Chapter 15 - Lipids
15.1 - Lipids
Lipids are not water-soluble biomolecules
Lipid categories include waxes, glycerol triglycerides, glycerophospholipids, sphingolipids, and steroids.
15.2 - Fatty Acids
Unbranched carboxylic acids are fatty acids that typically contain an equal quantity of carbon atoms (12 to 20).
Saturated, monounsaturated, or polyunsaturated with two or double bonds may be fatty acids.
Almost always the double connection is cis in unsaturated fatty acids.
15.3 - Waxes and Triacylglycerols
Wax is an ester of a fatty acid with a long chain of alcohol.
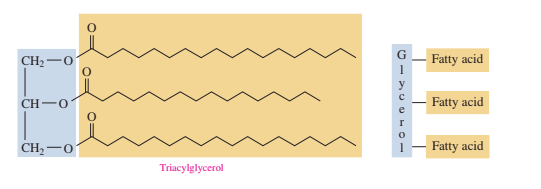
Triacylglycerols are three long-chain fatty acid esters of glycerol.
Fats have higher melting points than most vegetable oils, which contain more saturated fatty acids.
15.4 - Chemical Properties of Triacylglycerols
Triacylglycerol hydrogenation transforms double bonding into single bonding.
Glycerol and fatty acids are produced when the ester bonds are hydrolyzed in triacylglycerols when strong acids are present.
In saponification, glycerol and fatty acid salts are generated by triacylglycerol heated on a strong basis.
15.5 - Phospholipids
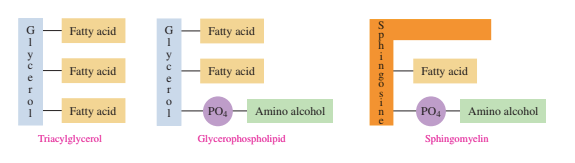
Glycerophospholipids are glycerol esters with two fatty acids and an amino alcohol phosphate.
Sphingomyelin forms an amide bond to fatty acid in amino alcohol sphingosine and a phosphodiester bonds to phosphate and amino alcohol.
15.6 - Steroids: Cholesterol, Bile Salts, and Steroid Hormones
Steroids are lipids that contain the four-ring fused structure of the steroid nucleus.
Cholesterol, bile salts, and steroid hormones are part of the steroids.
Synthesized with cholesterol, bile salts mix and break them apart with water-insoluble fats during digestion.
The triacylglycerides are transported from the intestines and liver, such as chylomicrons and LDL, to fat cells and muscles for storage and energy.
HDL carries cholesterol from tissue to the liver for removal
Steroid hormones are structurally closely associated with cholesterol and their synthesis depends upon cholesterol.
For sexual properties and reproductive properties, sex hormones such as estrogens and testosterone are responsible.
Adrenal corticosteroids, such as aldosterone and cortisone, regulate the cellular water balance and blood glucose.
15.7 - Cell Membranes
The semi-permeable membrane which separates the cellular content from the external fluids is surrounded by all animal cells.
The membrane consists of a lipid bilayer with two rows of phospholipids.
The lipid bilayer contains proteins and cholesterol and the surface is attached to the carbohydrates.
Nutrients and waste products are moved via passive transport (diffusion), easier transport, or active transport through the cell membrane.
 Knowt
Knowt
