Chapter 2 - Chemistry and Measurements
2.1 - Units of Measurement
Physical amounts in science are described in units of the metric or international units system (SI).
Some of the key units include volume liter (L), length meter (m), gram (g), weight kilogram (kg), temperature degree Celsius (°C) and Kelvin (K), and time second units.
2.2 - Measured Numbers and Significant Figures
Any number obtained by using a measuring instrument is a measured number.
An accurate number is obtained by counting items or from a definition.
The numbers reported in measurement including the estimated number are significant figures.
Zeros are not significant before the decimal number or at the end of the non-decimal number.
2.3 - Significant Figures in Calculations
The final answer is written in multiplication and division to have the same number of significant numbers as the most insignificant measurements.
The final answer has been written so that there is the same number of decimal places as the least decimal places measurement.
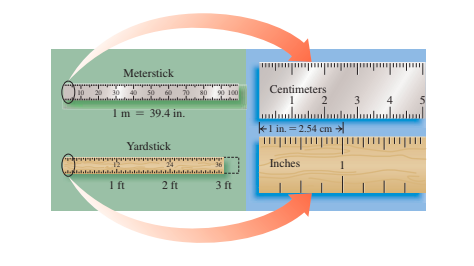
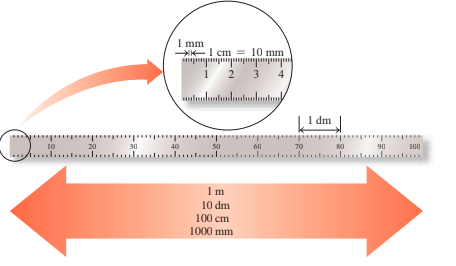
2.4 - Prefixes and Equalities
A prefix located before a metric or SI device changes the unit's size by 10.
Prefixes like centi, milli, and micro are smaller, prefixes like kilograms, megagrams, and there are large.
The relationship between two units, measuring identical volume, length, weight, or time, shows equal equality.
2.5 - Writing Conversion Factors
To express a relation in a fraction, conversion factors are used for any relationship in the metric or in the US system, two conversion factors may be written.
By speaking matching components in 100 parts, a percentage is written as a conversion factor.
2.6 - Problem Solving Using Unit Conversion
Conversion factors are helpful if a quantity in one unit is changed to a quantity in another one.
A given unit is multiplied by one or more transformation factors in the problem-solving process which cancels the units until the answer has been obtained.

2.7 - Density
The volume is usually g/mL or g/cm3, a ratio of its mass to the volume of the substance.
Conversion factors between mass and volume of a material can be written using the units of density
The density of a substance is comparable to the water density, 1.00 g/mL.
 Knowt
Knowt
