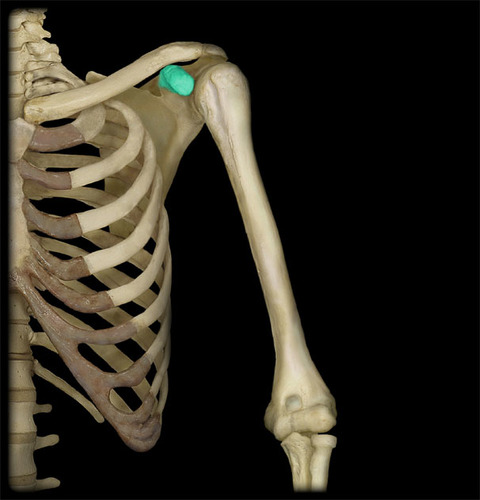
43
New cards
glenoid cavity
socket in scapular that receives head of humerus
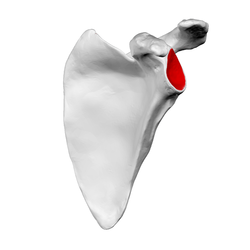
44
New cards
acrominoclavicular joint
the area where the clavicle and scapula connect
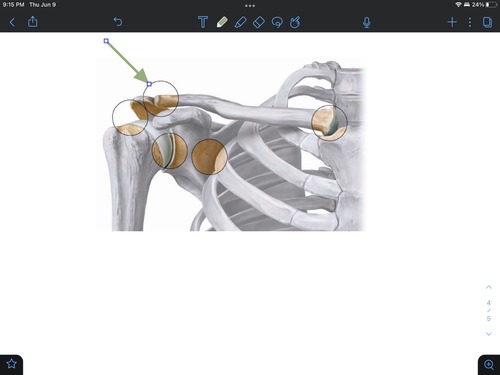
45
New cards
glenoid fossa of scapula
articulates with the head of the humerus
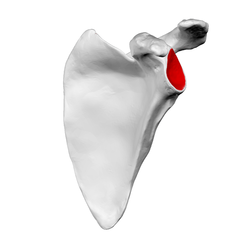
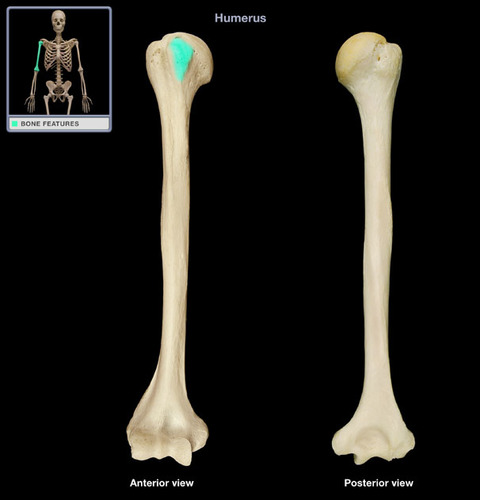
46
New cards
lesser tubercle
insertion of subscapularis muscle
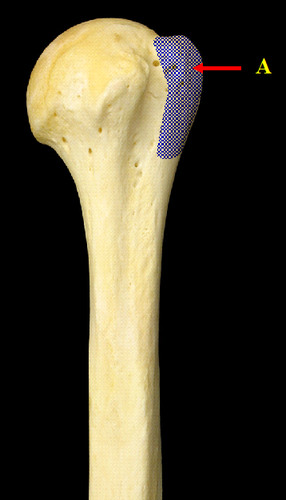
47
New cards
greater tubercle
Large lateral prominence; site of the attachment of rotator cuff muscles
48
New cards
radial fossa of humerus
anterior depression that receives the radial head with flexed forearm
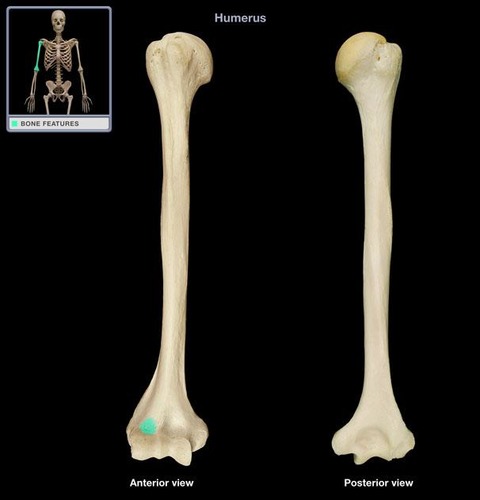
49
New cards
trochlear notch
articulates with trochlea of humerus
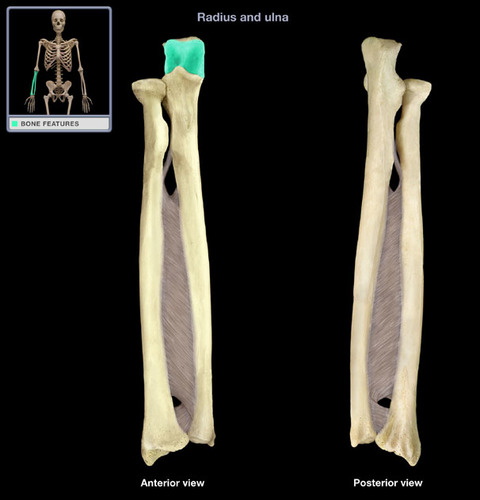
50
New cards
proximal radioulnar joint
head of radius articulates with radial notch of ulna
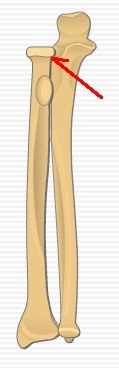
51
New cards
radial tuberosity
Name this specific part of the radius.
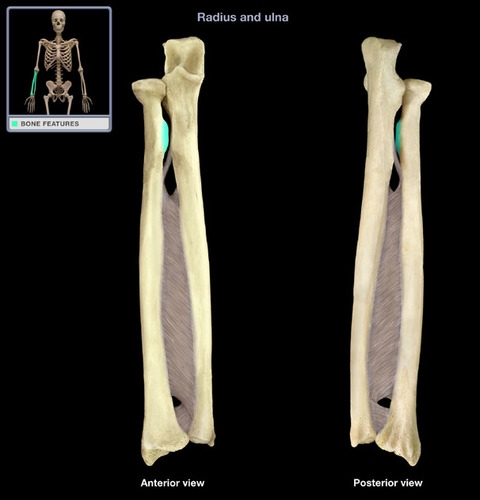
52
New cards
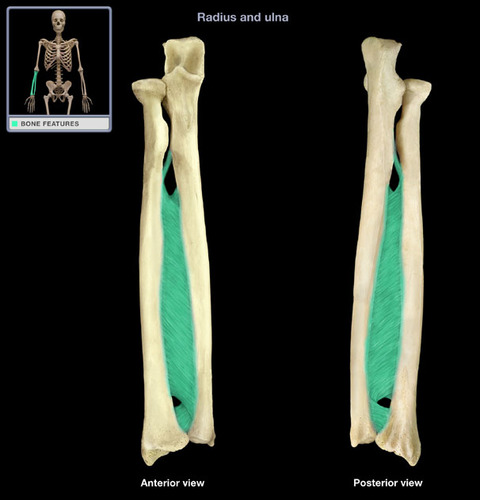
interosseous membrane
connects the tibia and fibula
53
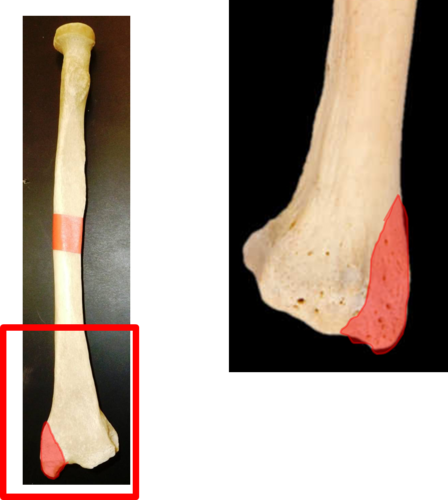
New cards
syloid process of radius
insertion of brachioradialis
54
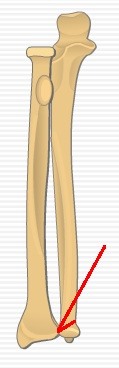
New cards
distal radioulnar joint
head of ulna articulates with ulnar notch of radius
55
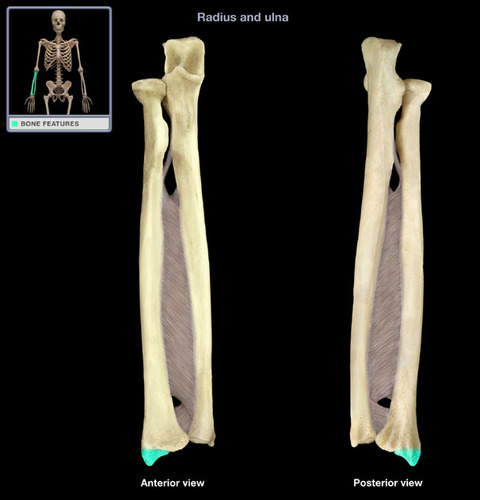
New cards
styloid process of ulna
Name the structure.
56
New cards
coronoid fossa
anterior depression that receives the coronoid process of the ulna during forearm flexion
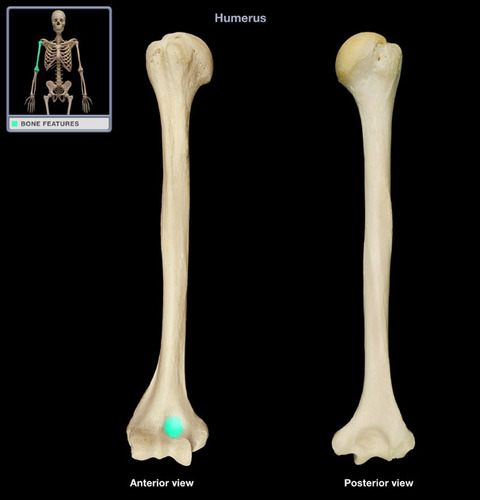
57
New cards
illiac crest
the upper curved edge of the ilium; has anterior (anterior iliac spine) and posterior projections
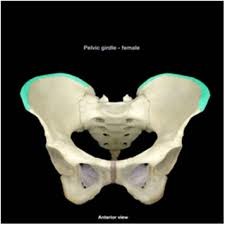
58
New cards
intercondylar eminence
irregular projection located between the two condyles
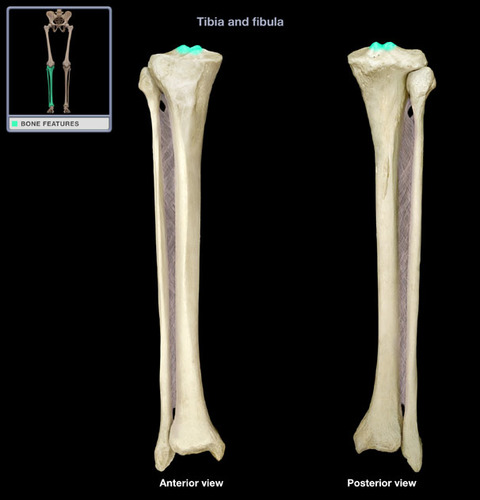
59
New cards
closes and protrudes lips is called the
orbicularis oris
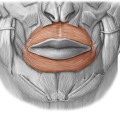
60
New cards
compresses cheek ( as in sucking), holds food between teeth during chewing. THis is called
buccinator
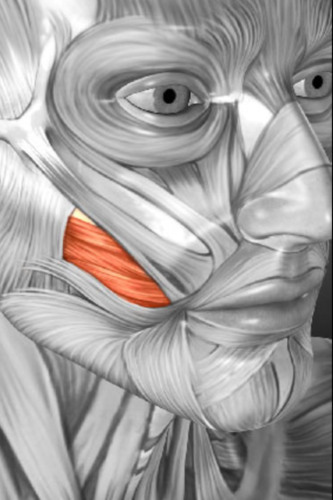
61
New cards
blinks and closes eyes, squints and winks
orbicularis oculi
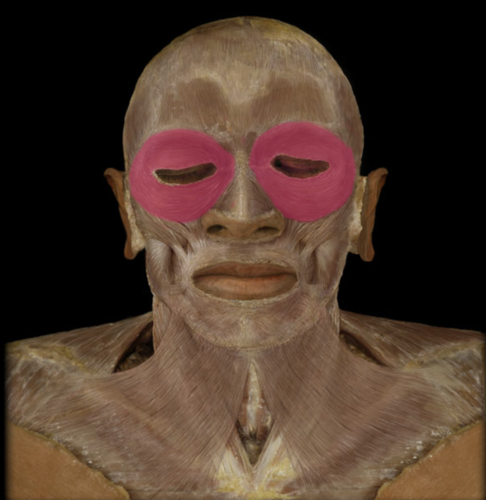
62
New cards
extends from the corner of the mouth to the cheekbone
zygomaticus
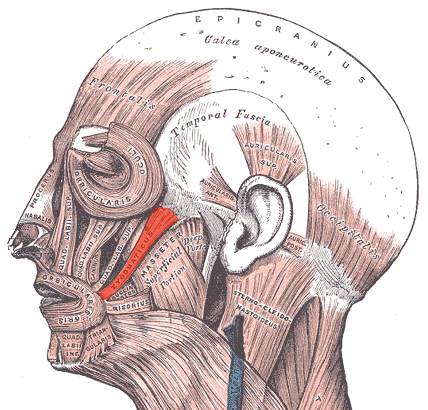
63
New cards
PULLS THE CORNERS OF THE MOUTH INFERIORLY
PRODUCING A DONWARD SAF OF THE MOUTH
PRODUCING A DONWARD SAF OF THE MOUTH
temporalis
64
New cards
Frontalis
muscle of the forehead that moves the forehead skin and eyebrows
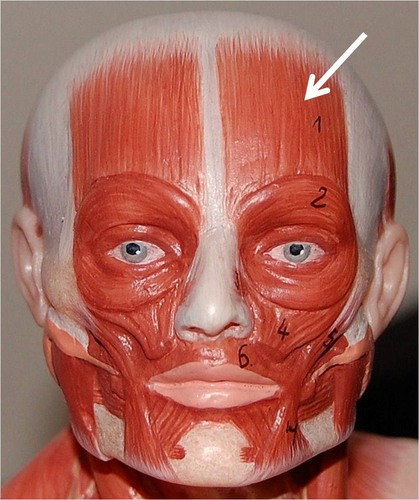
65
New cards
cranial aponeurosis
connects frontalis and occipitalis
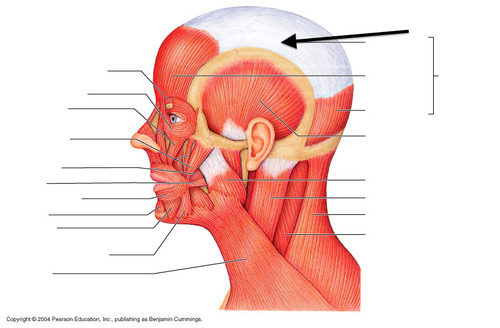
66
New cards
rectus abdominis
this type of muscle is called the
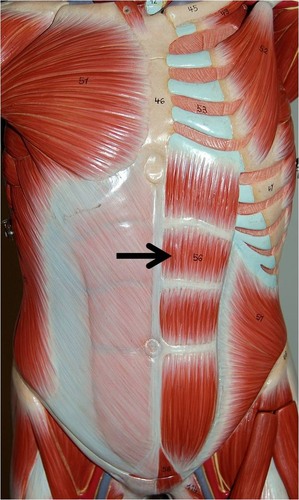
67
New cards
transversus abdominis
compresses abdomen, this is called the
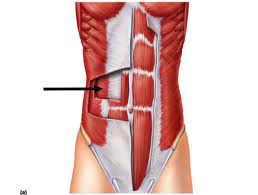
68
New cards
internal oblique
tenses abdominal wall and compresses abdominal contents. this is called
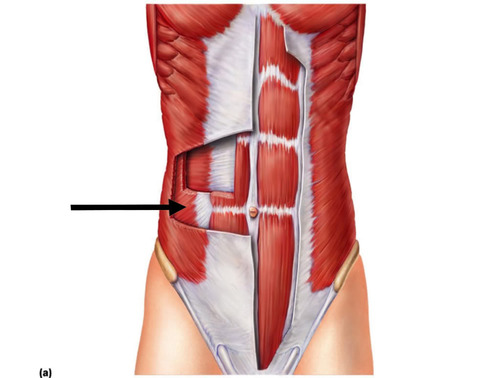
69
New cards
External onlique
flex and rotate vertebral column, this is called
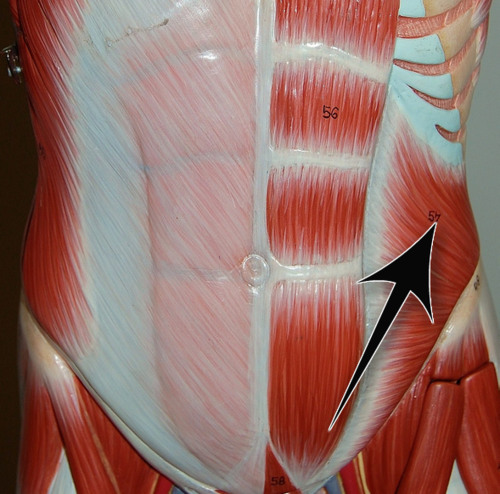
70
New cards
Brachialis
flexes forearm at elbow, this is called the
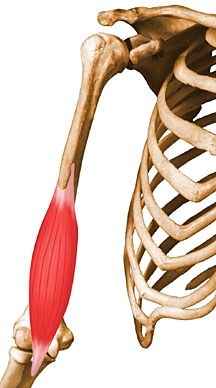
71
New cards
Brachioradialis
flexes forearm
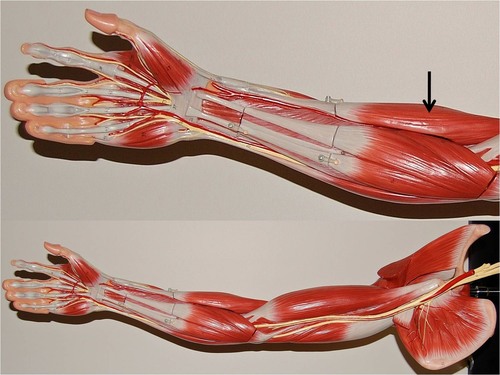
72
New cards
biceps brachii
Flexes and supinates forearm
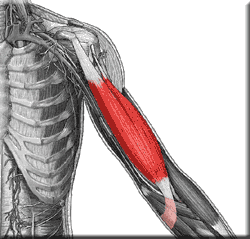
73
New cards
gluteus maximus
extends thigh
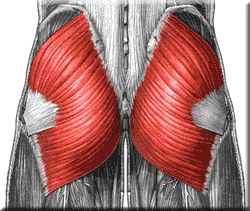
74
New cards
gluteus medius
abducts and medially rotates thigh
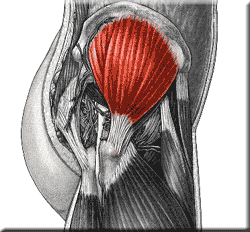
75
New cards
felxor carpi radialis
flexes and abducts wrist
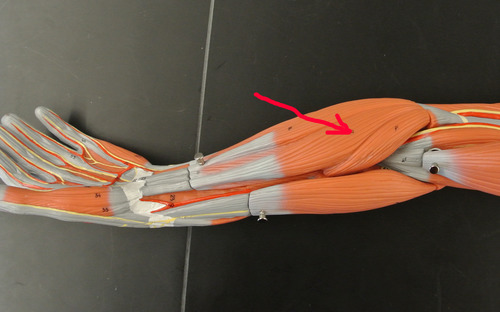
76
New cards
trieps brachii
insertions: olecranon of ulna
origin: shoulder girdle and proximal numerus
functions: extend elbow
origin: shoulder girdle and proximal numerus
functions: extend elbow
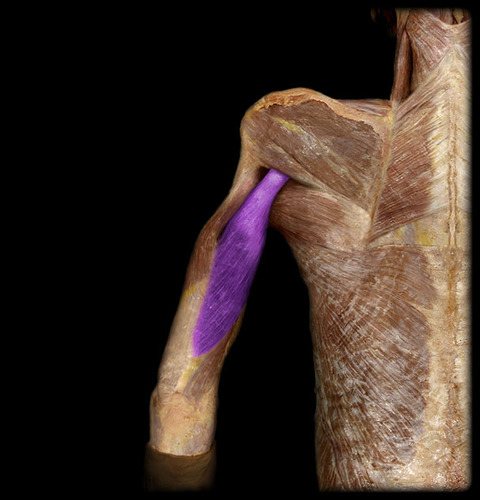
77
New cards
felxor carpi radialis
Origins: distal humerus
insertions: second and third metacarpals
functions: flexes wrist and abducts hands
insertions: second and third metacarpals
functions: flexes wrist and abducts hands
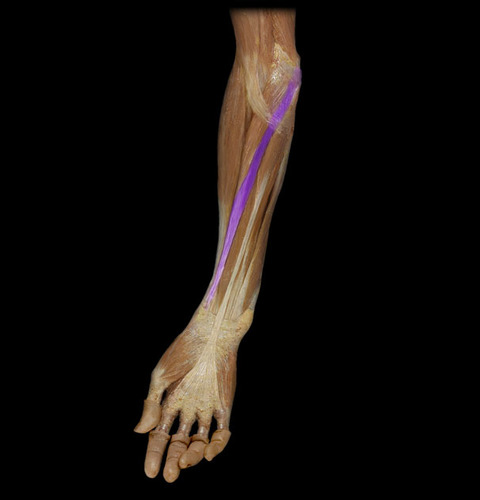
78
New cards
flexor digitorum superficialis
Orgin: distal humerus, ulna and radius
insertions: middle phalanges of second fifth finger
functions: flexes wrist and finger
insertions: middle phalanges of second fifth finger
functions: flexes wrist and finger
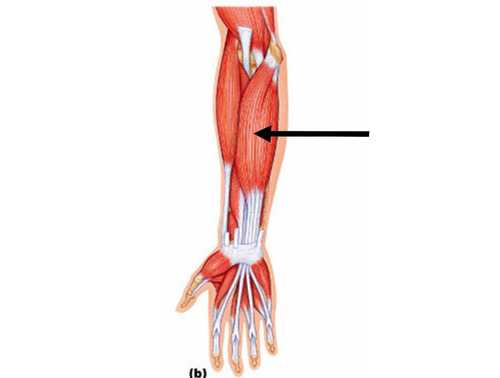
79
New cards
gluteus maximus
Functions: extends hip, abducts thigh; steadies pelvis during walking and flex knee and extend hip
insertions: proximal femur
origin: sacrum and ilium
insertions: proximal femur
origin: sacrum and ilium
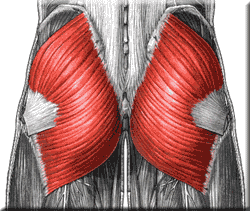
80
New cards
pectoralis major
Adducts and flexes humerus
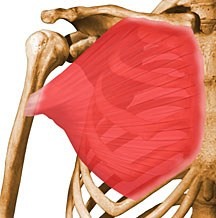
81
New cards
unipennate muscle
all the muscle fibers are on the same side of the tendon

82
New cards
extensor digitorum longus
extends toes and dorsiflexes foot
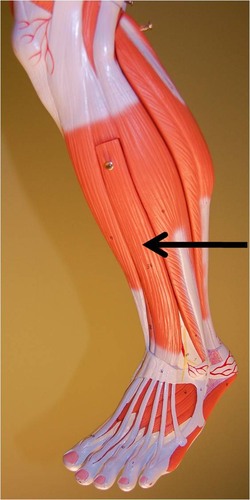
83
New cards
multipennate muscle
forms an angle with a tendon; do not move as far as parallel; contains more myofibrils than parallel muscles; develop more tension than parallel muscles; tendon branches within the muscle; ex: deltoid
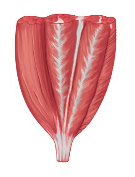
84
New cards
Bipennate
rectus femoris
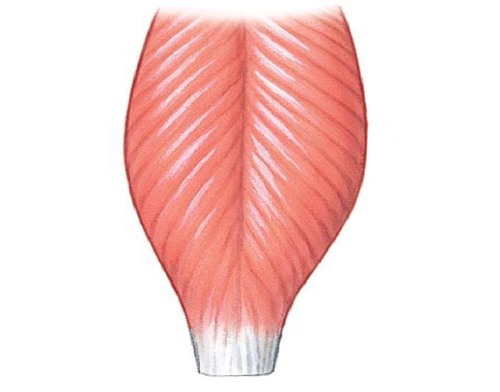
85
New cards
Gastrocnemius
Calf muscle
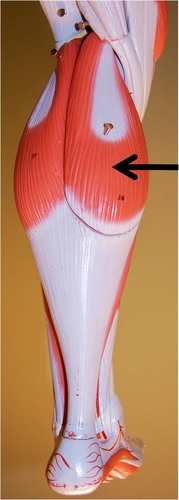
86
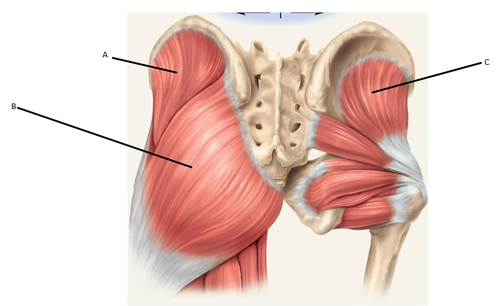
New cards
gluteal group muscles
gluteus maximus, gluteus medius, gluteus minimus
87
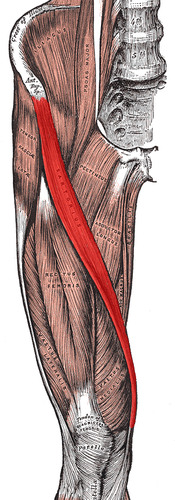
New cards
Sartorius
Flexes, abducts, and laterally rotates thigh at the hip; flexes knee
88
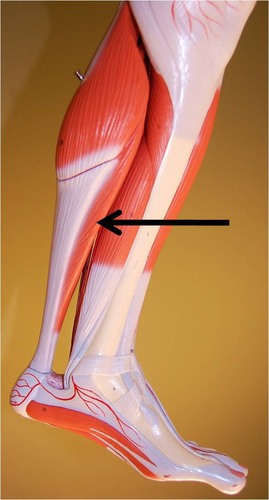
New cards
Soleus
plantar flexes foot
89
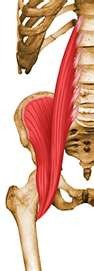
New cards
Illiopsoas
flexes hip
90
New cards
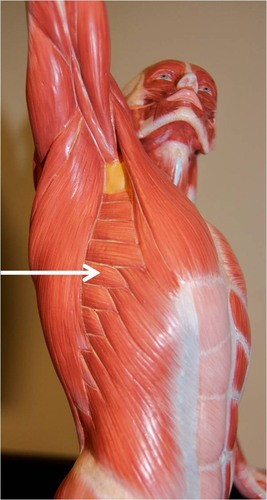
serratus anterior
pulls scapula anteriorly and downward
91
New cards
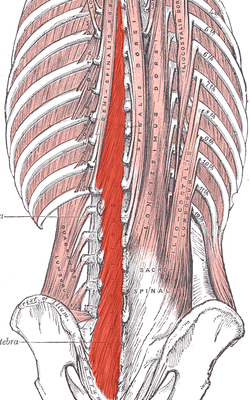
multifidus muscle
stabilizes lower thoracic and lumbar region of vertebral column
92
New cards
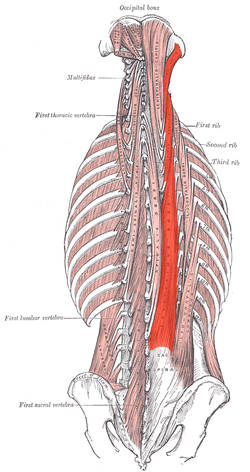
longissimus capitis
extends and rotates head
93
New cards
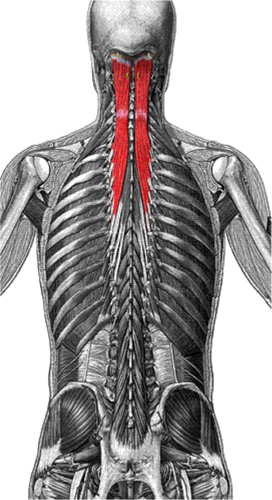
semispinalis capitis
extends head, bends head to one side, or rotates head
94
New cards
Flexion
bending a joint
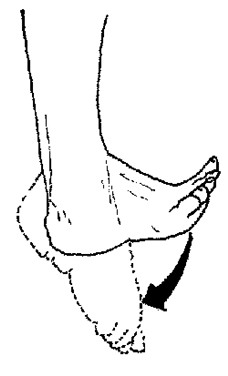
95
New cards
extension
Straightening of a joint
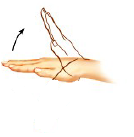
96
New cards
Rotation
CIRCULAR MOVEMENT AROUND AN AXIS
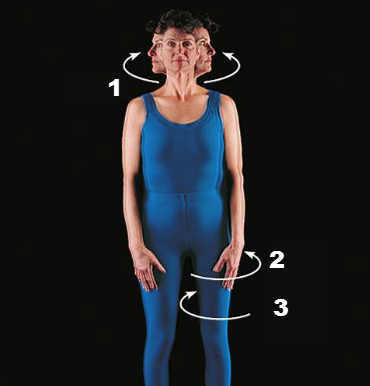
97
New cards
circumduction movement
moving the joint in a circular manner
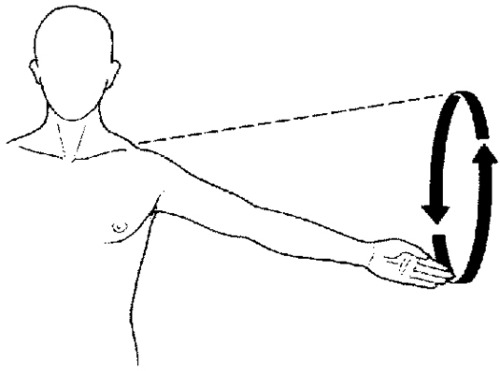
98
New cards
Inversion
turning inward
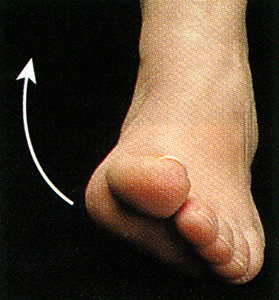
99
New cards
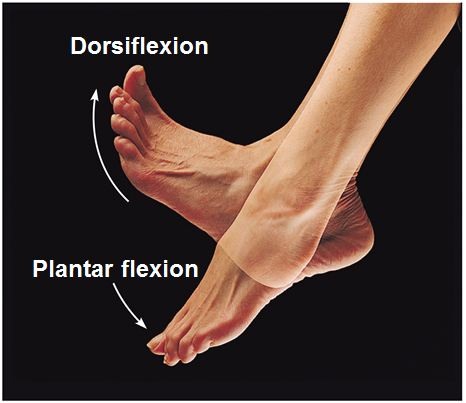
plantar flexion
bending of the sole of the foot by curling the toes toward the ground
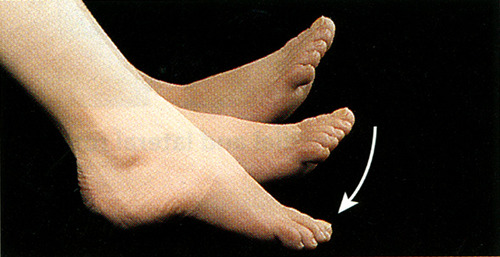
100
New cards
Dosiflexion
bending of the foot or the toes upward